 |
IV. Understanding the main points.
|
|
|
|
Answer the following questions:
1. What is the official name of your home country?
2. What part of the earth's surface does Russia occupy?
3. What countries does Russia border on?
4. What natural resources is Russia rich in?
5. What mountains divide Russia into two parts?
6. What river is the longest in Europe?
7. When was the Constitution adopted in Russia?
8. What is the Federal Assembly?
9. What can the President do under the Constitution?
10. What is the first action of the Chairman of the Government on appointment?
V. VOCABULARY FOCUS.
Find synonyms and translate into Russian:
1. the uppermost layer of something (par. 1);
2. be close to (par. 2);
3. different natural surroundings (par.3);
4. it may be (par. 6);
5. all the inhabitants (par.7);
6. supplies of smth. (par.8);
7. a group of people elected to make laws (par. 12);
8. a head of state in supreme command of a country's armed forces (par. 15)
VI. LANGUAGE DEVELOPMEWNT
A. Find Russian equivalents to the following list of English idioms:
1) throw a party, 2) hit the roof, 3) fight like cat and dog, 4) swim like a fish, 5) cut a long story short, 6) have a memory like an elephant, 7) eat like a horse, 8) take smth. into account, 9) take part in smth., 10) take place, 11) take a look at, 12) give a hand, 13) give a ring, 14) be at loss for words, 15) be in smb.'s shoes, 16) be in a good mood for smth., 17) be broke, 18) do one's best, 19) do a favour, 20) do (smth) for a living, 21) feel/be/look worn out, 22) learn by heart, 23) lose one's head, 24) lose heart, 25) lose one's temper, 26) change one's mind, 27) tell the world, 28) spend money like water, 29) fall in love, 30) get along, 31) get into a mess, 32) get on smb.'s nerves, 33) get rid of, 34) to give smb. one's word, 35) make allowance, 36) put the blame on smb., 37) put an end to, 38) put smth by for a rainy day, 39) no kidding? 40) (do smth) behind sb's back.
B. Make up a story using at least 5 Idioms above.
C. Make a similar description for an encyclopedia of any tree or animal from below. Use dictionary to help you if necessary.
Bird: beak, wings, breast, nest, eggs
Fish: tail, scales, gills
Cat: whiskers, claws, paw
Horse: hoof, mane, tail
Tree: twig, bark, branch, bough, trunk, leaf, roots
Flower: bud, pollen, thorn, stalk, petals
Specific animals: bee, shark, frog, bat, seagull, worm, parrot, dolphin, seal, snail, pigeon, peacock, hedgehog, crab, eagle
Names of trees: oak, willow, elm, fir, pine
D. Everyday expressions.Telephone talk. In a game with a ball practice asking questions (student A) and answering to them (student B). Then exchange the roles.
- Call me up at the office (at home), will you? - Hold the line, don't hang up, please. - Will you give me your phone number (address), please. - I've got a call to make. - May I use your phone? - Would you mind waiting a little? - Take the phone off the hook. - Put the phone on the hook. - Sorry, it's the wrong number. - I'd look if he were in. - Sorry he is not in. - Could you call back later? - I can't get through. - May I leave a message?
|
|
|
VII. COMMUNICATION SKILLS
A. Make up a dialog according to two situations: a) You are making an appointment by phone. b) You are phoning to a Travel Agency and asking about the trips.
B. Speak for a minute about the animals which can be pets in our country and others which can’t. Why?
C. Work in groups. One of you is a president and others are deputies. You should create a project on the improvement of our life. Think about possible suggestions and amendments to Russian Constitution about education, economy, transport, culture, services, etc.
D. Prepare the report “Famous Russian people”. Choose only one personality and prove to the other groupmates that this person is worth talking about for the next hundred years. Also you can choose the topic “My favourite city” and prepare the report talking about reasons why everyone should go there.
VIII. WRITING
Write a letter to your governmental representative, complaining about one of the sources of pollution you have noted and suggesting how it could be leaned up.
