 |
Present Continuous (настоящее продолженное)
|
|
|
|
Compose your sentences.


Example: Sam is a doctor. He usually works in a hospital. But now he is playing football.
Обратите внимание на разницу в употреблении
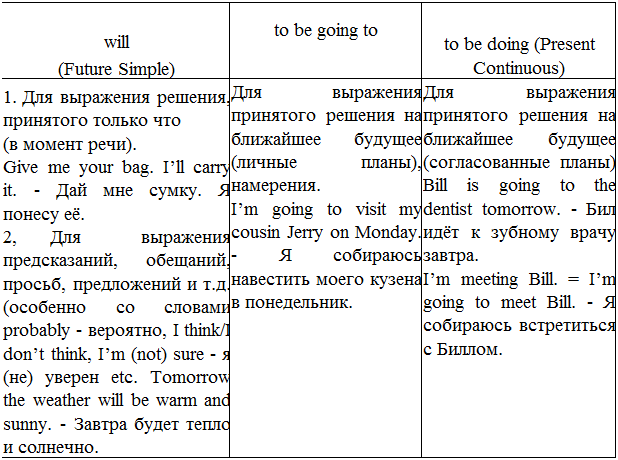
Exercise One. Read and translate the sentences. Объясните употребление глагола.
1) Good-bye! I will phone you on Sunday.
2) What are you going to do tomorrow evening?
3) They are getting married on July, 17.
4) The weather is nice today. We will have breakfast in the garden.
5) What time are you leaving tomorrow?
6) Dick is not going to the cinema tonight.
7) The director will be here in ten minutes.
8) There is no bread at home. I will go and buy some.
9) I’m not working next week.
10) What are you going to wear to the party?
Exercise Two. Put the verb into the Present Simple or Present Continuous. Translate the text.
It is Monday morning. The family is at home
My name (to be) Nan. I (to have got) a large family. We (to be) busy. My parents (to go) to work five times a week. They (not to work) on Saturday and Sunday. My sister (to go) to the Institute every day. She (to be) a student. Her name (to be) Alice. Now Alice (to take) a shower in the bathroom. My brothers (to go) to school. Their names (to be) Jake and David. They (to be) good pupils. Now Jake and David (to have) breakfast. They (to be) good eaters. I (not to be) a pupil. I (to be) six. But I can read very well. Now I (to read) a very interesting fairy-tale. It (to be) eight o’clock. Our parents (to leave) home for work now.
Exercise Three. a) What opportunities do students have at our University? Tell what they can/cannot do. Complete the list.
· work at computer rooms
· have new equipment
· take books from the library
· go to concerts, parties, discos,
· learn any foreign language
· use the Internet center
· attend sport sections
· go to the swimming pool
· study by correspondence
· use crib sheets (шпаргалки) during exams
· take part in international conferences
b) What obligations and prohibitions do students have? Tell what they must/ mustn’t (needn’t) do. Complete the list.
· be late for classes
· pass their exams during sessions
· get ready for lectures and seminars
· think about their future
· write lecture notes
· respect teachers
· attend lectures and seminars regularly
· hand in their course papers in time
· study hard
· lead active social life
Exercise Four. Compose your own list of “can/cannot do” or “must/ mustn’t (needn’t)” for the students of your group.
Exercise Five. Discussion.
1. Can students choose the subjects they study in the first year of the law course?
2. Must students take an exam in all the subjects they study?
3. How many exams do you take this term?
Lesson 4
Rules and Prohibitions.
Each country in the world, and even each state of the United States, has its own system of law. All the systems have different and common aspects. Some rules we should know, because they help us behave correctly and protect us. The simplest example is the rules for driving a car. Let’s discuss this topic.
|
|
|
Task One. Is it True or False? Prove your point of view.
9) All the passengers must wear a seatbelt. (= it’s the law. It’s compulsory)
10) He mustn’t exceed the speed limit. (= it’s against the law. It’s illegal)
11) If you park in a non-stopping area, you have to pay a fine.
12) If you drive too fast, you may have an accident.
13) Drivers mustn’t have vehicle insurance.
14) If the driver doesn’t have a license, he might be arrested. (be arrested - арестован)
15) You mustn’t use dangerous driving.
16) If you drink and drive, you may/might lose you license.
17) Everyone has to pay the fine.
18) If the driver exceeds the speed limit, he may get penalty points on his license.
Task Two. Read and translate the phrases from the possible conversation between the policeman and driver. Скажите, при каких ситуациях данные фразы могли быть произнесены.
20) Can I see your passport and driving license?
21) Can you get out of the car, please?
