 |
The Universe: Density and Destiny
|
|
|
|
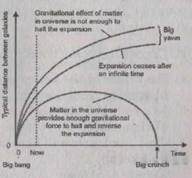 Scientists suppose that the fate of the universe depends on the average density of the universe. This effect is a consequence of gravity. The universe is believed to have begun 15,000 million years ago with a 'big bang' as a result of which all the matter has kinetic energy and the galaxies are all moving away from one another. But this kinetic energy of expansion struggles against the inward force of gravity attracting galaxies together. Depending on the density of the universe this may result in three options:
Scientists suppose that the fate of the universe depends on the average density of the universe. This effect is a consequence of gravity. The universe is believed to have begun 15,000 million years ago with a 'big bang' as a result of which all the matter has kinetic energy and the galaxies are all moving away from one another. But this kinetic energy of expansion struggles against the inward force of gravity attracting galaxies together. Depending on the density of the universe this may result in three options:
• a flat universe (with the critical density of approximately 10~26 kg m~3 - of the order of three hydrogen atoms per cubic metre) which will slowly expand forever;
• an open universe (the density is less than critical); it will expand
quickly till the galaxies lose contact with each other, stars expire and
all activity has ceased;
• a closed universe (with the density greater than critical); it will
ultimately contract in a reversal of the 'big bang', called the 'big
crunch' which would mean the end of everything - space, time and
matter; however, the 'big crunch' may be followed by a new big bang.

|
Currently, no one is sure what the density of the universe is. The simplest way to estimate it is to determine the amount of visible matter (stars and gas clouds.). It turns out to be about 1% of the required for critical density and is not nearly enough to pull the flying galaxies back. There is also strong evidence of the presence of invisible 'dark matter', which, if exists, will account for 10% of the critical density -still too low to explain the motion of stars. The scientists are certain there must be even more matter in the universe. Where is the missing mass? One possible candidate for the missing mass is particles called neutrinos.
Since their discovery in 1933, neutrinos have been believed to have zero mass (like protons). However, a team working at the Super-Kamiokande detector in Japan has proved otherwise. The results of the Super-Kamiokande experiment are much more than simply the means to predict whether a tiny particle has mass. They are a step towards humans being able to predict the ultimate fate of everything.
III. Choose the correct option to complete the sentences.
1. The future of the universe is affected by its....
a) gravity; b) destiny; c) density.
2. As a result of the 'big bang' the universe has been....
a) expanding; b) contracting; c) static.
3. The... universe will expand till it uses up its energy and becomes
cold and dead.
a) flat; b) open; c) closed.
4. A closed universe is expected to result in....
a) the 'big bang'; b) the 'big crunch'; c) the 'big flash'.
5. The density of the universe is determined by the amount of....
a) visible and dark matter; b) missing mass; c) both.
6. The amount of luminous matter is... of the critical density.
a)l%; b)10%; c)ll%.
7. The scientists believe that there is more matter in the universe
because its estimated density is....
|
|
|
a) not exact; b) only 10% of the critical density;
c) not enough to explain the motion of stars.
8. Neutrinos have proved to have....
a) zero mass; b) tiny particles; c) tiny mass.
IV. Translation Check. Use the dictionary if necessary.
Neutrinos
All the matter in the universe is made up of tiny particles, the electron neutrino, the muon neutrino and the tau neutrino being among them. Neutrinos are unlikely to be the dark matter that influences the motion of stars as it is assumed to exist in 'clumps'. Nevertheless, if neutrinos have even a tiny mass, there are enough of them to determine the density and, consequently, the destiny of the universe.
If neutrinos do have mass, it may be possible for them to 'oscillate' into different types of neutrino. Since the 1960s, experiments have proved the number of electron neutrinos reaching the Earth from the Sun to be smaller than expected. This suggests that electron neutrinos oscillate into other types of neutrino during their journey and therefore that they have mass. The scientists could only estimate neutrino masses being around 2 x 10"38 kg (50 million times smaller than the mass of the electron). This tiny mass per neutrino could be very significant considering the number of neutrinos - they are likely to account for much more mass than all the atoms in the universe! If neutrinos do have mass, as the Super-Kamiokande results suggest, a source of the missing mass has been found and the density of the universe must be greater than the observed density required to explain fully the motion of stars.
