 |
Tools for evaluating a story
|
|
|
|
Any work of fiction consists of relatively independent elements — narration, description, dialogue, interior monologue, digressions, etc. Narration is dynamic, it gives a continuous account of events, while description is static, it is a verbal portraiture of an object, person or scene. It may be detailed and direct or impressionistic, giving few but striking details. Through the dialogue the characters are better portrayed, it also brings the action nearer to the reader, makes it seem more swift and more intense. Interior monologue renders the thoughts and feelings of a character. Digression consists of an insertion of material that has no immediate relation to the theme or action. It may be lyrical, philosophical or critical. The interrelation between different components of a literary text is called composition.
Most novels and stories have plots. Every plot is an arrangement of meaningful events. No matter how insignificant or deceptively casual, the events of the story are meant to suggest the character's morals and motives. Sometimes a plot follows the chronological order of events. At other times there are jumps back and forth in time (flashbacks and foreshadowing). The four structural components of the plot are exposition, complication, climax and denouement. Exposition contains a short presentation of time, place and characters of the story. It is usually to be found at the beginning of the story, but may also be" interwoven in the narrative by means of flashbacks, so that the reader gradually comes to know the characters and events leading up to the present situation. Complication is a separate incident helping to unfold the action, and might involve thoughts and feelings as well. Climax is the decisive moment on which the fate of the characters and the final action depend. It is the point at which the forces in the conflict reach the highest intensity. Denouement means "the untying of a knot" which is precisely what happens in this phase. Not all stories have a denouement. Some stories end right after the climax, leaving it up to the reader to judge what will be the outcome of the conflict.
The way a story is presented is a key element in fictional structure. This involves both the angle of vision, the point from which the people, events, and other details are viewed, and also the words of the story. The view aspect is called the focus or point of view, and the verbal aspect the voice. It is important to distinguish between the author, the person who wrote the story, and the narrator, the person or voice telling the story. The author may select a first-person narrative, when one of the characters tells of things that only he or she saw and felt. In a third-person narrative the omniscient author moves in and out of peoples thoughts and comments freely on what the characters think, say and do.
Most writers of the short story attempt to create characters who strike us, not as stereotypes, but as unique individuals. Characters are called round if they are complex and develop or change in the course of the story. Flat characters are usually one-sided, constructed round a single trait; if two characters have distinctly opposing features, one serves as a foil to the other, and the contrast between them becomes more apparent.
|
|
|
Round and flat characters have different functions in the conflict of the story. The conflict may be external, i.e. between human beings or between man and the environment (individual against nature, individual against the established order/values in the society). The internal conflict takes place in the mind, here the character is torn between opposing features of his personality. The two parties in the conflict are called the protagonist and his or her antagonist. The description of the different aspects (physical, moral, social) of a character is known as characterization when the author describes the character himself, or makes another do it, it is direct characterization. When the author shows the character in action, and lets the reader judge for himself the author uses the indirect method of characterization.
The particular time and physical location of the story form the setting. Such details as the time of the year, certain parts of - the landscape, the weather, colours, sounds, or other seemingly uninteresting details may be of great importance. The setting can have various functions in a given story: 1) it can provide a realistic background, 2) it can evoke the necessary atmosphere, 3) it can help describe the characters indirectly.
The author's choice of characters, events, situations, details and his choice of words is by no means accidental. Whatever
leads us to enter the author's attitude to his subject matter is called tone. Like the tone of voice, the tone of a story may communicate amusement, anger, affection, sorrow, contempt. The theme of a story is like unifying general idea about Life that the entire story reveals. The author rarely gives a direct statement of the theme in a story. It is up to the reader to collect and combine all his observations and finally to try to formulate the idea illustrated by the story. The most important generalization the author expresses is sometimes referred to as the message. The message depends on the writer's outlook, and the reader may either share it or not.
There are no hard and fast rules about text interpretation but one is usually expected to sum up the contents and express his overall view of the story. The following questions will be useful in the analysis if a story.
