 |
Task V I. Read the text and draw up the programme of the women’s gymnastics competition.
|
|
|
|
GYMNASTICS
ГИМНАСТИКА
Учебное пособие по английскому языку
для студентов II курса БГУФК
Минск
 ВВЕДЕНИЕ
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Настоящее учебное пособие является уроком-темой курса “Английский язык” для студентов учебных заведений физкультурного профиля. Его цель – содействовать профессионально ориентированному обучению студентов иностранному языку (английскому): приобретению знаний терминологической лексики по теме “Гимнастика”, навыков общения в профессиональной деятельности и чтении литературы по специальности.
Учебное пособие составлено в соответствии с требованиями программы по английскому языку для неязыковых вузов.
В самой сжатой форме оно охватывает всю основную терминологию по гимнастике.
При отборе лексики автор руководствовался принципом тематичности, сочетаемости, частотности употребления ее в современном английском языке. Текстовой материал знакомит студентов с основными типами соревнований по гимнастике, их программой и упражнениями; правилами судейства; историей развития гимнастики; белорусскими чемпионами Олимпийских игр по спортивной и художественной гимнастике и их достижениями.
При отборе текстового материала в качестве основного критерия служила информативная ценность текстов и их соответствие интересам студентов. Тексты взяты из оригинальных спортивных материалов.
Учебное пособие не претендует на полноту охвата всех реалий в области гимнастики, однако оно должно расширить словарный запас учащихся; активизировать знания, умения и навыки, полученные на ранних этапах изучения английского языка, за счет их тренировки в различных видах речевой деятельности.
|
|
|
Материал рекомендуется проходить в порядке, изложенном в пособии.
GYMNASTICS
I. Discuss with your group-mates before you read the text:
What sport is the most graceful and artistic?
II. Say in Russian:
• what you know about gymnastics competition
• how many events a men’s gymnastics competition has
• how many events a women’s gymnastics competition has
• what gymnastic equipment must be in the gymnasium
• what gymnastics equipment is used for men’s training (for women’s training).
Task I. Study the vocabulary to the text “Gymnastics” and translate the word combinations and sentences:
1. be regarded as... считаться
e.g. Gymnastics is regarded as one of the best means of physical education.
2. compulsory a обязательный
w.comb
| compulsory | element |
| exercise | |
| programme | |
| education |
3. handicapped n инвалид
4. artistic gymnastics спортивная гимнастика
syn. competitive gymnastics
5. rhythmic gymnastics художественная гимнастика
6. perform v выполнять, исполнять
e.g. Each contestant performs compulsory elements.
7. performance n исполнение, результат
8. naked a обнаженный, голый
e.g. The word gymnasium comes from a Greek word meaning to exercise naked.
9. judge n судья
e.g. Judges watch each performance.
10. equipment n 1. cнаряд 2. предмет 3. оборудование
syn. apparatus
11. gymnastic equipment гимнастический снаряд
syn. apparatus
12. routine n программа (спортивная)
e.g. Gymnast’s performance is called a routine.
w.comb.
| compulsory | routine | |
| optional | ||
13. earn v заработать, получить
w.comb.
| earn | money |
| score |
14. balance n равновесие
15. endurance n выносливость, стойкость
16. flexibility n гибкость
e.g. Gymnastics helps develop balance, endurance, flexibility, and strength.
17. television coverage n трансляция по телевидению
18. remarkably adv значительно
Task II. Read the text and find the answers to the questions:
1. What is gymnastics?
2. Where does gymnastic competition take place?
3. Is gymnastics included in the programme of the Olympic Games?
Text 1. Gymnastics
Gymnastics is regarded as one of the best means of physical training. Its exercises develop human body harmoniously and all sided and are
a compulsory element of the training in many sports.
|
|
|
It is one of the most graceful and artistic sports and popular all over the world. It is also used as a means of rehabilitation for handicapped.
Gymnastics is a sport in which each contestant performs acrobatic exercises on various types of gymnastic equipment. It can be divided into artistic gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastics and acrobatics. Artistic gymnastics has special programmes for men and women.