IX.WORD LIST
(do smth)behind sb’s back
are engaged in
Armed Forces.
Assembly
bark
bat
be at loss for words
be broke
be in a good mood for smth.
be in smb.'s shoes
beak
bee
borders on
bough
branch
breast
bud
Chambers
change one's mind
claws
Constitutional Court
copper
covers
crab
cut a long story short
densely
deputies
do (smth) for a living
do a favour
do one's best
dolphin
eagle
eat like a horse
eggs
elected
elm
enforced
executive
fall in love
feel/be/look worn out
fight like cat and dog
fir
Flower
flows into
frog
get along
get into a mess
get on smb.'s nerves
get rid of
gills
give a hand
give a ring
hardly
have a memory like an elephant
hedgehog
highlands
hit the roof
hoof
Horse
iron ore
is located on
judicial
leaf
learn by heart
leaves
legislative
lose heart
lose one's head
lose one's temper
make allowance
mane
mild
moderate
mountain chain
nest
no kidding?
notable
oak
occupies
on the bottom
outskirts
override
parrot
paw
peacock
Perhaps
petals
pigeon
pine
pollen
populated
possesses
put an end to
put smth by for a rainy day
put the blame on smb.
rather
roots
scales
scenery
seagull
seal
separates
shark
snail
spend money like water
stalk
such as
surface
swim like a fish
tail
tail
take a look at
take part in smth.
take place
take smth. into account
tell the world
thorn
throw a party
to give smb. one's word
total area
trunk
twig
variety
vast
vegetation
whiskers
willow
wings
worm
 UNIT 4. The United Kingdom of Great
UNIT 4. The United Kingdom of Great
Britain and Northern Ireland
I. WARM UP
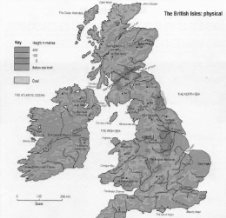
Find the colour map of The British Isles and compare Britain with your own country. Which are the most obvious geographical differences?
II. BEFORE YOU READ
A. Imagine you have to live in one of the following places: Cardiff, Edinburgh, The Lake District, Bournemouth, Birmingham, Liverpool, the Cotswolds or John o’Groats. (Find eight places on the maps).
|
|
|
a) Find as much information as you can about each place, including its weather, its distance from London, the size, and the sort of scenery you would find nearby.
b) Decide which place you would prefer to live in. Make list of all reasons for living there. Discuss your choice with other students.
B. Match the following English words and phrases with their Russian equivalents:
| 1. the official name of the state | a. сырье |
| 2. to occupy most of the territory | b. быть населенным |
| 3. to be washed by | c. быть отделенным от… |
| 4. to be separated from | d. знакомиться с… |
| 5. to consists of four parts | e. омываться |
| 6. to be inhabited | f. занимать большую часть территории |
| 7. to be appointed | g. состоять из четырех частей |
| 8. raw materials | h. официальное название государства |
| 9. to get acquainted with | i. быть назначенным |
C. Practice your pronunciation:
Great Britain ['greɪt'brɪtn]
British Isles ['brɪtɪʃ'aɪlz]
England ['ɪŋglənd]
Scotland ['skɔtlənd]
Wales [weɪlz]
Northern Ireland [,nɔːðən'aɪələnd]
London ['lʌndən]
Edinburgh ['edɪnb(ə)rə]
Cardiff ['kɑːdɪf]
Belfast ['belfɑːst]
Hyde Park [ˌhaɪd'pɑːk]
the Atlantic Ocean
[ðiː ət'læntɪk'əuʃ(ə)n]
the North Sea [ðiː 'nɔːθ'siː]
the Irish Sea
[ðiː 'aɪ(ə)rɪʃ'siː]
the Gulf Stream
[ðiː 'gʌlf'striːm]
the Clyde [ðiː klaɪd]
the Thames [ðiː temz]
Australia [ɔs'treɪlɪə]
New Zealand [njuː'ziːlənd]
India ['ɪndɪə]
Shakespeare ['shākˌspi(ə)r]
Handel ['handl]
III. READING
Read the text and make sure you know the translation of the highlighted words and phrases.