7 Часть 2
| ACTIVE VOCABULARY |
Unit 13
Section A
affect, v влиять
apron, n фартук
arc, n электрическая дуга
attach, v прикреплять(ся); присоединять(ся)
bead, n сварной шов
boot, n ботинок
brush against, v слегка задевать
by means of, посредством
clothing, n одежда protecting clothing защитная спецодежда
conventional, adj =ordinary обычный, общепринятый
crack, n трещина
currently, adv действующий в настоящее время
damage, v, n повреждать; повреждение
decade, n десятилетие
desirable, adj желанный
despite, prep несмотря на
drastic, adj коренной, радикальный
effect, n влияние
electrode, n электрод
establish, v устанавливать
exhibit, v показывать, проявлять
follow, v придерживаться, следить
fuse, v плавить(ся), сплавлять(ся)
fusion, n плавка, слияние
glove, n перчатка
helmet, n шлем, каска
hence, prep следовательно
holder, n ручка, рукоятка
join, v соединять
joint, n стык
latter, adj последний (из двух названных; противополож. the former)
location, n местоположение
neither...nor... ни... ни...
nevertheless, cj тем не менее
overall, n рабочий халат; спецодежда
owing to, prep пo причине, вследствие, благодаря
|
|
|
penetration, n глубина про-плавления
response, n реакция (на воздействие); срабатывание
rot, n стержень, прут
rule, n правило
safe, adj безопасный safety rules правило безопасности
significant, adj значительный, важный, существенный
soften, v размягчать; смягчать
strike, v ударять; зажигать дугу
surface, n поверхность
tensile, adj прочный на разрыв
the same, adj одинаковый
tip, n кончик
transformer, n трансформатор
unique, adj единственный в своём роде; уникальный
wear, v быть одетым (во что-л.); носить (одежду и т. п.)
weld v, n сваривать; сварной шов
welding, n сварка
widespread, adj широко распространённый
Section В
allow, v позволять, разрешать
block, v заклинивать(ся), засо-ряться)
both... and... и ... и ...
clean, v чистить
coil, n спираль coil spring цилиндрическая (винтовая) пружина
condition, n условие, состояние
consequently, adv следовательно
consume, v потреблять, использовать
consumption, n потребление
contract, v сжиматься
convenient, adj удобный, подходящий; пригодный
cool, v остывать
deliver, v поставлять; доставлять; снабжать
ease, v ослаблять, освобождать, облегчать
even, adj одинаковый; тот же самый
exact, adj точный
expand, v расширять(ся); увеличиваться) в объёме
expansion, n увеличение в объёме, расширение
gauge, n измерительный прибор
fuel gauge топливный расходомер
fit, v устанавливать, монтиро-вать
function, v, n действовать; функция
immediately, adv немедленно
inside, prep внутри
leading, adj ведущий; передовой
light, n свет
warning light предупреждающий световой сигнал
load, v, n нагружать, нагрузка
means, n средство, способ means of transport средство передвижения
overhaul, v, n ремонтировать; ремонт
particle, n частица fine particles мелкие частицы
prevent, v не допускать, препятствовать
quantity, n количество, величина
sensitive, adj чувствительный
stress, n нагрузка
supervision, n наблюдение
thermostat, n термостат
wax, n воск
Unit 14
Section A
abbreviate, v сокращать
alteration, n изменение
bulb, n лампочка
burn out, v выгорать, перегорать
capacitor, n конденсатор
cell, n батарейка, (фотоэле-мент
fuel cell топливный элемент
charged, adj заряженный
circuit, n цепь closed circuit замкнутая цепь
condenser, n конденсатор
core, n стержень, ядро
coursework, n курсовая
current, n ток direct current прямой ток alternating current переменный ток
dielectric, n непроводник
electricity, n электричество
expect, v предполагать, ожидать
filament, n нить накала
force, v вынуждать
frequency, n частота
gap, n зазор, промежуток air gap воздушный зазор
|
|
|
generate, v вырабатывать, генерировать
glow, v гореть, светиться
grid, n энергетическая сеть transmission grid сеть электропередач
induce, v вызывать
insulator, n изолятор, непроводник
loss, n потеря; (мн.) потери
mica, n слюда
negative, adj отрицательный
notice, v замечать
notion, n понятие