COMPOSITION AND PLOT; FOCUS; VOICE
What are the bare facts of the story? What is the exposition, complication, climax and denouement? Are the elements of the plot ordered chronologically? How does the story begin? Is the action fast/slow moving? Which episodes have been given the greatest emphasis? Is the end clear-cut and conclusive or does it leave room for suggestion? On what note does the story end? Is the plot of major or minor importance? Does the author speak in his own voice or does he present the events from the point of view of one of the characters? Has the narrator access to the thoughts and feelings"of all the characters? — Only a few? Just one? Is the narrator reliable? Can we trust his judgement? Is there any change in the point of view? What effect does this change have? Is the narrative factual/dry/emotional? Are the events credible or melodramatic?
|
|
|
CHARACTERS AND SETTING
What are the characters names and what do they look like? Does this have any significance? Are the characters round or flat? Does the narrator employ interior monologue to render the thoughts and feelings of the characters? Are the characters credible? Do they act consistently? If not, why not? With what main problem is the protagonist faced? Is it a conflict with another individual? With society? Within himself? In the
course of the story do the characters change as a result of their experience? Does the narrator sympathise with the characters? Remains aloof and detached? Is the particular setting essential or could the story have happened anywhere at any time? Has the narrator emphasised certain details? Which? Why? What functions does the setting have?
THEME AND ARTISTIC EFFECT
What is the general effect achieved? Has the writer caused characters, and settings to come alive? What was the conflict and how was is solved, if at all? Were there any striking repetitions of actions, words, thoughts or symbols? Has the protagonist learned anything? Has he or she acquired a greater knowledge or insight or reached a new awareness? Does the title of the story indicate anything about the theme? Are the theme and story fused and inseparable? How does the word choice and syntax contribute to the atmosphere? Does the story abound in tropes or does the narrator use them sparingly? What images lend the story a lyrical, melancholy, humorous effect? Are they genuine, poetic, fresh, trite, hackneyed, stale? Is the general tone matter-of-fact, sentimental, moralizing, bitter, ironical, sarcastic? What attitude to life does the story express? What seems to be the relationship between the author, the narrator and the reader?
w. s.
By L.P. Hartley
(continued)
A little comforted, Walter went home. The talk with the police had done him good. He thought it over. It was quite true what he had told them — that he had no enemies. He was not a man of strong personal feelings such feelings as he had went into his books. In bis books he had drawn some pretty nasty characters. Not of recent years, however. Of recent years he had felt a reluctance to draw a very bad man or woman: he thought it morally irresponsible and artistically unconvincing, too. There was good in everyone: Iagos were a myth. Latterly — but he had to admit that it was several weeks since he laid pen to paper, so much had this ridiculous business of the postcards
weighed upon his mind — if he had to draw a really wicked person he represented him as a Nazi — someone who had deliberately put off his human characteristics. But in the past, when he was younger and more inclined to see things as black or white, he had let himself go once or twice. He did not remember his old books very well but there was a character in one, "The Outcast'’, into whom he had really got his knife. He had written about him with extreme vindictiveness, just as if he was a real person whom he was trying to show up. He had experienced a curious pleasure in attributing every kind of wickedness to this man. He never gave him the benefit of the doubt He had never felt a twinge of pity for him, even when he paid the penalty for his misdeeds on the gallows. He had so worked himself up that the idea of this dark creature, creeping about brimful of malevolence, had almost frightened him.
Odd that he couldn't remember the man's name.
He took the book down from the shelf and turned the pages — even now they affected him uncomfortably. Yes, here it was, William... William... he would have to look back to find the surname. William Stamsforth.
|
|
|
His own initials.
Walter did not think the coincidence meant anything but it coloured his mind and weakened its resistance to his obsession. So uneasy was he that when the next postcard came it came as a relief.
'I am quite close now’, he read, and involuntarily he turned the postcard over. The glorious central tower of Gloucester Cathedral met his eye. He stared at it as if it could tell him something, then with an effort went on reading. 'My movements, as you may have guessed, are not quite under my control, but all being well I look forward to seeing you sometime this week-end. Then we can really come to grips. I wonder if you'll recognize me! It won't be the first time you have given me hospitality. My hand feels a bit cold to-night, but my handshake will be just as hearty. As always, W.S.’
'P.S. Does Gloucester remind you of anything? Gloucester gaol?'
Walter took the postcard straight to the police station, and asked if he could have police protection over the week-end. The officer in charge smiled at him and said he was quite sure it was a hoax; but he would tell someone to keep an eye on the premises.
'You still have no idea who it could be?' he asked.
Walter shook his head.