GREAT BRITAIN
1. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (the UK) occupies most of the territory of die British Isles. It consists of four main parts, which are England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Their capitals are London, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast.
2. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the official name of the state, which is sometimes referred to as Great Britain or Britain (after its major isle), England (after its major historic part) or the British Isles. The country is washed by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Irish Sea, which is between Great Britain and Ireland. Great Britain is separated from the Continent by the English Channel and is connected with many countries by sea. The greater part of the surface of England and Ireland is flat. Most of the mountains are in the North, in Scotland, but they are not very high. Scotland is also famous for its beautiful lakes. The rivers in Great Britain are not long but many of them are deep. The longest rivers are the Clyde and the Thames.
3. The climate of Britain is mild and warm because of the warm Gulf Stream. The climate in Britain is usually described as cool, temperate and humid. The weather is so changeable that the English often say that they have no climate but only weather. The English say that they have three variants of weather: when it rains in the morning, when it rains in the afternoon or when it rains all day long. Sometimes it rains so heavily that they say "It's raining cats and dogs".
4. The population of the United Kingdom is over 60 million people. The distribution of the population is rather uneven. Over 46 million people live in England and about 1.5 million in Northern Ireland. The UK is inhabited by English, the Scots, the Welsh, and the Irish who constitute the British nation.
|
|
|
5. English is the official language of Great Britain. But some people speak Gaelic in western Scotland, Welsh – in parts of northern and central Wales. English is now spoken in many countries of the world: the USA, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, India and others.
6. The flag of the United Kingdom known as the Union Jack is made up of three crosses. The upright red cross is the cross of St. George, the patron saint of England. The white diagonal cross is the cross of St. Andrew, the patron saint of Scotland. The red diagonal cross is the cross of St. Patrick, the patron saint of Ireland.
7. The UK is a constitutional monarchy. The official head of the state is the King or the Queen. But the power of the monarch is limited by Parliament, which is made up of the House of Lords and the House of Commons. Members of the House of Lords are appointed, and members of the House of Commons are elected by people. Parliament makes laws. The head of the Government is the Prime Minister, who is the leader of the party in power. There are four main political parties in Great Britain: the Conservative, the Labour, the Liberal and the Social- Democratic Party.
8. The most important industrial cities are Manchester, Leeds, Bristol, Edinburgh, Birmingham and others. Cambridge and Oxford are famous university cities. The UK is a highly developed industrial country. It exports machinery, vessels, motors and other goods. One of its main industries is the textile industry and a lot of British textiles are exported. The UK buys more goods than it sells because it has to import food products and raw materials from many countries of the world.
9. London, the capital of the country, is the largest city in Britain and one of the largest in the world. London dominates the life of Britain. It is a big port and most important commercial, manufacturing and cultural centre. London is divided by the Thames into two parts: the West End and the East End. The West End is called the centre of London. There are a lot of places of interest there. The Houses of Parliament is situated in the most important part of London, in Westminster. The Houses of Parliament is a beautiful building with two towers: the Clock Tower with Big Ben and the Victoria Tower with the national flag over it. Opposite the Houses of Parliament is Westminster Abbey. Many English kings and queens were crowned and are burried there. Another interesting sight in the West End is Hyde Park. It is the largest of London's parks and it is famous for its Speaker's Corner which attracts a lot of tourists. In the centre of the City there is the Tower of London and St. Paul's Cathedral. The Tower has a very long history. It used to be a fortress, a royal residence, then a prison, and now it is a museum. The West End is associated with wealth, luxury, and goods of high quality. It is the area of the largest department store s, cinemas and hotels. The East End of London is formerly unattractive in appearance, but now changing because of the introduction of new industries and very expensive housing. London is one of the leading world centres for music, drama, opera and dance. Festivals held in towns and cities throughout the country and attract much interest. Many British playwrights (W. Shakespeare), composers (G.F. Hendel), sculptors, painters, writers, actors, singers and dancers are known all over the world.