22) Do you know that the seatbelts for children are compulsory, sir?
23) You must wear helmet at all times you go on motorbike.
24) It’s illegal to drive without a seatbelt.
Task Three. Write positive (+) and negative (-) sentences. Use must/mustn’t
18) Drivers/drive/on the right-hand side of the road. (in our country/in England)
19) You/drive/when you are drinking alcohol.
20) Small children/sit/in the front seat/of the car.
21) Vehicles/have/child seats/for small children.
22) Motorcycle drivers/and passengers/wear helmets.
23) You/drive at more than 50 km per hour on the city’s road.
24) You/use a mobile phone when you are driving.
Task Four. Translate the sentences.
15) Nick is in hurry. He is to be on the conference in time. Now he has to leave the town as soon as possible. Don’t call him. He is driving a car.
16) This van is going too fast. Its driver is overtaking lots of vehicles. It’s very dangerous. Police must stop him.
17) Now she’s turning left. You may go to the same direction and come on the motorway.
18) He can’t go further. His car is stopping. It has no more petrol.
19) Be careful. You shouldn’t come so close to the next car. Look! The driver is opening the door and he’s getting out.
Grammar Exercise
Exercise 1. Translate the sentences with the different modal verbs.
12) Ann can speak English well.
13) We can take books from the library.
14) You can find all necessary information here.
15) Can your brother help me with mathematics?
16) My friend cannot come in time.
17) I cannot enter the room. The door is locked (закрыт).
18) We couldn’t translate this article without a dictionary.
19) Will you be able to come to the lecture?
20) I ain't able to write my lecture notes. (ain't = am not)
21) We must study hard.
22) You must learn the words.
23) You must not talk at the lessons.
24) Must she write a report?
25) They must not be late for the lecture.
|
|
|
26) You mustn’t use your lecture notes during the exam.
27) - Must we retell the text? - No, you needn’t. You can read it.
28) We will have to learn programming this term.
29) I have to finish the work today, but I don't have enough time.
30) He must be in time. Not to be late, he has to take a taxi.
31) Hope, the weather will be good, otherwise we will have to come back from the hiking (поход).
Exercise 2. Образуйте сначала форму будущего времени каждого модального глагола, затем прошедшего. Помните, что некоторые глаголы не имеют формы в будущем и /или прошедшем времени и необходимо использовать эквиваленты.
· I can attend different sport sections at our University.
· He is able to come and see us every Sunday.
· We can stay at the laboratory after classes.
· Can you write your course paper in time?
· I cannot come to the lecture. I am ill.
· We must pass our exams during the session.
· Every young man must serve in the army.
· You mustn’t park your car here.
· Must they read or retell their report?
· Must we get ready for the seminar?
· Sometimes I have to go to the library to look for information for writing my course paper.
· Do I have to print this information?
Exercise 3. Put the sentences into negative (-) and interrogative (?) form.
· Students must know how to use this program.
· I can work with a computer.
· You must learn the rule.
· He will be able to attend the conference on programming.
· They could find the correct answer.
· She had to attend lectures on higher mathematics regularly.
· We have to wait for the next lecture.
· He has to cook his breakfast himself.
Exercise 4. Read the sentences and ask for additional information with question words in brackets (с помощью вопросительных слов в скобках).
17. We must stay after classes today. (how long)
18. I can’t agree with you. (why)
19. I can’t speak German. (what language)
20. You mustn’t smoke here. (where)
21. We will have to study new subjects next term. (what subjects)
22. She had to speak at the conference. (when)
23. We could use new equipment during the experiment. (what equipment)
24. I will be able to pass my exams soon. (when)
25. We couldn’t stay at that hostel. (where)
26. He has to do this work today. (why)
Exercise 5*. Translate the sentences. All the new words write into your vocabulary.
7. You may use my computer, if you want.
8. All lawyers must pass the special exam before they can start practice.
9. In most states (USA) a person may apple for a driver's license at 16.
10. He should apply for this job.
11. A police officer cannot normally enter your home against your wishes without a search warrant.
12. The policeman will fine the driver if he exceeds the speed limit.
13. He must investigate this crime as soon as possible.
Exercise 6*. Поставьте подходящий по смыслу модальный глагол в пропуски. Переведите предложения. All the new words write into your vocabulary.
All citizens ___ observe laws.
You ____ ask your friends to help you with your English.
These young lawyers ___ speak English.
We ____ discuss this problem at the next seminar.
Judges ____ act according to the law.
He _____work as a judge: he is too young.
You ____ work hard to improve your English.
Both parents ____ support their children
You ___ take part in contract negotiations tomorrow.
