 |
Topic: Antigens, their properties. Antigens of Microorganisms. Major Histocompartability Complex (MHC) antigens. Mechanisms of endogenous and exogenous antigens processing.
|
|
|
|
Teacher’s signature ________________
Date__________________
CLASS 4
Topic: Antigens, their properties. Antigens of Microorganisms. Major Histocompartability Complex (MHC) antigens. Mechanisms of endogenous and exogenous antigens processing.
Questions to be discussed:
- Antigens, their properties (immunogenicity, antigenic specificity, cross reactivity).
- Microbial antigens.
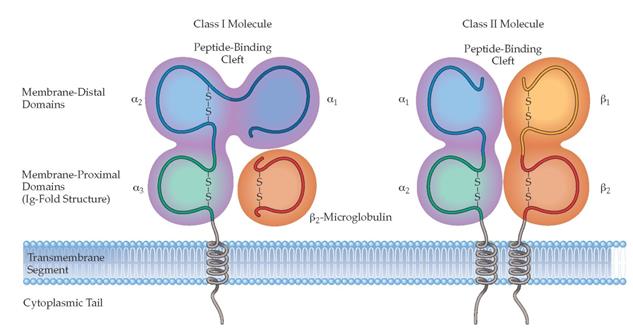
- Human antigens. Human leukocyte antigens. Major Histocompartability Complex (MHC) antigens, their structure.
- The importance of classes МНС-I и МНС-II in immunogenesis.
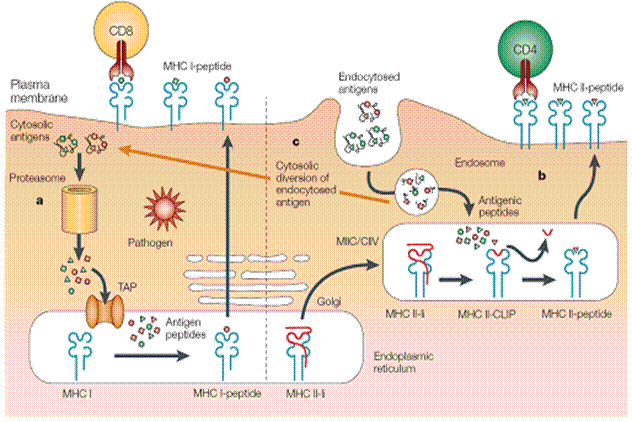
- Mechanisms of an exogenous (phagocytosed or endocytosed) peptide antigens processing.
- Mechanisms of an endogenous (synthesized on the ribosome) peptide antigens processing.
Practical tasks:
1. Draw a scheme of major bacterial antigen localization.
2. Draw a scheme of major naked virus antigens and enveloped virus antigens localization.
3. Describe a scheme of classes I and II МНС molecules.
4. Describe mechanisms of endogenous and exogenous antigens processing:
Teacher’s signature __________________
Date___________________
CLASS 5
Topic: Acquired (specific) immunity. Immunocompetent cells, stages of their maturation and differentiation. Characteristic of the receptors, cytokine profile and immunological function of the T- and B-lymphocytes subpopulations.
Questions to be discussed:
1. Cells of the immune system: immunocompetent, antigen-presenting, antigen-independent effector cells.
2. Human leukocyte membrane markers – Clusters of Differentiation (CD – markers), ways of their identification. Human leukocyte markers.
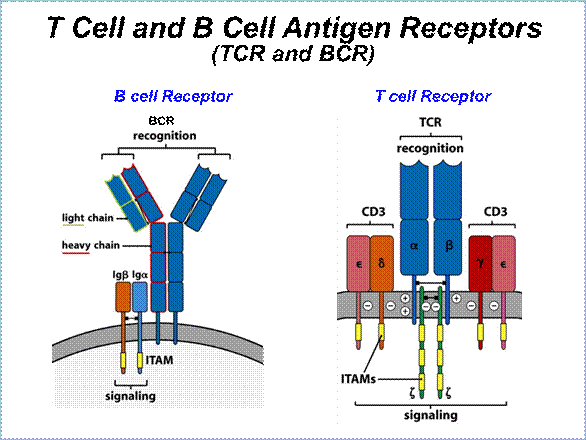
3. B-lymphocytes: stages of differentiation, main surface receptors, function. BCR.
4. Т-lymphocytes, stages of differentiation, subpopulations, main surface receptors, functions.
