 |
Ultrasound examinations during the third trimester
|
|
|
|
Ultrasound examinations during the third trimester
Ultrasound in the third trimester
The purpose of ultrasound in the third trimester (30-34 weeks gestation) assessment is not so much anatomical, many of the functional characteristics of the fetus to ascertain the capacity of key life-support systems (placenta, heart, Feto-placental hemodynamics) for elaboration of further tactics of management of pregnancy and childbirth. During this period, the most active use of ultrasonic methods based on the Doppler effect (Doppler investigation of vessels of fetoplacental uniot and cardiotocography).
Doppler ultrasound
Evaluation of blood flow in the umbilical artery with the help of the Doppler effect is used to monitor the fetal condition in the third trimester of pregnancy. Disturbance of blood flow in the umbilical artery, identified with the Doppler study is a marker of utero-placental insufficiency, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or the development of pre-eclampsia
Doppler indicated for:
1. Patients with history of low baby weight at birth, and prenatal death.
2. Patients with extragenital disease; cardiovascular, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, etc.
3. Patients with hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
4. Patients with intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) in pregnancy
5. Patients with multiple gestation.
6. Patients with high risk of developing anemia in the fetus.
7. In case of use inhibitors of prostaglandins (to avoid premature closure of the
ductus arteriosus) in pregnancy
8. In case of doubtful or negative result of the evaluation of biophysical profile
profile (BPP)
9. Patients with impaired reactivity of cardiac activity of the fetus by antenatal
cardiotocography (CTG).
The umbilical arterial waveform usually has a " saw tooth" pattern with flow always in the forward direction. (Fig. 71)
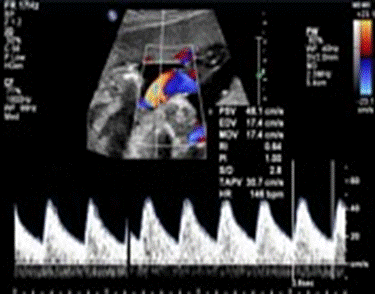
Fig. 71. “Saw tooth" pattern” of the umbilical arterial waveform
The commonly used parameters are:
umbilical arterial SD ratio(SDR): systolic velocity / diastolic velocity
Pulsatility Index (PI): (PSV-EDV) /TAV
Resistive Index (RI): (PSV-EDV) /PSV
Where:
PSV: peak systolic velocity
EDV: end diastolic velocity
TAV: time averaged velocity
In growth-retarded fetuses and fetuses developing intrauterine distress, the umbilical - artery blood velocity waveform usually changes in a progressive manner as below:
reduction in end diastolic flow: increasing RI values, PI values and SD ratios;
- absent end diastolic flow (AEDF): RI = 1;
- reversal of end diastolic flow (REDF).
Cardiotocography
In obstetrics, cardiotocography (CTG) is a technical method for recording (-graphy) the fetal heartbeat using ultrasound (cardio-) and the uterine contractions (-toco-) during pregnancy, typically in the third trimester. The machine which is used to perform the monitoring is called a cardiotocograph, commonly known as a fetal monitor. Cardiotocography or CTG is a test usually done in the third trimester of pregnancy.
|
|
|
The advantages of CTG:
1. the simplicity and accessibility;
2. reliable method;
3. inexpensive;
4. noninvasive;
5. receiving information at the time of the study;
6. assessment of the fetus condition continuously and in dynamics;
7. documentary evidence about the status of the fetus and nature of labor activity in the form of a graph.
CTG is used both antenatally (before birth) and during labor to monitor the baby for any signs of distress. Sensors are placed against the mother's abdomen and are connected to a heart rate monitor, which produces a record of the baby's heartbeat. CTG records changes in the fetal heart rate and their temporal relationship to uterine contractions. The goal is to identify fetuses that may experience a lack of oxygen (hypoxia), as well as identify possible fetal heart response to the periodic decrease in oxygenation due to uterine contractions during childbirth. The baby's heart rate can be heard as a beating or pulsing sound which the machine produces. The machine also provides a printout which shows the baby's heart rate over a certain length of time. It also shows how the heart rate changes with contractions.
The technique
It involves the placement of 2 transducers on the abdomen of pregnant women.
One transducer records the fetal heart rate using ultrasound. The other transducer monitors the contractions of the uterus. It does this by measuring the tension of the maternal abdominal wall. This provides an indirect indication of intrauterine pressure. The result is displayed as a graph on paper or the monitor.
CTG is performed 1 time in 7-10 days in all pregnant women, in cases of suspected violation of blood supply in feto-placental unit - 1 every 2-3 days. For an accurate diagnosis 3-4 consecutive studies required. CTG is made mainly from 32 weeks of pregnancy, it is technically possible with the 26 th week. Recording is carried out for 40 minutes and lasts up to 1 hours as needed
|
|
|


