|
Department of infectious diseases
|
|
|
|
Department of infectious diseases
1. The word for treatment and isolation of patients
2. It must be in a distant building
3. The building with two entrances one for medical personals and the other for patients
4. There must be a special room for reception
5. There are two types of rooms for patients
A - Highly secured room (box) for one or two patients These rooms must be on the ground floor Direct from out side there are special entrance for each and every room These rooms are for patients with:
1. Contagious air born diseases measles and diphtheria
2. Patients with undiagnosed infectious diseases
В - Secured room (polubox) for one or two patients. These must be in the first floor. Patients must enter the room through department.
These rooms are for patients with disease which can be transmitted indirectly e g infective hepatitis and typhoid fever.
Exercise
Write your conclusion about the department of infectious diseases, after studying the plan.
Questions
1 - Situation of the department?
2 - Types of rooms?
3 - Total number of beds?
4 - Number of beds in each room?
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT OF CHILDREN'S
The definition of physical development of children s, one of importantmethod for health estimation.
Growth: physical maturation of the body.
Development: functional or physiological maturation of the body.
Every doctor must have full information about growth and development of the children, and the methods by which he can estimate the signs of growth and development.
Factors influencing growth and development:
1. Economic status
2. Social as: a) Living conditions b) Literacy c) Family size
3. Genetic
4. Nutritional status
5. Bad habits
6. Environmental
7. Prenatal
8. Diseases
Various periods of growth
• prenatal
• postnatal
• new-born up to 4 weeks
• infancy first year
• toddler up to 3 years
• pre-school up to 6 years
• school-going up to 11 years
• pubescent up to 16 years
|
|
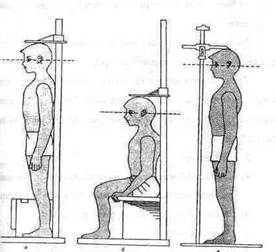
Pictvre 5. Assessment of length
Signs for assessment of growth
3 Somatometric signs as:
a) Body weight. The normal birth weight must be around 3, 4 kg. In the first 10 days the baby looses about 10% of his body weight, then he doubles his weight in the end of 4 month, and treepels it in the end of 10 month.
b) Weight at 7-12 years = age (years) x 3. The length at 9 month of age is about 75 cm After 4 years, the body height is over 5 cm every year until puberty
c) Body ration, as head circumference and chest circumference.
For measuring head size you have to place the tape over occiput and just above the supraorbital ridges.
The head/chest circumference ratio at birth, the head circumference larger than chest circumference, about 2, 5 cm, at 12 month's, both are equal. After the first year chest becomes greater than head, about 2, 5 cm.
|
|
|
2 Somatoscopy:
a) skin fat thickness, it is recorded at the level of the umbilical, in or over the triceps the back Normal size 1-2 cm.
b) The chest shape cylindrical, trivial and mixed.
c) Vertebral shape
d) The shape of the foot it may be normal or flat feet.
e) Dentition and puberty, for example the breast changes, appearance of pubic hair, change of the voice, and menstruation.
3 Physiometnc as:
the muscles power, pulse, blood pressure and pulmonary capacity.
| |
 Picture 6. The shap of the foot
Picture 6. The shap of the foot
The main principles of growth and development:
1. There is no relation between the growth and development f internal organs
|
|
|