It was Tuesday; Walter Streeter had plenty of time to think about the week-end. At first he felt he would not be able to live through the interval, but strange to say his confidence increased instead of waning. He set himself to work as though he could work, and presently he found he could — differently from before, and, he thought, better. It was as though the nervous strain he had been living under had, like an add, dissolved a layer of non-conductive thought that came between him and his subject: he was nearer to it now, and his characters, instead of obeying woodenly his stage directions, responded wholeheartedly and with all their beings to the tests he put them to. So passed the days, and the dawn of Friday seemed like any other day until something jerked him out of his self-induced trance and suddenly he asked himself, "When does a week-end begin?"
A long week-end begins on Friday. At that his panic returned. He went to the street door and looked out. It was a suburban, unfrequented street of detached Regency houses like his own. They had tall square gate-posts, some crowned with semi-circular iron brackets holding lanterns. Most of these were out of repair: only two or three were ever lit. A car went slowly down the street; some people crossed it: everything was normal.
Several times that day he went to look and saw nothing unusual, and when Saturday came, bringing no postcard, his panic had almost subsided. He nearly rang up the police station to tell them not to bother to send anyone after all.
They were as good as their word: they did send someone. Between tea and dinner, the time when week-end guests most commonly arrive, Walter went to the door and there, between two unlit gate-posts, he saw a policeman standing — the first policeman he had ever seen in Charlotte Street. At the sight, and at the relief it brought him, he realized how anxious he had been. Now he felt safer than he had ever felt in his life, and also a little ashamed at having given extra trouble to a hardworked body of men. Should he go and speak to his unknown guardian, offer him a cup of tea or a drink? It would be nice to hear him laugh at Walter's fancies. But no — somehow
he felt his security the greater when its source was impersonal, and anonymous. 'P.C. Smith' was somehow less impressive than 'police protection’.
Several times from an upper window (he didn't like to open the door and stare) he made sure that his guardian was still there: and once, for added proof, he asked his house-keeper to verify the strange phenomenon. Disappointingly, she came back saying she had seen no policeman; but she was not very good at seeing things, and when Walter Went a few minutes later he saw him plain enough. The man must walk about, of course, perhaps he had been taking a-stroli when Mrs. Kendal looked.
|
|
|
It was contrary to his routine to work after dinner but tonight he did, he felt so much in the vein. Indeed, a sort of exaltation possessed him; the words ran off his pen; it would be foolish to check the creative impulse for the sakeof a little extra sleep. On, on. They were right who said the small hours were the time to work. When his housekeeper came in to say good night he scarcely raised his eyes.
In the warm, snug little room the silence purred around him like a kettle. He did not even hear the door bell till it had been ringing for some time..
A visitor at this hour?
His knees trembling, he went to the door, scarcely knowing what he expected to find; so what was his relief on opening it, to see the doorway filled by the tall figure of a policeman: Without waiting for the man to speak —
'Come in, come in, my deaf fellow,' he exclaimed. He held his hand out, but the policeman did not take it. 'You must have been very cold standing out there. I didn't know that it was snowing, though,' he added, seeing the snowflakes on the policeman's cape and helmet. 'Come in and warm yourself:'
'Thanks,' said the policeman. 'I don't mind if I do.'
Walter knew enough of the phrases used by men of the policeman's stamp not to take this for a grudging acceptance. 'This way,' he prattled on. 'I was writing in my study. By Jove, it is cold, I'll turn the gas on more. Now won't you take your traps off, and make yourself at home?'
'I can't stay long,' the policeman said, 'I've got a job to do, as you know.'
'Oh yes,' said Walter, 'such a silly job, a sinecure.' He stopped, woadering if the policeman would know what a sinecure was. 'I suppose you know what it's about — the postcards?'
The policeman nodded.
'But nothing can happen to me as long as you are here,' said Walter. 'I shall be as
safe... as safe as houses. Stay as long as you can, and have a drink.'
'I never drink on duty,' said the policeman. Still in his cape and helmet, he looked round. 'So this is where you work,' he said,
'Yes, I was writing when you rang.'
'Some poor devil's for it, I expect,' the policeman said.
'Oh, why?' Walter was hurt by his unfriendly tone, and noticed how hard his gooseberry eyes were.
'I'll tell you in a minute,' said the policeman, and then the telephone bell rang. Walter excused himself and hurried from the room.