Two or more teams compete in a competition, which takes place in
a gymnasium. Gymnasium is a special room or building for instruction and practice in physical training. The word gymnasium comes from a Greek word meaning to exercise naked in ancient Greece, the word was used to mean public places set aside for athletic sports. Greek boys and young men wore no clothes when taking part in games, in order to have freedom of bodily movement.
Men’s and women’s team have separate competitions. Judges watch each gymnast’s performance called a routine and decide what score he or she has earned. Gymnastics helps develop balance, endurance, flexibility, and strength.
Gymnastics has been a part of the Olympic Games since the modern Olympics began in 1896. During the 1970’s, world wide television coverage of the Olympics helped gymnastics grow remarkably as a spectator sport. The International Gymnastics Federation is the governing body of gymnastics.
Vocabulary, Grammar and Speech Exercises
Ex. 1. Give the nouns corresponding to these verbs:
to develop, to perform, to compete, to instruct, to practice, to decide, to help, to begin, to grow.
Ex. 2. Form adverbs from these adjectives:
harmonious, graceful, artistic, separate, remarkable.
Ex. 3. Find Russian equivalents for the following English words and word- combinations:
| artistic gymnastics rhythmic gymnastics performance judge gymnastics equipment routine television coverage flexibility earn score compulsory | обязательный гибкость спортивный снаряд трансляция по телевидению исполнение зарабатывать очки художественная гимнастика спортивная программа судья спортивная гимнастика |
Ex. 4. Replace the following Russian words and word-combinations by their English equivalents from the text:
1. Одно из самых лучших средств тренировки. 2. Всесторонне и гармонично. 3. Обязательный элемент. 4. Выполнять акробатические упражнения. 5. В гимнастическом зале. 6. Программа гимнаста.
7. Зарабатывать очки. 8. Равновесие, гибкость, выносливость. 9. Зрелищный спорт. 10. Обнаженный.
Ex. 5. Give extensive answers to the following questions:
1. Why is gymnastics regarded as one of the best means of physical training?
2. What is gymnastics?
3. What forms is gymnastics divided into?
4. Where do gymnasts compete?
5. What word does the word gymnasium come from?
6. How is each gymnast’s performance called?
7. What qualities does gymnastics help to develop?
8. Since when has gymnastics been a part of the Olympic Games?
9. What is the governing body of gymnastics?
Ex. 6. Some statements are not true to the fact. Correct them:
1. Gymnastic exercises develop human body harmoniously and all-sided, but they are not compulsory elements of the training in many sports.
2. It is one of the most graceful and artistic sports, but it is not popular all over the world.
3. Coaches watch each gymnast’s performance and decide what score he or she has earned.
4. Gymnastics helps to develop balance, speed, flexibility, and strength.
Ex. 7. Make up ten questions to the text using the vocabulary of the text.
|
|
|
Ex. 8. Describe gymnastics as a sport. Say what you know about:
· • forms of gymnastics;
· • how gymnastics develop human body;
· • the place for practising gymnastics;
· • the International Gymnastic Federation.
Task I I I. Study the vocabulary to text 2 “Men’s events”:
1. consist v состоять
e.g. A men’s gymnastics competition consists of six events
2. set n серия, цикл, система
a последовательный, определенный
e.g. In a set order
3. floor exercises n вольные упражнения
e.g. The floor exercises give competitors a chance to warm up.
4. pommel horse n 1. конь-махи (упражнение)
2. конь с ручками (снаряд)
e.g. The pommel horse is the equipment that is used for men’s training.
5. rings n кольца
e.g. The gymnast must be very strong to perform on the rings.
6. horse vault n опорный прыжок для мужчин
7. parallel bars n параллельные брусья
e.g. The parallel bars are used only by men.
8. horizontal bar n перекладина
syn. high bar
e.g. The horizontal or high bar produces the most exciting moments in gymnastics.
