 |
This illustration shows the wireframe of a hand made from relatively few polygons -- 862 total.
|
|
|
|

The outline of the wireframe can be made to look more natural and rounded, but many more polygons -- 3,444 -- are required.
Surface Textures
When we meet a surface in the real world, we can get information about it in two key ways. We can look at it, sometimes from several angles, and we can touch it to see whether it's hard or soft. In a 3D graphic image, however, we can only look at the surface to get all the information possible. All that information breaks down into three areas:
Color: What color is it? Is it the same color all over?
Texture: Does it appear to be smooth, or does it have lines, bumps, craters or some other irregularity on the surface?
Reflectance: How much light does it reflect? Are reflections of other items in the surface sharp or fuzzy?
One way to make an image look "real" is to have a wide variety of these three features across the different parts of the image. Look around you now: Your computer keyboard has a different color/texture/reflectance than your desktop, which has a different color/texture/reflectance than your arm. For realistic color, it’s important for the computer to be able to choose from millions of different colors for the pixels making up an image. Variety in texture comes both from mathematical models for surfaces ranging from frog skin to Jell-o gelatin to stored “texture maps” that are applied to surfaces. We also associate qualities that we can't see -- soft, hard, warm, cold -- with particular combinations of color, texture and reflectance. If one of them is wrong, the illusion of reality is shattered.

Adding a surface to the wireframe begins to change the image from something obviously mathematical to a picture we might recognize as a hand.
We'll take a look at lighting and perspective in the next section.
Lighting and Perspective
When you walk into a room, you turn on a light. You probably don't spend a lot of time thinking about the way the light comes from the bulb or tube and spreads around the room. But the people making 3D graphics have to think about it, because all the surfaces surrounding the wireframes have to be lit from somewhere. One technique, called ray-tracing, plots the path that imaginary light rays take as they leave the bulb, bounce off of mirrors, walls and other reflecting surfaces, and finally land on items at different intensities from varying angles. It's complicated enough when you think about the rays from a single light bulb, but most rooms have multiple light sources -- several lamps, ceiling fixtures, windows, candles and so on.
Lighting plays a key role in two effects that give the appearance of weight and solidity to objects: shading and shadows. The first, shading, takes place when the light shining on an object is stronger on one side than on the other. This shading is what makes a ball look round, high cheekbones seem striking and the folds in a blanket appear deep and soft. These differences in light intensity work with shape to reinforce the illusion that an object has depth as well as height and width. The illusion of weight comes from the second effect -- shadows.
|
|
|

Lighting in an image not only adds depth to the object through shading, it "anchors" objects to the ground with shadows.
Solid bodies cast shadows when a light shines on them. You can see this when you observe the shadow that a sundial or a tree casts onto a sidewalk. And because we’re used to seeing real objects and people cast shadows, seeing the shadows in a 3D image reinforces the illusion that we’re looking through a window into the real world, rather than at a screen of mathematically generated shapes.
Perspective
Perspective is one of those words that sounds technical but that actually describes a simple effect everyone has seen. If you stand on the side of a long, straight road and look into the distance, it appears as if the two sides of the road come together in a point at the horizon. Also, if trees are standing next to the road, the trees farther away will look smaller than the trees close to you. As a matter of fact, the trees will look like they are converging on the point formed by the side of the road. When all of the objects in a scene look like they will eventually converge at a single point in the distance, that's perspective. There are variations, but most 3D graphics use the "single point perspective" just described.

In the illustration, the hands are separate, but most scenes feature some items in front of, and partially blocking the view of, other items. For these scenes the software not only must calculate the relative sizes of the items but also must know which item is in front and how much of the other items it hides. The most common technique for calculating these factors is the Z-Buffer. The Z-buffer gets its name from the common label for the axis, or imaginary line, going from the screen back through the scene to the horizon. (There are two other common axes to consider: the x-axis, which measures the scene from side to side, and the y-axis, which measures the scene from top to bottom.)
The Z-buffer assigns to each polygon a number based on how close an object containing the polygon is to the front of the scene. Generally, lower numbers are assigned to items closer to the screen, and higher numbers are assigned to items closer to the horizon. For example, a 16-bit Z-buffer would assign the number -32,768 to an object rendered as close to the screen as possible and 32,767 to an object that is as far away as possible.
In the real world, our eyes can’t see objects behind others, so we don’t have the problem of figuring out what we should be seeing. But the computer faces this problem constantly and solves it in a straightforward way. As each object is created, its Z-value is compared to that of other objects that occupy the same x- and y-values. The object with the lowest z-value is fully rendered, while objects with higher z-values aren’t rendered where they intersect. The result ensures that we don’t see background items appearing through the middle of characters in the foreground. Since the z-buffer is employed before objects are fully rendered, pieces of the scene that are hidden behind characters or objects don’t have to be rendered at all. This speeds up graphics performance. Next, we'll look at the depth of field element.
|
|
|
Depth of Field
Another optical effect successfully used to create 3D is depth of field. Using our example of the trees beside the road, as that line of trees gets smaller, another interesting thing happens. If you look at the trees close to you, the trees farther away will appear to be out of focus. And this is especially true when you're looking at a photograph or movie of the trees. Film directors and computer animators use this depth of field effect for two purposes. The first is to reinforce the illusion of depth in the scene you're watching. It's certainly possible for the computer to make sure that every item in a scene, no matter how near or far it's supposed to be, is perfectly in focus. Since we're used to seeing the depth of field effect, though, having items in focus regardless of distance would seem foreign and would disturb the illusion of watching a scene in the real world.
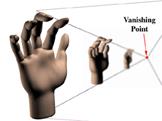
The second reason directors use depth of field is to focus your attention on the items or actors they feel are most important. To direct your attention to the heroine of a movie, for example, a director might use a "shallow depth of field," where only the actor is in focus. A scene that's designed to impress you with the grandeur of nature, on the other hand, might use a "deep depth of field" to get as much as possible in focus and noticeable.
Anti - aliasing
A technique that also relies on fooling the eye is anti-aliasing. Digital graphics systems are very good at creating lines that go straight up and down the screen, or straight across. But when curves or diagonal lines show up (and they show up pretty often in the real world), the computer might produce lines that resemble stair steps instead of smooth flows. So to fool your eye into seeing a smooth curve or line, the computer can add graduated shades of the color in the line to the pixels surrounding the line. These "grayed-out" pixels will fool your eye into thinking that the jagged stair steps are gone. This process of adding additional colored pixels to fool the eye is called anti-aliasing, and it is one of the techniques that separates computer-generated 3D graphics from those generated by hand. Keeping up with the lines as they move through fields of color, and adding the right amount of "anti-jaggy" color, is yet another complex task that a computer must handle as it creates 3D animation on your computer monitor.