power, n энергия power plant электростанция thermal power термическая энергия
nuclear power ядерная энергия underground steam power энергия подземного пара
solar power солнечная энергия kinetic power кинетическая энергия
chemical power химическая энергия
rectifier, n выпрямитель reverse, v менять направление
на противоположное
rotate, v вращаться
socket, n патрон, розетка stand for, v символизировать,
означать
supervisor, n научный руководитель
through, prep через, по transformer, n трансформатор step-up transformer повышающий трансформатор step-down transformer понижающий трансформатор
turn, n виток (проволоки)
turn out, v вывёртывать
wind, v наматывать
winding, n обмотка input winding входная обмотка output winding выходная обмотка
primary winding первичная обмотка
secondary winding вторичная обмотка
wire, n провод
overhead conductor wire провод воздушной линии
Section В
absorb, v поглощать
account, n расчет, отчет to take into account принимать во внимение
accumulate, v накапливать
array, n панель
cell, n элемент photovoltaic cell фотоэлемент
circulate, v циркулировать
collect, v собирать
collector, n коллектор solar collector солнечный коллектор
cover, v покрывать
divert, v отводить
excess, adj излишний
exhaust, v истощать
fossil, adj ископаемый fossil fuel ископаемое горючее
furnace, n печь; топка solar furnace солнечная печь
housing, n жилой фонд housing development жилой массив
huge, adj огромный
inexhaustible, adj неистощимый
pollute, v загрязнять
pollution, n загрязнение
pollution-free, adj экологически чистый
run, v работать, действовать, приводить в движение
search for, n искать
solar-powered, adj приводимый в движение солнечной энергией
solution, n решение
sunlight, n солнечный свет
tackle sth., v пытаться найти решение
transfer, v передавать
variation, n изменение
Unit 15
Section A
constantly, adv постоянно
evident, adj очевидный
exhaust, v истощать
immensely, adv чрезвычайно
nearly, adv почти
option, n вариант
reason, n причина
resource, n ресурс renewable resources, pl возоб-новляемые ресурсы
satisfy, v удовлетворять satisfy needs удовлетворять нужды
|
|
|
sensible, adj разумный, ощутимый
shortage, n недостаток, нехватка
source, n источник alternative energy sources альтернативные источники энергии
threaten, v угрожать
time, n раз
(...) times as much в (...) раз больше
turn into, v превращать
twice, adv дважды
usable, adj годный к употреблению
Section В
antifreeze, n антифриз backwards, adv назад
common, adj обычный
coolant, n смазочноохлаждаю-щая эмульсия
dirt, n грязь
dissipate, v рассеивать
dust, n пыль
emit, v выбрасывать, выделять external, adj внешний
fault, n ошибка, неисправность
fill up, v заполнять, наполнять
flat, adj разряженный flat battery разряженная батарея
fluid, n жидкость. foresee, v предсказать, предвидеть
forwards, adv вперёд; дальше
gap, n искровой промежуток
hose, n шланг, гибкий трубопровод
impurity, n загрязнение, грязь
jam, v заедать, заклини-
вать(ся)
mixture, nсмесь
fuel mixture топливная смесь
order, n порядок in order в порядке out of order не в порядке
overhaul, n (капитальный) ремонт
overheat, v перегревать(ся) pipe, n труба
exhaust pipe выхлопная труба
plug, n пробка, заглушка spark plug свеча зажигания
point, n точка
freezing point температура замерзания, точка замерзания boiling point температура кипения, точка кипения
pull, v тянуть
pump, v подавать насосом, качать
push, v толкать
release, v освобождать, разблокировать
ring, n кольцо
piston ring поршневое (уп-лотнительное) кольцо
service, v обслуживать service station станция техобслуживания
start, v заводить, запускать, включать, начинать
starter, n стартер (устройство для пуска двигателя)
thorough, adv основательный, тщательный
unobstructed, adj беспрепятственный, свободный
Unit 16
Section A
assure, v обеспечивать
award, v награждать
beam, n луч
reference beam опорный луч object beam объектный луч
coat, v покрывать
coating, n покрытие, светочувствительный слой
colourful, adj красочный, яркий
dichromatic, adj двухцветный