9. specialist n спортсмен, выступающий в одном или двух видах программы
10. measure v иметь размеры
e.g. The mat measures 12 metres square.
11. require v требовать
e.g. The gymnast performs a continuous series of movements that require balance, flexibility, and strength performing the floor exercises.
12. handspring n переворот прогнувшись через прямые руки (назад, вперед, боком)
e.g. Each gymnast must perform handsprings.
13. leap n прыжок
e.g. Gymnasts movements include leaps in floor exercises.
14. somersault n сальто
e.g. Somersault in the air
15. tumbling n акробатика
syn. acrobatics
e.g. Series of movements include tumbling in floor exercises.
16. pad v набивать ватой или волосом
e.g. The padded piece of equipment
17. support n поддержка, опора, упор
v поддерживать
e.g. The gymnast uses the pommels to support the weight.
18. swing n взмах, мах, раскачивание
v махать, перемахивать, делать оборот
e.g. He swings his legs
19. the scissors n ножницы (скрестный мах ногами
(на коне))
|
|
|
e.g. The gymnast performs a movement called the scissors.
20. switch v переключать, менять
e.g. The gymnast switches the position of the legs, as he swings them from side to side.
21. frequently adv часто
e.g. The gymnast must frequently support himself with only one hand.
22. suspend v висеть, подвешивать
23. cable n канат, трос
e.g. The event is performed on two wooden rings suspended from cables.
24. grasp n хват, сжатие
v хватать, сжимать, выполнять хват
e.g. The gymnast leaps up and grasps the rings.
25. cross n крест
e.g. Azaryan’s cross.
26. extend v вытягивать, протягивать
e.g. The sportsmen extended his arms sideways.
27. upright a вертикальный, прямой
e.g. He supports himself in an upright position with his arms extended sideways.
28. remain v оставаться
e.g. The sportsman remained in the upright position.
29. motionless a неподвижный
e.g. The gymnast remained motionless.
30. resemble v быть похожим
e.g. The stand resembles the one on the pommel horse.
31. vault n опорный прыжок
v выполнять опорный прыжок
e.g. Men vault across the length of the horse.
32. approach v подходить, приближаться
e.g. He approached the parallel bars.
33. springboard n гимнастический мостик
e.g. After a running start, the gymnast jumps from a springboard.
34. twist n поворот на 360 градусов, вращение, винт
v поворачиваться, вращаться
e.g. The competitor may twist or turn before landing.
35. average n среднее число (величина)
e.g. The gymnast’s final score comes from an average of his two vaults.
36. apart adv врозь, широко, в отдельности
e.g. The parallel bars are two long wooden bars about 16.5 centimetres high and slightly more than shoulder width apart.
37. handstand n стойка на руках
e.g. The gymnast supports himself on the bars with his hands while performing handstands.
38. support swing размахивание в упоре
swing to handstand стойка на руках из упора махом назад
39. hold n хват, захват, выдержка (статический элемент)
v хватать, держать, выдерживать, фиксировать
e.g. The gymnast may perform several holding positions on the parallel bars.
40. reverse a обратный (хват, мах)
v выполнять в другую сторону, плечом назад
e.g. The competitor must reverse his position on the bar.
41. stagger v шататься
42. grip n хват (на параллельных брусьях)
43. regain v возвратить, получать обратно
e.g. On the bar the competitor releases his grip and regains while in the air.
44. dismount n соскок
v выполнять соскок
e.g. Many gymnasts finish their performance with a spectacular dismount from the bar.
45. all-around competition n соревнование по многоборью
e.g. All-around competition for men consists of six events.
46. all-around gymnastics champion n
чемпион в гимнастическом многоборье, абсолютный чемпион по гимнастике
|
|
|
Task I V. The men’s gymnastics competition consists of six events. Read the text and draw up the programme of a men’s gymnastics competition.
Text 2. Men’s events
There are three types of gymnastics competitions: 1) artistic gymnastics; 2) rhythmic gymnastics and 3) acrobatics. Artistic gymnastics is gymnastics without apparatus and gymnastics on apparatus.