5. α, β and γ, δ types of TCR, their fictional differences.
6. Characteristic features of the main T-helper lymphocyte subpopulations (Th) - Th1, Th2: CD markers, membrane receptors, cytokines, functions.
7. Characteristic features of the T-cytotoxic lymphocytes: CD markers, membrane receptors, functions.
|
|
|
8. Regulatory T-lymphocytes (Тreg): CD28+, CD28- , and others.
9. Mechanisms of an exogenous (phagocytosed or endocytosed) peptide antigens processing.
10. Mechanisms of an endogenous (synthesized on the ribosome) peptide antigens processing.
11. Presentation of exogenous and endogenous polypeptide antigens and non-protein antigens.
Practical tasks:
1. Compare and describe structure and function of BCR and TCR.
2. Draw s simplified scheme of Th0 cells differentiation into Th1 and Th2. Indicate interleukins that activate differentiation and a profile of ILs secreted by subpopulations of Th cells.
3. Study the properties of newly found subpopulations of T helper cells:
| Proper-ties | Th1 | Th2 | Th9 | Th17 | Tfh (follicular helper) | Treg (regulatory) |
| Major cytokines produced | IFNg, IL-2, TNFa, TNFβ | IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13 | IL-9 | IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, IL-22, IL-25, IL-26, TNFa | IL-21, IFNg, IL-4 | TGF-β, (Transforming growth factor), IL-10 |
| Trans-cription factors | STAT4, STAT1, T-bet, Hlx | STAT6, GATA3, c-maf, IRF4, Gfi-1 | STAT6, GATA3, Smads | ROR-a, ROR-gt, STAT3 | BCL-6, MAF | FoxP3 |
| Inducing cytokines | IL-12(APCs), IL-18, IL-27, IFNg | IL-4 | TGF-β, IL-4 | TGF-β, IL-1β, IL-6, and/or IL-1a, IL-21, IL-23 | IL-21, IL-6 | TGF-β, IL-10, IL-2, TSLP |
| Patho-gens inhibited | Viruses, Intracellular bacteria, protozoa, fungi | Extracel-lular pat-hogens (helmints and others) | Hel-mints | Extracellular bacteria, fungi | Extracellu-lar patho-gens ac-cessible to IgM, IgG, and IgA | Negative regula-tion of patho-gens clearance |
| Immuno-pathology | Autoimmu-ne disea-ses, Graft-versus-host disease | Hyper-sensiti-vity type I | ? | Autoimmune diseases, Allergy | ? | Mainte-nance of immuno-logic tolerance |
4. Describe mechanisms of endogenous and exogenous peptide antigens presentation:
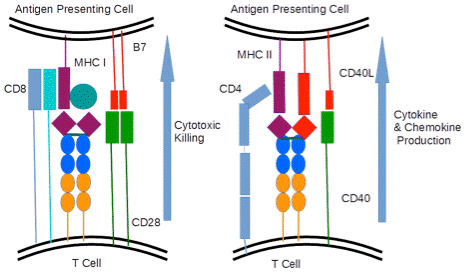
5. Compare peptide and non-peptide antigens presentation.
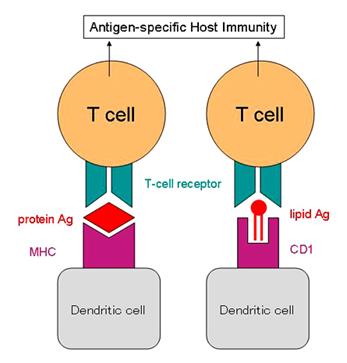
|
|
|