direction, n направление
emboss, v чеканить
film, n пленка
foil, n фольга
hologram, n голограмма
holography, n голография
illuminate, v освещать
image, n образ
three-dimensional image трёхмерное изображение multidimensional image многомерное изображение
imagine, v воображать, представлять
imperfect, adj несовершенный
indefinitely, adv неограниченно, неопределенно
intend, v предназначать, наме-реваться
interference, n взаимное влияние; интерференция interference pattern интерференционная картина
lack, v испытывать недостаток, нуждаться, не иметь
lens, n линза, лупа
master, n мастер-модель, про-
модель
mirror, n зеркало
monochromatic, adj монохромный
numerous, adj многочисленный
opposite, adj противоположный
originally, adj первоначально
plate, n фотопластин(к)а holographic plate голографи-ческая пластина
power, n способность, (оптическое) увеличение
record, v записывать
reflect, v отражать
reflection, n отражение
respectively, adv соответсвенно
safelight, n неактиничный
свет, безопасное освещение separate, adj отдельный
|
|
|
single-colour, adj одноцветный split, v разбивать
splitter, n разделитель beam splitter, n расщепитель электронного луча
stable, adj устойчивый
stamp, v отпечатывать, оттискивать
the former, the latter, adj пер-вый, последний (из двух)
vibration, n вибрация, колебание
view, v рассматривать viewable, adj наблюдаемый visible, adj видимый
whole, adj =complete целый
SectionВ
ability, n способность
act, v действовать
additional, adj дополнительный
approach, v, n приближаться, подводить; подход
artificial, adj искусственный
conscious, adj сознательный
control, n управление remote control дистанционное управление
count (on), v рассчитывать
creature, n существо
definition, n определение
defuse, v взрывать
environment, n окружающая среда
eventually, adv со временем
explore, v исследовать
gather, v собирать
imitate, v имитировать
insert, v вставлять
intelligence, n разум, интеллект
linear, adj линейный
manipulate, v манипулировать
motor, n двигатель stepper motor шаговый (элек-тро) двигатель servomotor серводвигатель, сервомотор
navigate, v управлять, направлять
neural, adj нейронный neural network нейронная сеть
qualify, v определять
respond, v реагировать, срабатывать
response, n реакция (на воздействие), срабатывание (устройства)
sense, v ощущать, чувствовать,
понимать
solenoid, n соленоид
specific, adj определенный stimulus, n сигнал возбуждения, стимул
suggest, v предлагать, советовать
supervise, v контролировать surroundings, n окружающая
среда
system, n система rule-based system экспертная система ultrasonic, adj ультразвуковой
Unit 1 7
Section A
amplification, n усиление amplifier, n усилитель amplify, v усиливать
area, n область
back and forth, adv назад-вперёд
behaviour, n поведение bounce, v отскакивать
cavity, n полость
coherence, n когерентность coherent, adj связанный concave, adj вогнутый continuous, adj непрерывный denote, v означать directionality, n направленность
distructon, n разрушение dozen, n дюжина
excited, adj возбужденный flash, n вспышка flash lamp импульсная лампа, фотовспышка
flat, adj плоский
intense, adj интенсивный inversion, n инверсия population inversion инверсия заселённости (энергети-ческих уровней)
majority, n большинство
mean, v значить
medium, n среда monochromatic, adj одноцветный, монохроматический oscillator, n генератор, осциллятор
partially, adv частично
pulse, v пульсировать
pulsed, adj пульсирующий radiate, v излучать
reflective, adj отражающий resonator, n резонатор
ruby, adj рубиновый
similar to, adj подобный, похожий
totally, adv полностью transparent, adj прозрачный treat, v обращаться
unlike, cj в отличие
upper, adj верхний, высший variety, n разнообразие via, prep через, посредством
wavelength, n длина волны
Section В
abundant, adj изобилующий acid, n кислота
acid rain кислотный дождь average, adj средний
ban, v запрещать
colourless, adj бесцветный
combustible, adj горючий
compound, n соединение
consequences, n последствия
consist in, v заключаться в