A men’s gymnastics competition consists of six events that are held in a set order. These events, in order of performance, are the (1) floor exercise, (2) pommel horse, (3) rings, (4) horse vault, (5) parallel bars, and
(6) horizontal bar. Men who compete in all six events are called all-round gymnasts. Those who enter only one or two events are called specialists.
The floor exercise
The floor exercise is performed on a mat that measures 12 metres square. The gymnast performs a continuous series of movements that require balance, flexibility, and strength. These movements include handsprings, leaps, somersaults in the air, and tumbling. The floor exercise must be completed in not less than 50 seconds and not more than 70 seconds. In competition all parts of the floor area and all directions should be used. Strength movements should be performed slowly and static positions must be held for at least two seconds. Somersaults should be done at shoulder height.
The pommel horse
The pommel horse, or side horse, is named after the padded piece of equipment on which this event is held. The horse measures about 165 centimetres long and about 35 centimetres wide. It has two wooden handles on top called pommels which are about 125 centimetres from the floor. The gymnast uses the pommels to support his weight entirely with his hands. He swings his legs in circles around the sides and top of the horse without stopping. He also performs a movement called the scissors, beginning with one leg on each side of the horse. He switches the positions of his legs as he swings them from side to side. He must frequently support himself with only one hand while raising the other hand to swing his legs past.
The rings
This event is performed on two wooden rings suspended from cables about 250 centimetres above the floor. The gymnast leaps up and grasps the rings and then tries to keep them motionless while performing various movements. These include handstands and complete circular swings. The athlete supports his body in various strength positions, which require exceptional power. In a movement called the cross, for example, he supports himself in an upright position with his arms extended sideways. The event also includes holding positions, which require him to remain motionsless for two seconds. The gymnast performs his routine, concluding by landing on the floor with both legs together.
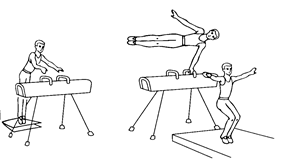
The horse vault
The horse vault is performed on a stand that resembles the pommel horse but has no pommels. In this event, the gymnast vaults across the length of the horse. He approaches the horse at a run and jumps up and forward from a low springboard. He places one or both hands on the horse for support as he goes over. He may twist around in the air, do a somersault, or perform any one of several movements. Competitors must not stagger on landing. In some competitions, the gymnast vaults twice and his final score comes from an average of his two vaults. In international competition, the gymnast vaults once.
The parallel bars
In this event, the gymnast performs on two long wooden bars about 165 centimetres high and slightly more than shoulder width apart. He supports himself on the bars with his hands while performing handstands, swings, twists, and other acrobatic movements. The gymnast may perform several holding positions on the parallel bars. In each one, he must remain motionless for one or two seconds. In addition, he performs various strength movements that require great arm power and must be done slowly.
The horizontal bar
The horizontal bar event takes place on a somewhat flexible steel bar fastened about 250 centimetres above the floor between two supports. The gymnast holds the bar with one or both hands and swings around it repeatedly. He performs several acrobatic movements without coming to a full stop. During this routine, he must reverse his position, which involves a change of grip on the bar. He also must perform manoeuvres that require him to release his grip and regain it again while in the air. Many gymnasts finish this event with a spectacular dismount from the bar. They swing rapidly around the bar, let go, and twist or somersault in the air before landing on their feet.
All-around competition
All-round competition for men consists of all six events. In national and international competitions, an all-around competitor must perform a compulsory routine in each event. This routine involves a set sequence of movements. The gymnast then performs an optional routine in each of the six events, doing whatever movements he chooses. Only all-around gymnasts compete in international competition.
Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
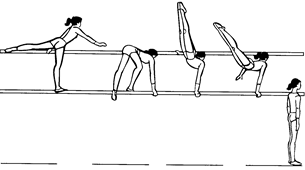
Ex. 1. Look at the pictures and name the events a men’s gymnastic competition consists of. Put the pictures in the events performing order.
