|
d ) Toxicology. Lead poisoning. It enter in body through. Exercises. e) Ionising radiation. Ionising radiation are either electromagnetic as gamma radiation and roentgen, and particulate as alpha and beta particles. They are derived from natural or arti
|
|
|
|
d ) Toxicology
Toxin: is a substance which may causing human disease or injury.
Toxicology: is the study of external substances and their effects on human.
Duration of exposure:
a) Acute poisoning: as a result from single exposure tohigh doses,
d) Chronic poisoning: as a result from exposure for a long period to low doses.
The chemical agents may occure in the:
1. Form solid dust as rocks, and coal
2. Cases as carbon dioxide, and hydrogen cyanide.
3. Vapours of hydrochloride and nitric acids.
The chemical poisoning by industries commonly take place in, ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption.
Example of chemical poisoning:
Lead poisoning
It enter in body through
1. Ingestion - such as tetraethyl lead
2. Skin absorption - as paints and oil
5. Inhalation - as fumes and dust of lead
Table 16. Class of harmnuss ( chemical agents) (State standard 1976)
| signs | ||||
| The level of dose caused death by ingestion nig/kg | less than 1 5 | 15-150 | 151-5000 | more than 5000 |
| The level of dose caused death by skin absorption mg/kg | less than 100 | 100-500 | 501-2500 | more than |
| The level of dose caused death by inhalation mg/kg | less than 500 | 500-5000 | 5001-50000 | more than 50000 |
| Coefficient of poisoning by inhalation | more than 300 | 300-30 | 29-3 | less than 3 |
| Zone of severe influence Zac | less than 6 | 6-18 | 18, 1-54, 0 | more than 54 |
| Zone of chronic influence Zch | more than 1 0 | 10-5 | 4, 9-2, 5 | less than 2, 5 |
| Admissible concentration in the air of workshop mg/m | less than 0, 1 | 0, 1-1 | 1, 1-10 | more than |
The source:
Manufacture of batteries, paints, lead pipes, ship industry
Clinical picture: motor weakness, neurobehavior abnormalities, Spongy gums, lead colic softening of the bones, and high level of lead in blood and urine.
Mercury poisoning:
It inter in body through ingestion, inhalation and veri rarethrough skin absorption.
Sources:
Medical industries ( thermometer), gold manufacture, electrical apparatus and pesticides.
Clinical picture of chronic poisoning:
Stomatitis, bronchitis, line on the gums, colitis, anaemia, weakness, tremor arid excitement (e. g. irritability)
Preventive measures:
1. Regular medical examination of workers
2 Minimising environmental pollution
3. Proper ventilation
4. Periodically measuring the level ofchemical agents in the air ofworkshops
5 Use of protection instruments by workers
6. Regular find out the level of dangerous of chemical agents.
|
|
|
Exercises
1. Find out the level of concentration of dust inceramic factory, and write your recommendations.
The samples was taken by air aspiration
Air capacity - 2001
Weight of the filter before aspiration - 0, 494 g
Weight of the filter after aspiration - 0, 528g
Air temperature - 20°
Atmospheric pressure - 755mm
Type of dust - silica 75%
To find out the concentration you have to use the formula:
D Q • 1000
X = ————— mg/m
Vo
V1 • 273•B
V0 = ----------------
273 • t • P
Q - Weight of filter before aspiration
Q1 - Weight of filter after aspiration
D Q= Q – Q1
X - concentration of dust
V0 - normal capacity of air
P - atmospheric pressure = 760,
t- temperature of air
В - barometric pressure in the workshop
Table 1 7. The result you have to compare with sanitary standard table
| Agents | admissible level |
| Silica 70% | |
| Asbeste | |
| Capper | |
| Hexochloran | 0, 1 |
| Lead | 0, 01 |
| Cement | |
| Vegetable and animal dust | 2-4 |
2. Vibration
Find out the speed of vibration on the vibrogramma of workshop, and write your conclusion.
a) The distance between highest and lowest waves = 24 mm
b) Number of the waves = 32 =frequency - 32 Hz
c) Amplitude = 24: 2 = 0, 12 cm
use the formula: V =2p • f • a
V - speed of vibration
f - frequency
a - amplitude
After that compare the result with sanitary standard table to find the type of vibration.