densely populated, adj густонаселенный
deplete, v истощать, разрушать
depletion, n истощение, разрушение
destructive, adj разрушительный
dioxide, n диоксид
envelope, n оболочка
eutrophication, n эвтрофика-ция (зарастание водоёма водорослями)
far-reaching, adj далеко идущий
flammable, adj = inflammable легко воспламеняющийся, горючий
foam, n пенопласт
packaging foam упаковочный пенопласт
gas,n газ
industrial gas промышленный газ
natural gas природный газ man-made gas искусственный газ
greenhouse, n парник, теплица greenhouse effect парниковый эффект
infrared (IR), adj инфракрасный
insist on, v настаивать
layer, n слой
nitrogen, n азот
odourless, adj без запаха, непахнущий
overestimate, v переоценивать oxygen, n кислород
pollutant, n загрязняющее вещество
present, adj присутствующий
react, v реагировать
refrigerant, n охладитель
release, v высвобождать
result in, v приводить к
solvent, n растворитель
state, n состояние free state свободное состояние, несвязанное состояние
tasteless, adj безвкусный
toxic, adj токсичный
ultraviolet (UV), adj ультрафиолетовый
Unit 18
Section A
across, prep через
advanced, adj развитый
alien, adj внеземной
brief, adj краткий
bright, adj яркий
communication, n связь, коммуникация; система связи
compound, adj составной, сложный
detect, v замечать, находить, обнаруживать
distant, adj удаленный
entire, adj весь
establish, v устанавливать
eyepiece, n глазок
fascinating, adj увлекательный
fruitful, adj плодотворный
generate, v создавать
handheld, adj карманный
hardly, adv едва
interstellar, adj межзвездный
item, n предмет
last, v длиться
magnification, n увеличение
magnify, v увеличивать
maintain, v утверждать, заявлять
microscopy, n микроскопия
modify, v видоизменять
multitude, n множество
objective, n объектив
permanent, adj постоянный
practicable, adj осуществимый
resolution, n разрешение
scan, v наблюдать
sign, n знак, признак
significantly, adj значительно
spot, v находить
star, n звезда
sodium star натриевая звезда
X-rays, n рентгеновские лучи
Section В
appealing, adj привлекательный
booster, n ракета-носитель
combine, v сочетать(ся)
disintegrate, v распадаться
disposable, adj одноразового
использования
essentially, adv по существу
experience, v испытывать
gimbal, n универсальный шарнир
house, v размещать
initially, adv сначала, изначально
irreplaceable, adj незаменимый
land, v приземляться
launch, v запускать
lift off, v взлетать
locate, v размещать, устанавливать
maneuver, v, n маневрировать, маневр
orbiter, n орбитальная ступень, многоразовый транспортный космический корабль
payload, n полезный груз
practice, n практика; применение; осуществление на практике
put into practice осуществлять
propellant, n ракетное топливо
rate, n интенсивность
recoverable, adj восстановимый
re-entry, n вхождение в атмосферу
reusable, adj многоразового
пользования
satellite, n спутник
separate, v, adj отделять(ся), разделять(ся); отдельный
shuttle, n многоразовый транспортный космический корабль, МТКК
space, n космическое пространство, космос
outer space космическое пространство вне земной атмосферы
spacecraft, n космический
корабль
spaceship, n космический
корабль
storage, n резервуар, хранение, накопитель
store, v запасать; накапливать, хранить
take off, v взлелеть
take-off, n взлет
thrust, n тяга, сила тяги, (реактивная) сила,толчок
weightless, adj невесомый
GRAMMAR
Unit 13
The Infinitive is the initial form of the verb. It is usually used with the particle to.
| To explain the rule is rather difficult. | ||||
| difficult | ||||
| hard | ||||
| It is | rather | necessary | ||
| Subject | It was | quite | essential | to explainthe rule. |
| It will be | very | important | ||
| easy | ||||
| valuable, etc. |
| Adverbial Modifier of Purpose | To* explain the rule you should give examples. You should give examples in order to explain the rule. |
* to = in order to (here)
Consider 1. To explain the rule is 1. Очень тяжело объяс -
the difference: rather difficult. нить это правило.