10. In Britain children start going to school when they are five and continue studying until they are sixteen or older. Many children in Britain attend nursery school from the age of about three, but these schools are not compulsory. Compulsory education begins at the age of five when children go to primary school. Primary education lasts for six years. They attend the infant school from five to seven and then junior school until they are eleven. In infant school children don't have real classes. They get acquainted with the classroom, desks, they mostly play and learn through playing. They know some numbers and also how to add them.
|
|
|
12. When children are seven real studying begins. They have classes, sit at desks, read and write and don't play as much as they did in infant school. Then pupils go to secondary school. Children study English, mathematics, science, geography, history, art, music, a foreign language, and physical education. The first three are called "core" subjects. Pupils take examinations in the core subjects at the age of 7, 11 and 14. Most secondary schools teach French and some other schools - Spanish, German, Italian and Russian.
13. After five years of secondary education, pupils take the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) examination. Most pupils take examinations in all subjects. Ordinary levels are normally called "O"-levels. If you get good "O"-level results, you can stay at school until you are 18. Here you prepare for Advanced Level Exams ("A"-levels). Three good "A"-level exams are the entrance exams for Universities. But Oxford and Cambridge have special ones. Higher education begins at eighteen and usually lasts for three or four years. Students go to Universities, polytechnics, or colleges. There are about 80 universities in Britain now.
IV. UNDERSTANDING THE MAIN POINTS
React to the statements, correct the mistakes.
1. The UK consists of 4 main parts.
2. The country is washed by the Pacific Ocean, the Black Sea and the Irish Sea.
3. The official head of the state is the President.
5. There is the Spasskaya Tower in the centre of the City.
6. The Tower of London used to be a fortress, a royal residence, then a museum and now it is a hotel.
7. The East End of London is attractive in appearance because of expensive housing.
V. VOCABULARY FOCUS
A. Translate into English:
1. Первая ступень начального обучения - с 5 до 7 лет (младшие классы), вторая ступень — до 11 лет. Дети знакомятся с классной комнатой, партами; в основном, они играют и учатся через игру.
2. В 11 лет дети поступают в среднюю школу. В средней школе дети изучают английский язык, математику, естествознание, географию, историю, музыку, иностранный язык, занимаются физкультурой.
3. В 15-16 лет дети сдают экзамены обычного уровня, называемого «О»- уровнем. В 18-19 лет некоторые студенты (те, кто остались продолжать образование после 15) сдают экзамены продвинутого уровня - «А»-уровня.
4. Если три экзамена уровня «А» сданы хорошо, то они могут быть вступительными в университет. В вузах студенты обучаются 3- 4 года.
B. Complete the following table.
| Country | Nationality | Language(s) | Person |
| a Briton (rare) | |||
| English, Scots, Gaelic | |||
| Welsh | |||
| Ireland |
VI. LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT
| A. Using the words on the right make up sentences describing the weather in Great Britain. Make up positive as well as negative sentences. | Noun | Adjective | Noun | Adjective |
| sun | sunny | wind | windy | |
| cloud | cloudy | ice | ic(e)y | |
| fog | foggy | shower | showery | |
| heat | hot | humidity | humid |
B. There's a word missing from each of these proverbs. Choose the correct one from the three possibilities.
| 1. An Englishman's home is his _____. a) security b) castle c) palace 2. Let sleeping dogs _____. a) sleep b) dream c) lie 3. Many _____ make light work. a) servants b) hands c) cooks 4. It takes all sorts to make a _____. a) world b) war c) salad 5. Prevention is better than _____. a) cure b) punishment c) medicine | 6. _____ is thicker than water. a) coffee b) blood c) soup 7. A miss is as good as a _____. a) mister b) mile c) wife 8. Birds of a _____ flock together. a) family b) cage c) feather 9. It's no use crying over _____ milk. a) sour b) spilt c) tinned 10. _____ begins at home. a) charity b) learning c) love |
Match the Following English and Russian Proverbs:
|
|
|
| 1. A good name is better than riches. 2. He will never set the Thames on fire. 3. Make hay while the sun shines. 4. Live and learn. 5. An hour in the morning is worth two in the evening. | a) Куй железо пока горячо. b) Добрая слава лучше богатства. c) Век живи, век учись. d) Утро вечера мудренее. e) Он пороха не выдумает. |
Learn all of them by heart!