The jagged "stair steps" that occur when images are painted from pixels in straight lines mark an object as obviously computer-generated.
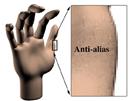
Drawing gray pixels around the lines of an image -- "blurring" the lines -- minimizes the stair steps and makes an object appear more realistic.
We'll find out how to animate 3D images in the coming sections.
Realistic Examples
When all the tricks we've talked about so far are put together, scenes of tremendous realism can be created. And in recent games and films, computer-generated objects are combined with photographic backgrounds to further heighten the illusion. You can see the amazing results when you compare photographs and computer-generated scenes.

This is a photograph of a sidewalk near the How Stuff Works office. In one of the following images, a ball was placed on the sidewalk and photographed. In the other, an artist used a computer graphics program to create a ball.


Image A Image B
Can you tell which is the real ball? Look for the answer at the end of the article.
Making 3D Graphics Move
So far, we've been looking at the sorts of things that make any digital image seem more realistic, whether the image is a single "still" picture or part of an animated sequence. But during an animated sequence, programmers and designers will use even more tricks to give the appearance of "live action" rather than of computer-generated images.
|
|
|
How many frames per second?
When you go to see a movie at the local theater, a sequence of images called frames runs in front of your eyes at a rate of 24 frames per second. Since your retina will retain an image for a bit longer than 1/24th of a second, most people's eyes will blend the frames into a single, continuous image of movement and action.
If you think of this from the other direction, it means that each frame of a motion picture is a photograph taken at an exposure of 1/24 of a second. That's much longer than the exposures taken for "stop action" photography, in which runners and other objects in motion seem frozen in flight. As a result, if you look at a single frame from a movie about racing, you see that some of the cars are "blurred" because they moved during the time that the camera shutter was open. This blurring of things that are moving fast is something that we're used to seeing, and it's part of what makes an image look real to us when we see it on a screen.
However, since digital 3D images are not photographs at all, no blurring occurs when an object moves during a frame. To make images look more realistic, blurring has to be explicitly added by programmers. Some designers feel that "overcoming" this lack of natural blurring requires more than 30 frames per second, and have pushed their games to display 60 frames per second. While this allows each individual image to be rendered in great detail, and movements to be shown in smaller increments, it dramatically increases the number of frames that must be rendered for a given sequence of action. As an example, think of a chase that lasts six and one-half minutes. A motion picture would require 24 (frames per second) x 60 (seconds) x 6.5 (minutes) or 9,360 frames for the chase. A digital 3D image at 60 frames per second would require 60 x 60 x 6.5, or 23,400 frames for the same length of time.
Creative Blurring
The blurring that programmers add to boost realism in a moving image is called "motion blur" or "spatial anti-aliasing." If you've ever turned on the "mouse trails" feature of Windows, you've used a very crude version of a portion of this technique. Copies of the moving object are left behind in its wake, with the copies growing ever less distinct and intense as the object moves farther away. The length of the trail of the object, how quickly the copies fade away and other details will vary depending on exactly how fast the object is supposed to be moving, how close to the viewer it is, and the extent to which it is the focus of attention. As you can see, there are a lot of decisions to be made and many details to be programmed in making an object appear to move realistically.
There are other parts of an image where the precise rendering of a computer must be sacrificed for the sake of realism. This applies both to still and moving images. Reflections are a good example. You've seen the images of chrome-surfaced cars and spaceships perfectly reflecting everything in the scene. While the chrome-covered images are tremendous demonstrations of ray-tracing, most of us don't live in chrome-plated worlds. Wooden furniture, marble floors and polished metal all reflect images, though not as perfectly as a smooth mirror. The reflections in these surfaces must be blurred -- with each surface receiving a different blur -- so that the surfaces surrounding the central players in a digital drama provide a realistic stage for the action.
|
|
|


