 |
Rectus abdominis (m. rectus abdominis/прямая мышца живота)
|
|
|
|
· Origin. From the anterior surfaces of the 5th, 6th and 7th costal cartilages.
· Insertion. The pubic crest and the pubic tubercle and the front of the symphysis. There are three tendinous intersections (intersectiones tendineae /сухожильные перемычки) in the upper part of the muscle which are adherent to the anterior rectus sheath.
· Actions. The muscle is enclosed in the rectus sheath. A strong flexor of the trunk, it can also tilt the pelvis backwards. In a person lying prone, the rectus abdominis contracts when the head is lifted from the pillow or when the leg is raised from the bed.
Pyramidalis (m. pyramidalis /пирамидальная мышца)
· Origin. From the superior pubic ramus.
· Insertion. To the linea alba.
· Actions. Tenses the linea alba.
Nerve supply. All these muscles are supplied by the lower six thoracic and the first lumbar nerves.
Quadratus lumborum (m. quadratus lumborum /квадратная мышца поясницы)
· Origin. From the posterior part of the iliac crest.
· Insertion. To the 12th rib.
· Action. Side flexion of the trunk.
· Nerve supply. Adjacent lumbar nerves.
Abdominal fascia
Superficial fascia (fascia superficialis /поверхностная фасция)
It is the part of the common superficial fascia of the body.
Abdominal fascia proper (fascia abdominis propria /собственная фасция живота)
It covers the muscles of abdomen.
Endoabdominal fascia (fascia endoabdominalis /внутрибрюшная фасция)
It lines the inner surface of the abdominal walls and in places is named according to the localization (transversalis fascia, iliac fascia etc.).
Topography of the abdomen
Linea alba (linea alba /белая линия)
· The aponeuroses of the two oblique and transverse muscles of the abdomen meet and fuse on the midline and form the tendinous band, linea alba, between two rectus abdominis muscles.
· It stretches from the xiphoid process of the sternum to the pubic symphysis.
· Almost in the middle of the linea alba is the umbilical ring (annulus umbilicalis /пупочное кольцо).
· The linea alba has a little vessels only, because surgeons make use of this circumstance during operations.
The inguinal canal (canalis inguinalis /паховый канал)
· The canal is the passage transmitting the spermatic cord in the male and the round ligament of the uterus in the female.
· The inguinal canal is located in the lower part of the abdominal wall on each side of the abdomen, just above the inguinal ligament (from middle of the ligament until its medial end).
· The canal has four walls:
- The anterior wall is formed by the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle.
- The posterior wall is formed by the transversalis fascia.
- The superior wall is formed by the inferior borders of the internal oblique and the transverse muscles.
|
|
|
- The inferior wall is formed by the inguinal ligament.
· The canal has two inguinal rings:
- The superficial inguinal ring (anulus inguinalis superficialis /поверхностное паховое кольцо) is a gap in the anterior wall of the canal. It is bounded by the two crura of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle, the lateral crus (crus laterale /латеральная ножка) inferiorly and the medial crus (crus mediale /медиальная ножка) superiorly. The ring is bounded by the intercrural fibres (fibrae intercrurales /межножковые волокна) laterally and by the reflected ligament (lig. reflexum /загнутая связка) medially. The reflected ligament is the continuation of the lateral crus.
- The deep inguinal ring (anulus inguinalis profundus /глубокое паховое кольцо) in the posterior wall is the depression in the transverse fascia.
The rectus sheath (vagina m. recti abdominis /влагалище прямой мышцы живота)
It is formed by the aponeurosis of the three lateral abdominal muscles.
In the upper part:
- The anterior layer (lamina anterior /передняя пластинка) consists of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle and the anterior plate of the aponeurosis of the internal oblique muscle.
- The posterior layer (lamina posterior /задняя пластинка) consists of the aponeurosis of the transverses abdominis muscle, the posterior plate of the aponeurosis of the internal oblique muscle and the transversal fascia.
In the lower part (4-5 cm below the umbilicus):
- The anterior layer consists of the aponeurosis of the external, internal oblique and the transverse abdominis muscles.
- The posterior layer consists of the transvesal fascia only.
The arcuatе line (linea arcuata /дугообразная линия) is the line where the aponeuroses of these muscles pass in front of the rectus muscle.
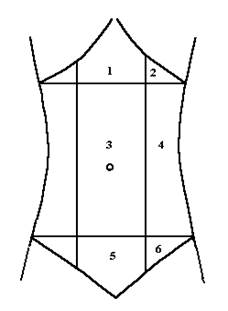 Fig. Abdominal regions.
1 - Epigastric region. 2 - Hypochondrium.
3 - Umbilical region. 4 - Lateral region or flank.
5 - Pubic region. 6 - Inguinal region or groin.
Fig. Abdominal regions.
1 - Epigastric region. 2 - Hypochondrium.
3 - Umbilical region. 4 - Lateral region or flank.
5 - Pubic region. 6 - Inguinal region or groin.
| Abdominal regions · The abdomen is divided by two horizontal and two vertical lines into nine regions (fig.). - The vertical lines pass along the lateral borders the rectus abdominis muscles. - The upper horizontal line passes through the anterior ends of the tenth ribs. - The lower horizontal line passes through the anterior superior iliac spines. · The superior region (above the upper horizontal line) is called the epigastric region. There are the epigastric region and two hypochondriums within it. · The middle region (between two horizontal lines) is called the mesogastric region. There are the umbilical and two lateral regions or flank within it. · The inferior region (below the lower horizontal line) is called the hypogastric region. There are the pubic and two inguinal regions or groin within it. |
The muscles of upper limb
(musculi membri superioris /мышцы верхней конечности)
|
|
|