2. To explain the rule you 2. Чтобы объяснить это
should give examples. правило, тебе следует
привести примеры.
| Predicative | The Its Their Olga's | aim duty idea function goal objective purpose, etc | is was will be | to measure the temperature. |
| Attribute | The car to be usedruns on solar Dower. | 1. Машина, которая будет использовать- ся, работает на сол- нечной энергии. 2. Машина. которая должна использо- ваться, работает на солнечной энергии. |
Unit 14
The Complex Object {the objective infinitive construction) is translated into Russian with the help of an object clause beginning with words чтобы, что, как.
| subject | predicate | object | |
| noun or pronoun in the objective case | (to)*+ infinitive | ||
| I/you/we/they Students | expect don't expect | me/you/him/her/ us/them the mechanic | to repair the car. |
| He/she/it Oleg | expects doesn't expect |
*Remember: to is never used after let, make, see, hear, feel, watch, notice, observe in the Active Voice:
e.g. We watched the engineer make a hologram. Then he let us experiment with a laser.
The Complex Object is used after the main verbs denoting:
| wish | mental activity | sense perception | awareness | inducement |
| to want | to suppose | to see | to know | to make |
| to wish | to expect | to hear | to find | to cause |
| to desire | to consider | to feel | to note | to force |
| need | to assume | to watch | to claim | to let |
| I would like | to prove | to notice | to state | to allow |
| (=I'd like) | to believe | to observe | to declare | to permit |
| to understand | to pronounce | to enable | ||
| to know | to announce | to ask | ||
| to think | to report | to tell | ||
| to find | to order | |||
| to understand | to command |
We would likе you to test the Мы хотели бы, чтобы вы протестиро-
device. вали этот прибор.
I consider him to be a pro- Я считаю, что он профессионал в сво-
fessional in his field. ей области.
She found the carburettor to be Она обнаружила, что карбюратор за-
blocked. сорился.
The engineer told us to stop Инженер сказал нам прекратить экс-
the experiment. перимент.
The teacher makes us study Учитель заставляет нас усердно
hard. учиться.
Не heard, the engine start after После громкого щелчка он услышал,
a loud click. что двигатель заработал.
Remember: The Infinitive in the Complex Object is often used in the Passive Voice but it is translated into Russian in the Active Voice and is placed before
the noun.
The engineer allowed the technology - Инженер разрешил использо-
to be used. вать эту технологию.
The Complex Subject (the subjective infinitive construction) is translated
into Russian with the help of a non-personal main clause followed by an
object clause beginning with the word что.
Compare: It is said that the car is
broken. Говорят, что машина сломана.
The car is said to be broken.
Remember: Always begin translating sentences with the Complex Subject from the predicate rendering it as a non-personal main clause followed by an object clause with the word что.
| subject | predicate (the expressions, the Passive Voice) | subject (to + infinitive) | |
| I | am (not) | likely supposed | to know Physics well. |
| You/we/they Students | are (not) | ||
| He/she/it Olga | is (not) | ||
| predicate (the Active Voice) | to know Physics well. | ||
| You/we/they Students | seem don't seem | ||
| He/she/it Olga | seems doesn't seem |
The Complex Subject is used with the following:
| expressions | verbs in the Passive Voice | verbs in the Active Voice | |
| to be likely to be unlikely to be sure to be certain | to say to know to think to report to suppose to expect | to consider to assume to believe to see to hear, etc. (see Complex Object) | to seem / to appear to prove / to turn out to happen / to occur |
The project is likely to be completed Вероятно, что проект скоро завер-
soon. шат.
The Sun is considered to provide us Считается, что Солнце обеслечива-
with all the energy we need. ет нас всей необходимой энергией.