C. Which description fits which game?
| 1) Soccer 2) Lawn tennis 3) Table tennis 4) Cricket | A. The most popular English summer game, played on a green field, very slow and long by two teams of 11 players each. B. One of the most popular English games, played from late August until the beginning of May on a large field with a round leather ball, by two teams of 11 players each. C. A very popular outdoor game, played on a court with rackets in which the ball must pass back and forth over a net. D. A game played by two of teams of two players on a rectangular table using wood paddles and a small plastic ball. |
D. Everyday expressions.In a game with a ball practice asking questions (student A) and answering to them (student B). Then exchange the roles.
- She's sneezing. She's coughing. She's got a sore throat. She's blowing her nose. She's got a temperature.
- Where's the clinic? - How do I get to the hospital? - How do I call the doctor? - Please, give me the doctor's phone-number. - I'd like to make an appointment to see the doctor. - Can I make an appointment to see the doctor? - That time would be fine. - Please, call a doctor. - It's an emergency.
- I feel sick. - I have a cold. - I have a headache. - I have a backache. - My leg hurts. - It hurts here. - I feel nauseous. - My stomach is upset. - I have something in my eye. - Is it serious? - I'm taking this medicine. - I feel worse. - I feel much better.
- a splinter, pain, painkilling, sharp pain, a prescription, a chemist, a heart attack, asthma, lung cancer, a rash, allergic, a bruise, a cough, diarrhea, flu.
VII. COMMUNICATION SKILLS
A. Imagine you are abroad and suddenly you feel badly. Ask to call a doctor. Make up dialogues, using everyday expressions.
B. Here are the ten most popular sports in Great Britain. Take the sports you know something about and grade them according to how exciting or boring you think they are. Association football (or soccer) Rugby football Cricket Racing Lawn tennis Badminton Table tennis Croquet Golf Fishing
C. To know more about Britain, answer the following questions (find the information from the other sources):
1. Is the Queen of the United Kingdom also the Queen of some other countries?
2. Who are called 'frontbenchers' and 'backbenchers'?
3. Who are called 'the Tories' and who were called 'the Whigs'?
4. What are the two groups of British newspapers?
5. What do the letters BBC stand for?
6. Why is the UK also called Great Britain, England or the British Isles?
7. Which is the highest point in the British Isles?
8. Which are the best-known streets of London?
9. When does selection usually take place? What do you think about selection procedures?
10. How do public schools differ from comprehensive ones?
11. Why do people call W. Shakespeare the 'Swan of Avon'?
12. What plays written by Shakespeare do you know?
13. What prominent English actors do you know?
14. What do you know about the National Youth Theatre?
15. What does the bagpipe look like? What sound does it produce?
D. Make the presentation about one of the Holidays in Great Britain. Tell about it to your groupmates.
VIII. WRITING
Collect information on the following topics:
a) Britain’s past connections with the rest of the world.
b) Britain’s future connections with the rest of the world.
Organise your information into two paragraphs and write an account of Britain’s international relations.
IX. WORD LIST
a bruise
a capital
a chemist
a cough
a heart attack
a part
a prescription
a rash
a splinter
a vessel
all day long
allergic
appearance
association football (soccer)
asthma
badminton
bagpipe
between
Can I make an appointment to see the doctor?
changeable
climate
cloud
cloudy
colleges
compulsory education
consist of
constitutional
core subject
cricket
croquet
crowned
deep
department store
described
diarrhea
distribution
dominate the life of
expensive
famous for
fishing
flat
flu
fog
foggy
foreign language
fortress
get acquainted with
golf
goods
government
heat
heavily
hot
How do I call the doctor?