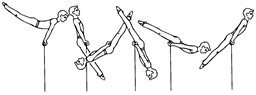
| 
|
| a | b |

| 
|
| c | d |
| 
|
| e | f |
Ex. 2. Say which English sentence contains Russian equivalent term:
| кольца | 1. The parallel bars is the apparatus that is used for men’s training. 2. He is a champion in the floor exercises. 3. A gymnast must be very strong to perform on the rings. |
| конь-махи | 1. The vaulting horse is shared by both men and women. 2. The horse vault is performed on a stand that resembles the pommel horse but has no pommels. 3. The rings is an event held on two wooden rings suspended from cables. |
| перекладина | 1. The parallel bars are used only by men. 2. The horizontal or high bar produces probably the most exciting moments in gymnastics. 3. The pommel horse event is performed on a piece of equipment called a horse. |
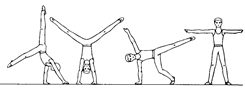
Ex. 3. Complete the sentences, using the pictures as prompts:
| 1. The most difficult apparatus for me is the... | 
|
| 2. Our national team was the best team in the... | 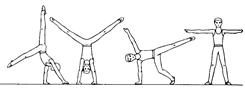
|
| 3. He was the best on the... | 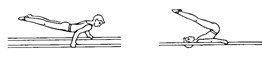
|
| 4. His favourite apparatus was the... | 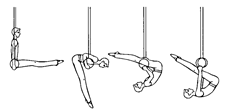
|
Ex. 4. Read the text. Insert the missing terms from the list:
floor exercises, rings, vaulting horse, pommel horse, horizontal bar, parallel bars
Many young men and women go in for gymnastics in our republic. They have necessary facilities, equipment and coaching in gymnastics. The gymnasts take part in competitions. Each gymnast may perform exercise on apparatus and the.... There are some kinds of apparatus for men and women and the... and the... for both of them.
It is necessary to distinguish the pieces of apparatus for supporting position and hanging position.
Among pieces of apparatus for supporting position the following are considered: the... and..., and among apparatus for handing position: the... and....
Ex. 5. Explain the terms used in gymnastics:
• all-around gymnast
• specialist
• apparatus
• compulsory routine
• optional routine
• all-around competition
• all-around champion
• motionless
• springboard
• grasp
Ex. 6. Name:
• the types of gymnastics competitions;
• the events of which a men’s gymnastics competition consist;
• the floor exercises;
• the exercises on the pommel horse;
• the exercises on the rings;
• the exercises on the parallel bars;
• the exercises on the horizontal bars.
Ex. 7. Say what you know about:
• the order of performing the events in a men’s gymnastics competition;
• the floor exercises;
• the pommel horse;
• the rings;
• the horse vault;
• the parallel bars;
• the horizontal bar;
• all-around competition for men.
Ex. 8. Speak on the topic:
• the apparatus for men’s gymnastic competitions;
• the programme of men’s gymnastic competitions;
• gymnast performance on the horizontal bar (rings, pommel horse, horse vault, parallel bars).
Task V. Study the vocabulary to the text “Women’s events” and translate the sentences:
1. side horse vault опорный прыжок (для женщин)
e.g. The side horse vault is performed on the same equipment used in men’s horse vaulting.
2. uneven parallel bars разновысокие брусья
syn. asymmetrical bars
e.g. In the uneven parallel bars the athlete switches rapidly back and forth
from one bar to the other.
3. balance beam бревно (гимнастическое)
e.g. The balance beam is used only by women in competitions.
4. count v засчитывать
e.g. Only the higher of the two scores counts.
5. agility n ловкость, быстрота
e.g. The athlete swings require great agility.
6. cartwheel n “колесо”
7. back handspring переворот назад, фляк
8. accompaniment n сопровождение, аккомпанемент
Task V I. Read the text and draw up the programme of the women’s gymnastics competition.
Text 3. Women’s events
A women’s gymnastics competition has four events. In order of performance, they are (1) side horse vault, (2) uneven parallel bars, (3) balance beam, and (4) floor exercise. Most women gymnasts enter all these events.