We happened to work together for Случилось так, что мы работали
the same company. вместе в одной компании.
| Forms of the Infinitive | ||
| Aspect / Voice | Active | Passive |
| Indefinite | He is likely to design a new car soon. | A new car is sure to be designed in the near future. |
| Continuous | He seems to be designing a new car now. | — |
| Perfect | He is said to have designed a new car recently. | A new car is reported to have been designed by our engineers. |
| Perfect Continuous | He proved to have been designing a new car for two years. | — |
Unit 15
The Participle is a non-finite form of the verb combining features of the verb, the adjective and the adverb. The two forms of Participles are Participle I and Participle II.
| Attribute | PI | We installed a new heating system. Мы установили новую обогревательную систему. We installed a new system heating our house naturally. Мы установили новую систему, обогревающую наш дом природным способом. | Active Voice |
| We live in a house being heated naturally at the moment. Мы живем в доме, обогреваемом сейчас природным способом. | Passive Voice | ||
| PII | We live in a solar-heated house. Мы живем в доме, обогреваемом солнечной энергией. We live in the house heated by the Sun all the year round. Мы живем в доме, который обогревается солнцем круглый год. |
| Adverbial Modifier | PI | Buildingsolar houses we save energy. Строя дома на солнечных батареях, мы сохраняем энергию. Having built a new solar heating system the engineers started to test it. Построив новую солнечную отопительную систему, инженеры начали ее проверять. | Active Voice |
| Being built in a new way the system offers many advantages. Будучи построенной новым способом, эта система имеет множество достоинств. Haying been built completely the plant was thoroughly inspected. После того, как завод был полностью построен, его тщательно проверили. | Passive Voice | ||
| PII | When built by skilled workers the experimental system worked well. Построенная опытными рабочими, эта система хорошо работала. If built on time the new power plant will start to work in May. Если новая электростанция будет построена вовремя, она начнет работу в мае. |
Unit 16
| Compare: | Participial Constructions |
| Active Voice | We observed the teacher making a hologram. Мы наблюдали, как учитель делал голограмму. |
| Passive Voice | The teacher was observed making a hologram. Наблюдали, как учитель делал голограмму. |
| Absolute Participial Constructions | The car having been repaired, the driver left the service station. После того, как починили машину, во- дитель уехал со станции техобслужи- вания. An experiment was carried out yesterday, new equipment being used. Вчера был проведён эксперимент, при- чём использовалось новое оборудование. |
The Gerund is a non-finite form of the verb combining features of the verb and the noun.
It is used independently and after the following words:
| prepositions | nouns+ prepositions | adjectives+ prepositions | verbs |
| on | the idea of | to be famous for | to mind |
| after | the method of | to be sorry for | to result in |
| before | the way of | to be sure of | to object to |
| without | the purpose of | to be capable of | to use for |
| instead of | the necessity of | to be tired of | to insist on |
| against | the technique of | to be good at | to rely on |
| in spite of, | the importance of, | to be surprised at, | to prevent from, |
| etc. | etc. | etc. | etc. |
Walking, talking and thinking like a human being will soon become possible
for robots.
Without gathering data it is impossible to prove the theory.
The new technique of compiling new programmes accelerated our work a lot.
Robots are capable of doing difficult tasks.
People cannot prevent robots from becoming too clever.
Unit 17
| Forms of the Gerund | ||
| Aspect / Voice | Active | Passive |
| Indefinite | We are against pollutingthe air. | We object to the air being polluted. |
| Perfect | We know of industry having pollutedthe air badly. | We have had of the air having been pollutedbadly. |
| Compare: | Gerund | Participle |
| Testing a laser takes time. | Testing a laser he made a discovery. | |
| Before switching on the laser we read the safety instructions carefully. | Switching on the laser we followed the safety instructions carefully. | |
| a driving license (= a license for driving) | a driving woman (= a woman that drives) |
| Compare: | Gerundial Constructions |
| Professor is interested in completing the research. | (he will complete it himself). |
| Professor is interested in the research being completed. | (somebody will complete it) |
| Professor is interested in students completing the research. | (students will complete it) |
| Professor is interested in our completing the research. | (we will complete it) |
Unit 18
Reported Statements
| We uselaser telescopes. | He says (that) they use laser telescopes. He said (that) they used laser telescope. | Он говорит, Он сказал, | что они используют лазерные телескопы. |
| We used laser telescopes long ago. | He says (that) they used laser telescopes long ago. He said (that) they had used laser telescopes long before. | Он говорит, Он сказал, | что они использовали лазерные телескопы уже давно. |
| We will use laser telescopes soon. | He says (that) they will use laser telescopes soon. He said (that) they would use laser telescopes soon. | Он говорит, Он сказал, | что они скоро будут использовать лазерные телескопы. |
Reported statements are introduced by these words: to say, to report, to announce, to inform, to point out, to consider, to assume, to suppose, to know, to believe, to state, to claim, to suggest, to predict, to think, to be sure, to be certain, to dream, etc.