How do I get to the hospital?
humid
humidity
I feel much better.
I feel nauseous.
I feel sick.
I feel worse.
I have a backache.
I have a cold.
I have a headache.
I have something in my eye.
ic(e)y
ice
I'd like to make an appointment to see the doctor.
I'm taking this medicine.
infant school
Is it serious?
It hurts here.
It's an emergency.
lawn tennis
lung cancer
luxury
major isle
manufacturing
member
monarch
monarchy
mostly
mountain
museum
My leg hurts.
My stomach is upset.
nursery school
official
opposite
pain
painkilling
patron
physical education
places of interest
playwright
Please, call a doctor.
Please, give me the doctor's phone-number.
primary school
prison
racing
rather
raw materials
royal residence
rugby football
sculptor
secondary school
sharp pain
She's blowing her nose.
She's coughing.
She's got a sore throat.
She's got a temperature.
She's sneezing.
shower
showery
sometimes
state
sun
sunny
surface
table tennis
temperate
textile industry
That time would be fine.
the party in power
throughout
to be appointed
to be associated with
to be connected with
to be divided into
to be elected by
to be exported
to be famous for
to be inhabited
to be limited by
to be made up of
to be referred to
to be separated from
to be washed by
to burry
to occupy
to rain
uneven
used to
variant
wealth
Where's the clinic?
wind
windy
Tongue-twisters
Read the following tongue-twisters as quick as you can, translate and learn them by heart.
Through three cheese trees three free fleas flew.
While these fleas flew, freezy breeze blew.
Freezy breeze made these three trees freeze.
Freezy trees made these trees' cheese freeze.
That's what made these three free fleas sneeze.
Betty Botter bought some butter but, said she, the butter's bitter.
If I put it in my batter, it will make my batter bitter.
But a bit of better butter will make my bitter batter better.
So she bought some better butter, better than the bitter butter,
put it in her bitter batter, made her bitter batter better.
So 't was better Betty Botter bought some better butter.
How much juice does a fruit juice producer produce
when a fruit juice producer produces fruit juice?
We can deduce a fruit juice produces as much juice
as a fruit juice produce can seduce from the fruit that produces juice.
A maid named Lady Marmalade
made mainly lard and lemonade.
M'lady lamely never made
a well-named, labelled marmalade.
Whether the weather be fine
or whether the weather be not.
Whether the weather be cold
or whether the weather be hot.
We'll weather the weather
whether we like it or not.
Which Witch snitched the Snitch Witch?
Or did the Snitch Witch snitch the Witch?
If the Snitch Witch snitched the Witch
then which Witch did the Snitch Witch snitch?
Содержание:
1. Unit 1 …………………………………………………………………………3
2. Unit 2 ………………………………………………………………………..11
3. Unit 3 ………………………………………………………………………..19
4. Unit 4 ………………………………………………………………………..24
5. Tongue-twisters……………………………………………………………...33
Literature:
1. Козлова Г.А., Козлова А.М. Английский для авиационный специалистов. М.: ГОУ «Учебно-методический центр по образованию на железно дорожном транспорте», 2007. 344с.
2. Методические указания по разговорным темам (английский язык) для студентов 1 курса всех специальностей дневной и заочной форм обучения. Ч. 1. / составители: Гриднева Б.О., Заичко М.В., Колчанова Т.А. и др. / отв. редактор: Ржевская Е.Л. Тюмень: ТюмГНГУ, 2005. 31с.
3. О Британии кратко. Книга для чтения на английском языке. Сос. В.В.Ощепкова, И.И.Шустилова. М.: Иностранный язык, Оникс, 2000. -224с.