The side horse vault
The side horse vault is performed on the same equipment used in men’s horse vaulting. But women gymnasts vault across the horse’s width rather than its length. In most competitions, the gymnast vaults twice, but only the higher of the two scores counts.
The uneven parallel bars
In the uneven parallel gymnasts compete on two parallel wooden bars, one about 230 centimetres above the floor and the other about 150 centimetres high. The athlete swings around one bar at a time, performing manoeuvres that require great flexibility and agility. She switches rapidly back and forth from one bar to the other, trying to keep in constant motion.
The balance beam
The balance beam involves a long wooden beam about 10 centimetres wide. Competitors perform jumps, leaps, running steps, and turns on it and try to use the beam’s full length. The best performers also do cartwheels, back handsprings, and somersaults. The routine must last at least 1 minute 10 seconds but not more than 1 minute 30 seconds.
The floor exercise
The floor exercise is performed on a mat that resembles the one used in the men’s floor exercise. Women gymnasts perform this event with a musical accompaniment. Each contestant designs her routine to match the tempo and mood of the music she has selected. She must take at least 1 minute 10 seconds and not more than 1 minute 30 seconds to demonstrate her skill in acrobatics, dancing, and tumbling.
All-around competition
All-around competition for women includes all four events. In national and international competitions, every competitor performs a compulsory routine in each event and then an optional routine in each. International competition is open only to all-around gymnasts.
Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
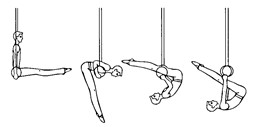
Ex. 1. Look at the pictures and name the events a women’s gymnastic ccompetition consists of. Put the pictures in the events performing order.
| 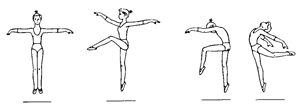
|
| a | b |
| 
|
| c | d |
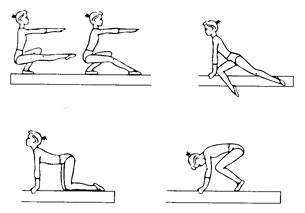
Ex. 2. Complete the sentences using the pictures as prompts:
| 1. For the majority of gymnasts and spectators, the most exciting event in women’s competition is the … | 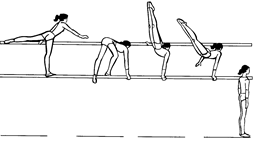
|
| 2. The only apparatus which is essentially feminine and has no counterpart in the men’s competition is the … | 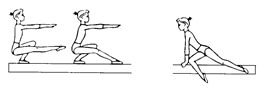
|
| 3. The exercise performed on the same equipment used in men’s horse vaulting is the … | 
|
| 4. The exercise performed with a musical accompaniment … | 
|
Ex. 3. Find out which English sentence contains Russian equivalent term:
| бревно | 1. Uneven bars is the only event for women – the only event in which the hands are almost constantly in use, gripping the rails. 2. Vaulting uniquely involves the element of flight of the four events in women’s gymnastics. 3. A beginner must spend many hours learning to move around on the beam in comfort – walking, running, skipping, leaping. |
| разновысокие брусья | 1. The vaulting runway is sixty to eighty feet long. 2. The intricate movements prescribed for uneven bars comprise a number of fear – producing elements, as do routines in all the events. 3. The balance beam adventure begins with the working surface of the beam itself. |
| конь | 1. In gymnastic vaulting there are two pieces of equipment: the horse and takeoff board. 2. Floor exercises is commonly regarded as the most beautiful event in gymnastics. 3. Uneven bars is a relatively new event in women’s gymnastics having been performed for the first time at the 1952 Olympics. |
| “колесо” | 1. Somersault is a leap or fall in which one turns heels over head before landing on one’s feet. 2. To skip is to jump lightly and quickly. 3. The best gymnasts perform cartwheels, back handsprings, and somersaults on the beam. |
Ex. 4. Read the text. Insert the missing terms from the list beam, six, four, leaps, somersault, floor exercises, balance, spins, vaulting horse, balances, uneven bars, gymnastics
Success in the...exercises for men and... for women at the Olympic Games requires that the gymnast develops a strong physique and all-round ability.