'This is the police station,' said a voice. 'Is that Mr, Streeter?'
Walter said it was.
'Well, Mr. Streeter, how is everything at your place? All right, I hope? I'll tell you why I ask. I'm sorry to say we quite forgot about that little job we were going to do for you. Bad co-ordination, I'm afraid.'
'But,' said Walter, 'you did send someone.'
'No, Mr. Streeter, I'm afraid we didn't.'
'But there's a policeman here, here in this very house.'
There was a pause, then his interlocutor said, in a less casual voice:
'He can't be one of our chaps. Did you see his number by any chance?'
'No.'
A longer pause and then the voice said:
'Would you like us to send somebody now?'
'Yes, p... please.'
'All right then, we'll be with you in a jiffy.'
Walter put back the receiver. What now? he asked himself. Should he barricade the door? Should he run out into the street? Should he try to rouse his housekeeper? A policeman of any sort was a formidable proposition, but a rogue policeman! How
long would it take the real police to come? A jiffy, they had said. What was a jiffy in terms of minutes? While he was debating the door opened and his guest came in.
'No room's private when the street door's once passed,' he said. 'Hadyou forgotten I was a policeman?'
'Was?' said Walter, edging away from him. 'You are a policeman.'
'I have been other things as well,' the policeman said. 'Thief, pimp, blackmailer, not to mention murderer. Youshould know.'
The policeman, if such he was, seemed to be moving towards him and Walter suddenly became alive to the importance of small distances — the distance from the sideboard to the table, the distance from one chair to another.
'I don't know what you mean,' he said. "Why do you speak like that? I've never done you any harm. I've never set eyes on you before.'
|
|
|
'Oh, haven't you?' the man said. 'But you've thought about me and' — his voice rose — 'and you've written about me. You got some fun out of me, didn't you? Now I'm going to get some fun out of you. You made me just as nasty as you could. Wasn't that doing me harm? You didn't think what it would feel like to be me, did you? You didn't put yourself in my place, did you? You hadn't any pity for me, had you? Well, I'm not going to have any pity for you.'
'But I tell you,' cried Walter, clutching the table's edge, 'I don't know you!'
'And now you say you don't know me! You did all that to me and then forgot me!' His voice became a whine, charged with self-pity. 'You forgot William Stainsforth.'
'William Stainsforth!'
'Yes. I was your scapegoat, wasn't I? You unloaded all your self-dislike on me. You felt pretty good while you were writing about me. You thought, what a noble, upright fellow you were, writing about this rotter. Now, as one W.S. to another, what shall I do, if I behave in character?'
'I... I don't know,' muttered Walter.
'You don't know?' Stainsforth sneered. 'You ought to know, you fathered me. What would William Stainsforth do if he met his old dad in a quiet place, his kind old dad who made him swing?'
Walter could only stare at him.
'You know what he'd do as well as I,' said Stainsforth. Then his face changed and he said abruptly,'No, you don't, because you never really understood me, I'm not so black as you painted me.' He paused, and a flicker of hope started in Walter's breast. 'You never gave me a chance, did you? Well, I'm going to give you one. That shows you never understood me, doesn't if?'
Walter nodded.:
"And there's another thing you have forgotten.'
'What is that?'
'I was a kid once,' the ex-policeman said.
Walter said nothing.
'You admit that?' said William Stainsforth grimly. 'Well, if you can tell me of one virtue you ever credited me with — just one kind thought — just one redeeming
feature —'
'Yes?' said Walter, trembling.
'Well, then I'll let you off.'
'And if I can't?' whispered Walter.
'Well, then, that's just too bad. We'll have to come to grips and you know what that means. You took off one of my arms but I've still got the other. "Stainsforth of the iron hand" you called me.'
Walter began to pant.
‘I’ll give you two minutes to remember,' Stainsforth said. They both looked at the clock. At first the stealthy movement of the hand paralysed Walter's thought. He stared at William Stainsforth's face, his cruel, crafty face, which seemed to be always in shadow, as if it was something the light could not touch. Desperately he searched his memory for the one fact that would save him; but his memory, clenched like a fist, would give up nothing. 'I must invent something,' he thought, and suddenly his mind relaxed and he saw, printed on it like a photograph, the last page of the book. Then, with the speed and magic of a dream, each page appeared before him in perfect clarity until the first was reached, and he realized with overwhelming force that what he looked for w&s not thererln all that evil there was not one hint of good. And he felt, compulsively and with a kind of exaltation, that unless he testified to this the cause of goodness everywhere would be betrayed.