4. Chris Barker. Boost your vocabulary 3. Pearson, Longman, 2000. P. 40.
5. Harvey P., Jones R. Britain Explored. Longman. 2002, 178 p.
6. I study at Tyumen State Oil and Gas University / Н. И. Кузьмицкая: Учебное пособие. Тюмень: ТюмГНГУ, 2000. 62с.
7. McCarthy M, O’Dell F. English Vocabulary in Use. Cambridge University Press. 2000. 298p.
Учебное издание
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК
Методические указания по разговорным темам (английский язык)
для студентов I курса всех направлений подготовки
дневной и заочной форм обучения
Составители:
ГРИДНЕВА Белла Олеговна
ЗАИЧКО Маргарита Васильевна
КОЛЧАНОВА Татьяна Андреевна
МЕЛИХОВА Анастасия Андреевна
РОДИНА Ольга Николаевна
ТЕРЛЕЦКАЯ Татьяна Николаевна
ХМЕЛЕВА Маргарита Константиновна
Редактор В.К. Бородина
Компьютерная верстка Т.И. Рощин
Подписано в печать Формат 60х90 1/16. Усл. печ. л. 2,25.
Тираж 30 экз. Заказ №
Библиотечно-издательский комплекс
федерального государственного бюджетного образовательного
учреждения высшего профессионального образования
«Тюменский государственный нефтегазовый университет».
625000, Тюмень, ул. Володарского, 38.
Типография библиотечно-издательского комплекса.
625039, Тюмень, ул. Киевская, 52.
KEYS
Unit 1.
Language study.
A. 1-b, 2-d, 3- f, 4-c, 5-g, 6-e, 7-a, 8-i, 9-h.
B. 1. medicine, 2. architecture, 3. agriculture, 4. psychology, 5. business studies, 6. history of art, 7. politics, 8. law.
Communication skills.
A. 1. How are you? 2. So am I. 3. a first-year student, 5. I am sorry. 6. a hostel, 7. I take part in, 8. do my best.
Unit 2.
Discussion.
B. Abba - I Am the City 1) street; 2) language; 3) city; 4) city; 5) hotels; 6) people; 7) parks; 8) air; 9) city; 10) be.
Language study
B. 1-h, 2-i, 3-k, 4-d, 5-c, 6-j, 7-p, 8-o, 9-e, 10-n, 11-f, 12-l, 13-a, 14-m, 15-g, 16-b
Unit 3
Language study
A. 1-q, 2-e, 3-s, 4-y, 5-d, 6-z, 7-ll, 8-kk, 9-p, 10-jj, 11-r, 12-o, 13-ii, 15-l, 16-hh, 17-gg, 18-c, 19-n, 20-m, 21-ff, 22-a, 23-t, 24-ee, 25-j, 26-k, 27-u, 28-dd, 29-f, 30-cc, 31-w, 32-v, 33-z, 34-b, 35-w, 36-h, 37-bb, 38-aa, 39-x, 40-g.
Translate the following Russian expressions into English using the Idioms above:
a. учить наизусть, b. дать слово, c. сделать все от себя зависящее, d. рассказать что-либо кратко, e. поднимать шум, f. влюбляться, g. делать за спиной что-либо (тайно), h. возлагать вину, обвинять, винить, i. не находить слов, j. злиться, выходить из себя, k. передумать, изменить решение, l. быть в таком же положении, как и кто-либо, m. зарабатывать на жизнь, n. сделать одолжение, оказать любезность, услугу, p. участвовать в чем-либо, q. устроить вечеринку, r. посмотреть на; ознакомиться, o. оказать помощь, s. сильно ругаться, t. потерять спокойствие, выйти из себя, u. рассказать всем, v. действовать кому-либо на нервы, w. делать поправку; учитывать, w. попасть в беду, x. это не шутка? y. плавать очень хорошо, z. иметь хорошую память, z. освободиться, aa. отложить на черный день, bb. положить конец чему-либо, ничтожить что-либо, cc. уживаться, ладить, dd. тратить деньги, ee. падать духом; впадать в уныние; отчаиваться, ff. чувствовать/быть/выглядеть уставшим, измученным, gg. обанкротиться, разориться, hh. быть в хорошем расположении духа/ расположенным к чему-либо, ii. позвонить по телефону, jj. случаться, kk. принимать во внимание, в расчет, ll. много есть.
|
|
|