____ you ___ sign any document?
Exercise 7. Translate the sentences.
6. Необходимо соблюдать правила дорожного движения.
|
|
|
7. Вам следует проконсультироваться у опытного адвоката
8. Собрание должно состояться в 10 утра.
9. Думаю, тебе придется переписывать свой доклад.
10. — Ты умеешь водить машину?
— Нет, но это, должно быть, не очень сложно. Я смогу научиться водить в ближайшее время.
| Глагол | Перевод | Эквивалент | Настоящее время | Прошедшее время | Будущее время |
| can | мочь, уметь | to be able to | Can, am able to, is able to, are able to | could, was able to, were able to | will be able to |
| may | можно, разрешается возможно | to be allowed to | may am allowed to, is allowed to, are allowed to | might, was (were) allowed to | will be allowed to |
| must | должен, должно быть | to have to | must, have to (has to) | had to | will have to |
Lesson 4.
What is Law?
People live in contact with other people; they work and cooperate with each other. This explains the need for laws. Laws protect people from “bad” actions of others. Some individuals become irritable, some angry and selfish, some aggressive and even violent. Their actions harm other people's lives and their property. Sometimes law protects us and limits our rights. Rules are the basic things of our everyday life. Some of them are obvious. We must not kill or rob. But people break the rules. For this reason there is a system of punishment. And we have police, court and prison.
Laws have several other aims. It set rules for our life. We use different rules in different spheres. The simplest example is sport. Every sport has its own set of rules. Without rules we have no football, tennis or cricket. Even the simplest sport such as running a race has rules. Otherwise anyone set off at different times and in different directions and stop at different places! If you break the rules in any sport, you will get penalty.
Or think about yourself. You form with your friends a club and at first you choose a leader and make up some rules. Perhaps you adopt something from any other society or you have your own ideas.
Finally, law establishes the system of government. The basic rule of every state is its constitution. It describes the structure of the government and lays down the rights and obligations of the citizens.
Vocabulary:
law – закон, юриспруденция
irritable – раздражительный
selfish - эгоистичный
to harm - приносить вред
property – собственность
punishment – наказание
to establish – устанавливать
to lay down – формулировать (нору закона, основы правил)
Answer the questions:
25) Are laws for ordinary people or for lawyers?
26) Do you always observe the law?
27) Do you think laws change in the course of time?
Exercises
Exercise 1. Give Russian equivalents:
32) constitutional law; administrative law; Roman law; civil law; criminal (penal) law; tax law; employment (labour) law; commercial (mercantile, business) law; banking law; financial law;
33) proceedings; civil proceedings; criminal (penal) proceedings; administrative proceedings;
|
|
|
34) legal; legacy; certified; human rules;
Exercise 2. Give English equivalents:
десятки студентов; сотни автомобилей; тридцать два судебных дела; тысячи книг; две тысячи восемьсот тридцать один доллар; тридцать шесть тысяч рублей; суд первой инстанции; тридцать вторая аудитория; страница четыреста семьдесят восьмая; в две тысячи четырнадцатом году; телефон юрисконсульта 756 43 28; миллионы телезрителей.
Exercise 3. Is it true or False? Prove your point of view.
20) The driver and passenger in a car must wear seat-belts.
21) Not all of us have certain freedoms and rights.
22) There are different types of laws.
Exercise 4. Translate.
25) District courts consider both civil and criminal cases.
26) This young lawyer speaks English very well.
27) My friend has a lot of books on civil law.
28) I translate two articles on criminal law.
29) I am going to the country tomorrow.
30) The train is starting in five minutes.
31) These students are studying law at the University.
Exercise 5. Put the proper verb form and translate. All new words with their meanings write into your vocabulary.
1. Criminals ____ (not to obey) laws.
2. The investigator _____ (to search) the crime scene according to the rules.
3. Tomorrow she _____ (to get) secret information about new technology.
4. The judge ____ (to sentence) people.
5. He often _____(to buy) the latest edition of today’s paper and reads about the most terrible crimes.
6. The investigator _____ (to analyze) footprints, fingerprints, impressions, traces and other physical evidence.
7. Next year Johnson’s legal fees ____ (to amount) to over $ 2.5 million.
Exercise 6*. Преобразуйте предложения из действительного в страдательный залог.Переведите предложения.
19) The police identifies the criminal.
20) He associates this defendant with the crime.
21) The policeman arrests the suspect.
22) Tomorrow the investigating officers will prove the guilt of the suspect.
23) The professor will examine students on Civil law next Friday.
Exercise 7. What do you think about the prohibition of smoking near the university building?
|
|
|