3. Toxicology:
Find out the level of harmness of CH3COOCH = CH2 (vinilacctate)
The volatile( flyer) = 415 mg/l
Limac (limit of acute concentration) = 25 mg/l
A. C (admissible concentration) = 10 mg/l
Lim ch (limit of chronic concentration) = 0, 005 mg/l
The result of laboratory work, where they used this agent in different concentration - 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 mg/l. To find their effect on six groups of mouse's in each group six mouse's, through inhalation.
After inhalation the number of dead mouse's was 3, 4, 5, 6, 6 and 6.
Use the following formulas
S ( a+b) • (m-n)
CL 50 = ----------------
200
CL 50 - the level of deadly dose.
C 20 CL 50 Lim ac
Kp = ----------, Z ac = ----------, Zch = ----------,
CL 50 Lim ch Lim ch
The results you have to compare with special table of class harness of chemical agents.
e) Ionising radiation
Ionising radiation are either electromagnetic as gamma radiation and roentgen, and particulate as alpha and beta particles. They are derived from natural or artificial radioactive isotopes.
The most harmful radiation is Alpha particles
|
|
|
Physical character.
Alpha radiation: The distance of movement in the air from f the source 15 cm, penetrating ability 3-5 mm. Beta radiation: The distance of movement in the air from the source 17m, penetrating ability 1 cm.
Gamma radiation: High energy shortwavelength radiation. Has deepest penetrating ability.
The natural sources of radiation to which most of the people are exposed to, are, cosmic rays, atmospheric radiation, and per-restrial radiation.
Half life: The time taken by radioactive isotope to decay to half of its radioactivity.
Rad: The unit of absorbed dose of radiation. unit of radioactivity, equivalent 10 ¯ 2 joules of energy absorbed per kg of irradiated substance. 1 rad = 1 ber
Roentgen: The unit of measure the quantity of gamma ionising radiation in the air.
Gray: The unit of measure the amount of energy absorbed in any substance gray = 100 rad.
Maximum permissible dose MPD (FDD) - The dose which ' must not produce of any pathological changing in the body of personal in the period of his work
a) For personal - 5 ber/year
b) For those who are living or working in the area of the source, but they have no direct contact with the radiation – 0, 5 per/year.
e) Total natural radiation per year for population – 0
Damage caused by ionising radiation two types:
c) Thе damage of the chromosomal structure (genetic effects)
d) Formation of H + ion, OH ion and hydrogen peroxide
The most sensitive tissues to ionising radiation is, bone morrow, lymphatic, germinal cells of the testes and ovaries.
The main complication:
Infection, haemorrhage, depression of immune system, septicaemia
Acute radiation syndrome:
Nousea, vomiting, diarrhoea. During the critical period there is, bone morrow failure with fever and oropharyngeal ulceration, massive doses of gamma rays may cause death in few hours or days.
Local radiation injury:
Chronic exposure; Cancer, mutation of chromosomes, skin lesions, signs of erythema over the area of exposure, late complications isotropy of the skin, and later hyperkeratosis.
The types of ionising radiation, and the protective methods:
I.
II. Closed source of ionising radiation:
Are those which do not cause radiopollution of surroundings area, as X-ray machine.
The protective methods:
a) Control the level activity of the ionising agent
120 • r²
m = —————
t
b) Limitation the time of work with ionising radiation
120 • r²
t = —————
m
с) Fixed distance between the workers and thesource (Theintensity of exposure varies inversely with the square of the distance from the source).
|
|
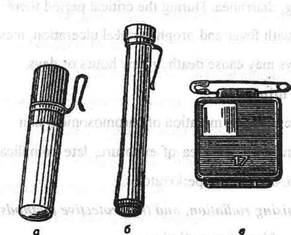
Picture 10. Individual dosemeter
a) КГО-2; b)DK-0, 2; c) Cassete IFK
|
|
|