 |
The physical principle of the methods using the Doppler effect
|
|
|
|
The physical principle of the methods using the Doppler effect
The physical principle used in modern medicine to measure blood flow velocity, was opened in 1842 by J. C. Doppler (Fig. 37).

Fig. 37. Christian Andreas Doppler
ULTRASOUND DIAGNOSTIC STUDY IN OBSTETRICS
Indications for ultrasound examination during pregnancy:
•Conducting mass triple screened studies for the purpose of prenatal diagnosis of congenital fetal malformations and the formation of high-risk groups for possible chromosomal aberrations;
•Implementation of visual control over the processes of embryo - and fetogenesis, the development of the organs;
•Identification of the uterus and appendages pathology;
•Ultrasonic support of invasive procedures, interventions, diagnostic procedures and medical treatment and surgical intervention during pregnancy.
Ultrasonic screening
The term " screening" is derived from the English verb " to screen", which means " to sift, sort. " The essence of the term encompasses the basic meaning and method.
Screening studies - is the research being undertaken in certain groups of patients regardless of the presence or absence of complaints and clinical manifestations of the disease under study.
Long-term randomized studies have shown that mass ultrasound is an effective method to reduce perinatal mortality due to antenatal detection of congenital malformations of the fetus. Thus, two or three times of mass ultrasound screening during pregnancy is required to maintain in many countries.
At the time of writing this document in accordance with the Order № 572n from 01. 11. 2012 Ministry of Health Service of the Russian Federation ultrasound screening is done three times during pregnancy:
The 1st mass ultrasound screening performed in the first trimester of pregnancy in terms of 11-14 weeks (optimally – 12wk) when crown-rump length of a fetus (CRL) is in the range from 45 to 84 mm;
• The 2nd ultrasound screening performed in the second trimester of pregnancy in terms of 18-21 weeks;
• The 3rd ultrasound screening performed in the third trimester of pregnancy in terms of 30-34 weeks.
The following is an extract from the order № 572n from 01. 11. 2012 year of the Ministry of Health Service of Russian Federation:
" At 11-14 weeks of gestation pregnant woman is sent to the medical organization that provides expert level of prenatal diagnosis, to conduct a comprehensive prenatal (antenatal) diagnosis of a child's development, including the US by medical specialists who have undergone special training and have a permit to conduct ultrasound screening in the first trimester, and the determination of maternal serum markers (Pregnancy associated plasma protein A(PAPP-A) and free β - subunit of HGC), with subsequent program complex calculation of individual risk of having a baby with a chromosomal abnormality.
At 18-21 weeks of gestation pregnant woman is sent to the medical organization performing prenatal diagnosis, in order to conduct ultrasound to exclude a later manifestation of congenital malformations of the fetus.
|
|
|
At term of 30-34 weeks ultrasound is made at the place of observation of the pregnant woman. "
Ultrasonography in the trimester of pregnancy
Ultrasound scan in the first trimester is carried out transabdominally (TA) and/or transvaginal (TV) method. To conduct transabdominal scan is desirable that the bladder was not completely empty, in contrast to transvaginal sonography (Fig. 38, 39).
At the 1st trimester of pregnancy transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS) and/or transvaginal US (TVUS) is performed. To carry out a pelvic transabdominal ultrasound scan, the patient will be asked to drink around a litre of water, or another clear liquid an hour before the scan appointment. To carry out a transvaginal US bladder might need to be empty or partially full.
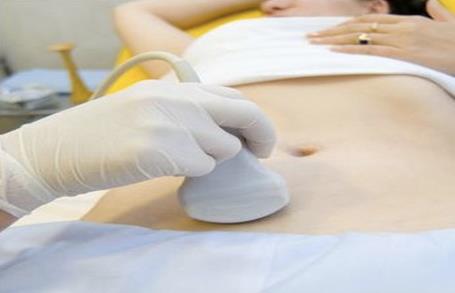
Fig. 38. Transabdominal ultrasound scanning
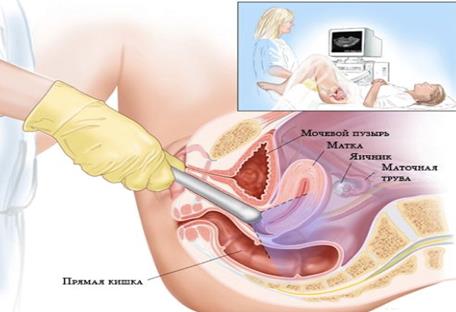
Fig. 39. Transvaginal ultrasound scanning
During ultrasound screening, the physician evaluates not only ultrasound anatomy of the fetus and excludes or detects ultrasound markers of chromosomal pathology, but also performs fetometry to clarify the term of pregnancy, assesses chorion / placental, point of attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta, specifies the number of fetuses and determines the type of chorionicity in multiple gestation, and others. (Fig. 40).
Fig. 40. Multiple gestation
In accordance with recommendations of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) at any case of multiple pregnancy the type of its “chorionicity” and “amnionicity” should be defined and documented in the first trimester by " lambda (λ )-sign" and " T-sign" (Fig. 41, 42).
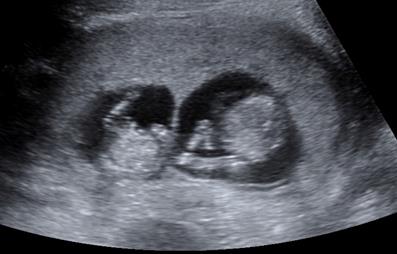
Fig. 41. The arrow points to the " lambda-sign" in dichorionic twin pregnancy

Fig. 42. The arrow points to the " T-sign" in monochorionic twin pregnancy
Indications for selective (if indicated) ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy:
1. The need to confirm the existence of intrauterine pregnancy (in case of irregular menstrual cycle, using methods of assisted reproductive technology, in the period of lactation amenorrhea, etc. );
2. The discrepancy between the estimated term of pregnancy and size of the uterus (suspected ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, missed abortion, to exclude anomalies of the uterus, leiomyomas, etc. );
3. Appearance of bleeding from the genital tract (to eliminate imminent abortion, abortion in progress, incomplete abortion, polyps, and others. );
4. The presence of tumor-like formations in the pelvic cavity during pregnancy;
5. Ultrasound support of medical abortion, vacuum aspiration of the ovum, chorionic villus sampling.
|
|
|