"There's nothing to be said for you!' he shouted. 'And you know it! Of all your dirty tricks this is the dirtiest! You want me to whitewash you, do you? The very snowflakes on you are turning black! How dare you ask me for a character? I've given you one already! God forbid that I should ever say a good word for you! I'd rather die!'
Stainsforth's one arm shot out. "Then die!' he said.
The police found Walter StreelEer slumped acrbss the din-ing-table. His/body was still warm, but he was dead. It was easy to tell how he died; for it was not hisijnand.that his visitor had shaken, but his throat. Walter Streeter had been strangled. Of his assailant there was no trace. On the table and on his clothes were flakes of melting snow. But how it came there remained a mystery, for no snow was reported from any district on the day he died.
Unit Six
magazine programme — programme which is a mixture of "hard" news and feature items.
wild/nature life programme — programme showing animals, birds, etc. in their natural environment
quiz programme — programme on which members of the audience are asked questions, in case of correct answer they receive prizes
sitcom (situation comedy) — short film providing entertainment
soap opera — play (an afternoon television regular feature) which originally appeared on the radio and was sponsored by soap advertisers, continuing from day to day, presenting emotional and melodramatic situations like many operas of the 19th century (thus named "soap operas")
video clip — minifilm, about the length of a song, interpreting or dramatising a song
Western — uniquely American film presenting myths about pioneering, courageous Americans
Major British and American Broadcasting Companies, Networks, News Agencies
Great Britain
BBC — British Broadcasting Corporation
ITV — Independent Television News Ltd. (company responsible for providing national news for independent television in Britain)
PA — Press Association (British national dohiestic news agency)
Reuter [‘r 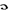 itә] — British-based agency supplying foreign news
itә] — British-based agency supplying foreign news
EBU — European Broadcasting Union
Eurovision — International network for the exchange of television programmes
the USA
ABC — American Broadcasting Company
CBS — Columbia Broadcasting System
NBC — National Broadcasting Company
AP — Associated Press (American news agency)
INTERVIEW TECHNIQUES
Ten-point plan to make a good impression
1. Be pleasant and polite to the receptionist or secretary who greets you. It will get you off to a good start.
2. If you are going through a closed door into an office, knock first and then walk in.
3. Don't sit down until you are offered a chair.
4. Don't smoke or chew.
5. Don't slouch, don't fold your arms or fidget. Sit in a relaxed upright position.
6. Speak up, don't mutter or mumble. Try to act with modest confidence.
7. Don't be flippant. Some candidates give jokey answers to cover up nerves. Be sure you are on the same wavelength as the interviewer before you introduce humour into the discussion.
8. Show a genuine interest in the work and the firm you have applied to.
9. Analyse what qualities the interviewer is looking for and try to demonstrate how far you match up.
10. Make sure you know the interviewer's surname, and use it if a natural opportunity occurs.
Questions the interviewer may ask you
There are a number of questions you are likely to be asked — so think about what you are going to say. It may help to discuss these with a friend before the interview. Probable questions include:
Tell me about yourself.
Why do you want the job?
What is your experience in the field?
What makes you think you would be good at the job?
What do you do in your spare time?
What qualities do you think you have to offer?
What is your ultimate career ambition?
What kind of books or newspapers do you read?
Questions you may want to ask the interviewer
During the course of the discussion, the interviewer will probably explain most of the details about the job. But there may be gaps and you may want to ask your own question.
Try not to appear too eager; wait until towards the end of the interview. He or she may then ask if there is anything you would like to know — and that's your chance to be offered the job, then you will need all the facts to enable you to make the right decision as to whether or not you will accept There are some of the points you may want to raise:
What are the normal hours of work?
Are there any unusual hours?
Will I be paid overtime?
What is the pay?
What holidays will I be entitled to?
Who will I be directly responsible to?
What training will I be given?
When may I expect a decision?
When would I be expected to start?
Whatever you do don't sound as if you are only interested in what you get out of the job. Remember the interviewer is looking for someone who is going to put a lot into the
job — ability, industry and enthusiasm.
ADDITIONAL EXERCISES1
COMPOSITION SUBJECTS
|
|
|