The...... are usually the first of the events since they give competitors a chance to warm up with movements not requiring tremendous strength. The sportswoman aims to impress the judges with a sequence of...,..., and together with the elements of acrobatics. Strength movements should be performed slowly and static position must be held for at least two seconds –... should be done at shoulder height.
The...... is the simplest of all the events. Men vault over the horse lengthways, passing first over the “croup” and then the “neck”. Women vault sideways, putting their hands on the middle of the horse which is not as high as for men.
Women use the....... Emphasis is on the suspension and momentary bracing positions and the female gymnast must change bars by turning or executing elegant movements.
The... is used only by women in competitions. It was originally envisaged as a method for women to demonstrate... but in recent years many of the skills of the floor exercises have been introduced. Many female competitors use ballet, which is very close to many of the... movements.
Ex. 5. Explain the terms used in gymnastics:
• the side horse vault
• the uneven parallel bars
• the balance beam
• cartwheel
• back handspring
• somersault
• running steps
• skips
Ex. 6. Name the
• women’s gymnastics competition events
• exercises on the uneven parallel bars
• exercises on the beam
• floor exercises for women.
Ex. 7. Say what you know about:
• the order of performing the events in a women’s gymnastics competition
• the exercises on apparatus for women
• all-around competition for women
Ex. 8. Speak on the topic:
• the apparatus for women’s gymnastics competitions
• the programme for the women’s gymnastic competitions
• gymnast performance on the balance beam (uneven bars, side horse).
Task VII. Read the text about the gymnastics competitions. Find out how the winner is determined
Gymnastics competition
Judging
Judging involves the assessment of a gymnastic performance by someone supposedly well-versed in the detailed and rather complex methods of evaluation.
Gymnastics has matured into a highly technical sport, and the evaluation of routines has become a complicated process.
Judges of gymnastics competitions carefully watch each compulsory routine for such flaws as falls, improper body position, omissions, slowness, and stops. In the optional routines, the judges base their scores on difficulty, form, and the combination of movements.
A perfect score for any event is 10.00. The judges subtract points or tenths of a point for each flaw. In optional routines, the judges may award bonus points for especially difficult or original movement.
In men’s competition, five judges, including one called a head or superior judge, score the performance of each gymnast. In most cases, the score of the head judge is not used. Instead, the head judge takes the scores of the other judges and eliminates the highest and lowest ones. The head judge computes an athlete’s final score by averaging the two middle scores. If the difference between the two middle scores exceeds a certain range, the head of judge’s own score is used as a guide in adjusting the final score. At an international competition, each team’s top five individual all-around scores are added together for the team score.
In women’s competition, there are seven judges, including a head judge. The highest and lowest scores of the six other judges are dropped and the remaining four are averaged to produce the final score.
Speech Exercises
Ex. 1. Answer the following questions:
1. What does judging involve?
2. What do the judges of gymnastics competitions watch for?
3. What do the judges of gymnastics competitions base their scores on?
4. Which is a perfect score for any gymnastics event?
5. What do the judges subtract points or tenths of a point for?
6. What actions do the judges award bonus points for?
7. How many judges are there in the men’s gymnastics competitions?
8. What are the head judge’s duties?
9. How does a gymnast get an average mark (score)?
10. When is the head judge’s own score used?
11. How is the team score determined at the international competition?
12. How many judges are there in the women’s competition?
13. How is the final score in the women’s gymnastics competition produced?
Ex. 2. Say what instruction you would give to a would-be judge.
Ex. 3. Say what you know about:
• judges in gymnastics competitions
• the evaluation of routines
• possibility for former gymnasts to become judges
Task VIII. a) Skim the text to understand what it is about. b) Time your reading. Its good if you can read this text for 75 words per minute.
|
|
|
12 |