Reported Questions
| Are you studying alloys now? | She wonders if we are studyingalloys now. She wondered whether we were studying allovs then. |
| Did you study alloys at the lesson yesterday? | She wonders if. we studied alloys at the lesson yesterday. She wondered whether we had studied alloys at the lesson the day before. |
| Will you studyalloys next year? | She wonders if we will study alloys next year. She wondered whether we would study alloys the next year |
Remember: if = whether. 194
| What alloys is he studying now? | They ask what alloys he is studying now. They asked what alloys he was studying at that time. |
| When did he study alloys? | They ask when he studied alloys. They asked when he had studied alloys. |
| Why will he study alloys in future? | They ask why he will study alloys in future. They asked why, he would study alloys in the future. |
Reported questions are introduced by these words: to ask, to inquire, to question, to wonder, to want to know, to be interested, it is interesting, to know, to find out, not to be sure, etc.
Word formation
An English word can be divided into three parts: a prefix, a stem and a suffix. Pre- means "before"; a prefix, therefore, is what comes before the stem. Prefixes usually change the meaning of the word; for example, un- changes a word to the negative. Unmagnetizable means 'not capable of being magnetized'. A suffix is what is attached to the end of the stem. Suffixes, on the other hand, change the word from one part of speech to another. For example, ly added to the adjective quick gives the adverb quickly. Both prefixes and suffixes are referred to as affixes.


| Noun-forming suffixes | ||||
| SUFFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES | ||
-ance
 -ence
-er
-or -ence
-er
-or
| state quality of a person who a thing which | performance | ||
| independence programmer, operator compiler, accumulator | ||||
 -ation
-tion -ation
-tion
| the act of | execution | ||
 -ist
-yst -ist
-yst
| a person who | analyst, typist | ||
| -ness -ion -ing -ment -ity -ian -ism -dom -ship | condition of action/state activity state, action state, quality pertaining to condition/state domain/condition condition/state | cleanliness conversion welding measurement electricity electrician magnetism freedom relationship, partnership | ||
| Verb-forming suffixes | ||||
| SUFFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES. | ||
 -ize
-ate
-fy
-en -ize
-ate
-fy
-en
| to make | ecomputerize automate, activate simplify harden, widen | ||
| Verb-forming suffixes | ||
| SUFFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES |
| -ly | in the manner of | electronically, logically |
| Adjective-formimg suffixes | ||
| SUFFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES |
| -al -ar -ic -ical | have the quality of | computational, logical circular magnetic, automatic electrical |
 -able
-ible -able
-ible
| capable of being | comparable divisible |
  -ous
-ious -ous
-ious
| capable of being | dangerous religious |
| -ful -less -ish -ed -ive -ing | characterized by without like having quality of to make or do | helpful careless yellowish computed, punched interactive processing, welding |

| Negative and positive prefixes | ||||
| PREFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES | ||
| Negative | un- in- im- il- ir- non- mis- dis- anti- de-under- | not,
not good enough
not connected with bad, wrong
 opposite feeling opposite action
against
reduce, reverse
too little opposite feeling opposite action
against
reduce, reverse
too little
|  unmagnetized, unpunched incomplete
impossible
illigal
irregular, irrelevant
non-programmable, non-impact mispronounce
disagree
discount
antisocial
demagnetize, decode underestimate unmagnetized, unpunched incomplete
impossible
illigal
irregular, irrelevant
non-programmable, non-impact mispronounce
disagree
discount
antisocial
demagnetize, decode underestimate
| |
| Positive | re-over | do again too much | rearrange overheat | |
| Prefixes of size | ||||
| PREFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES | ||
| semi-equi-maxi-micro-mini-macro-mega- | ||||
|
|
|


