 |
Appendix1. Teacher observation checklist. Student's name ________________________________________. Positive Aspects. Negative Aspects
|
|
|
|
Appendix1
Teacher observation checklist
Student's name ________________________________________
Positive Aspects
ü Completed the individual role-card.
ü Used extracts from the text to support his/her ideas.
ü Asked open-ended questions.
ü Listened while others talked.
ü Encouraged peers to share their ideas.
ü Added his/her own comments and ideas to other student's comments and ideas.
Negative Aspects
ü Didn't complete the individual role-card.
ü Didn't appear to be listening or interrupted when others were speaking.
ü Did not use text to support his/her opinions.
Comments ___________________________________________________
Conditional sentences
Exercise 1. Zero Conditional
Write about George’s day. Make sentences in the Zero Conditional.
bed late " up late
If George goes to bed late, he gets up late.
up late " breakfast late
breakfast late " not catch bus
not catch bus " work on foot
work on foot " not in office before 11 a. m.
not in office before 11 a. m. " boss angry
boss angry " George work badly
Exercise 2. First Conditional
Jill and Sue are waiting at the bus-stop. They are on their way to the cinema. Put the verbs in brackets in the proper tense.
Oh dear, the bus is late.
If the bus (not arrive) soon, we (be) late.
If we (be) late, we (miss) the beginning of the film.
If we (miss) the beginning of the film, we (not understand) the story.
If we (not understand) the story, we (be) bored.
If we (be) bored, we (fall asleep).
If we (fall asleep), we (miss) the end of the film.
Let’s not go to the cinema.
Exercise 3. Third Conditional
Read the text in the box and make sentences.
get up early Þ catch the 8. 15 train Þ sit by a beautiful foreign woman Þ fall in love and marry her Þ go to live in her country Þ work in her father's diamond business Þ become very rich Þ go into politics
If I had got up early, I would have caught the 8. 15 train.
Conditional sentences (First or Second)
Exercise 1. Look at the two underlined parts of these sentences. One part is right and the other is wrong. Correct the wrong part.
- When you come home tonight, we go and see Fred in hospital.
- I’m going to visit the Colosseum when I’ll be in Rome.
- Do you tell me what happened when I see you later?
- It’s a pity this room is so small. If it were bigger, we can put all our furniture in it.
- If I will see Ann, I will ask her about her exam.
- Sam doesn’t get up early enough to catch the 7. 30 train. If he would get up earlier, he wouldn’t be late.
- I’m sure Bill will ring you before he will go on holiday.
- If it won’t rain soon, all the plants will die in the garden.
- I haven’t got a bike, I’m afraid. If I have one, I would lend it to you.
- Barbara is in bed with a fever. She would be here with us if she wouldn’t be ill.
|
|
|



Short term lesson plan
| Unit of a long term plan Unit 9 Science and technology Lesson plan 94 | School: | ||||||||||
| Date: | Teacher’s name: | ||||||||||
| Class: 9 | Number present: | Number absent: | |||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Phobias. Discussion about phobias. p. 108 | ||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to | 9. L1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 9. C2 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 9. S1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 9. S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics 9. R7 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a limited range of written genres 9. W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics | ||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives | All learners will be able to: · Identify the theme, plot, new words in the reading passage and use them as the basis for discussion. · Listen to the passage and mark sentences concerning phobias; · Listen to the passage and fill inmissing words; Most learners will be able to: ·Select, compile, and synthesize information from the reading passage for an oral presentation. ·Provide unprepared speech to answer a variety of questions at sentence level and in conversations with some flexibility; Some learners will be able to: · Respond to and discuss the reading using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills and make a mini – dialogue with new words. | ||||||||||
|
Value links | Cooperation, respect each other's opinion, functional literacy. | ||||||||||
|
Crosscurricular links | Social Science, Science, Psychology, Physics, Geography, Information Technology. | ||||||||||
|
Previous learning | Talking about unreal situations in the past. | ||||||||||
|
Useof ICT | Smart board for showing a presentation, getting additional information, playing the audio files. | ||||||||||
|
Intercultural awareness | Discuss people’s phobias. | ||||||||||
|
Health and Safety | Breaks and physical activities used. Everyday classroom precautions will ensure that safety measures are provided to prevent the exposure of electrical power cords. | ||||||||||
| Planned timings |
Planned activities |
Resources | |||||||||
| Beginning of the lesson 8 min. | The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Then to create a positive learning environment the teachers asks students to start the lesson giving each other compliments about appearance, job performance, talent, etc. and also practice accepting compliments. Watching the words on the board, the learners are asked to predict the topic of the lesson.
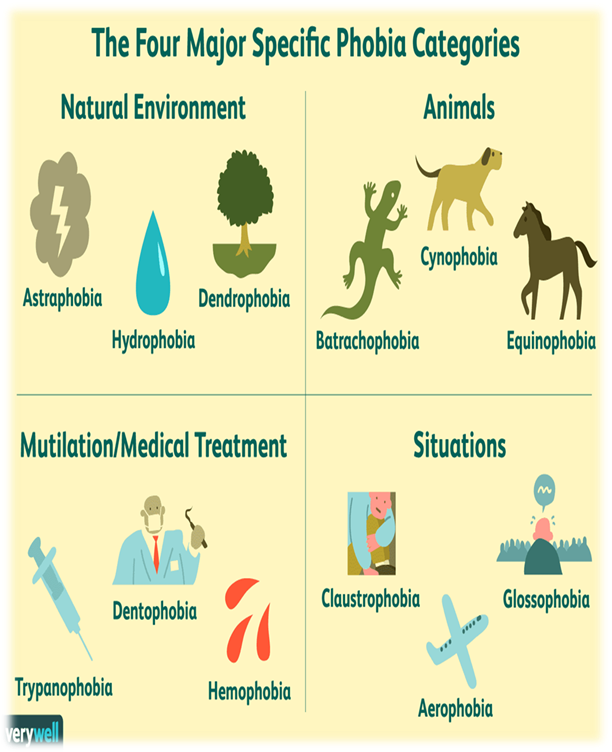
PHOBIA/ FEAR/ IRRITATION/ NERVOUS/ FRIGHT/ HORROR Warm up. Free talk about phobia. What is it? Who has got such illness in class? Phobia plural noun: phobias an extreme or irrational fear of or aversion to something. " she suffered from a phobia about birds"; Synonyms: fear, dread, horror, terror, dislike, hatred, loathing, distaste, revulsion, repulsion. When a person has a phobia, they will often shape their lives to avoid what they consider to be dangerous. The imagined threat is greater than any actual threat posed by the cause of terror. Phobias are diagnosable mental disorders. The person will experience intense distress when faced with the source of their phobia. This can prevent them from functioning normally and sometimes leads to panic attacks. In the United States, approximately 19 million people have phobias.
|
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT
Student Book p. 108 Writing Worksheet
Pictures PPT
Slide (useful phrases).
| |||||||||
| Main Activities 14 min. 12 min |
Main part Ex. 1 - 3 p. 108. Work with abbreviations to know if the students understand parts of speech. Complete the table of word – formation. Listen to the radio programme about phobias and speak about this illness. Ex. 4 - 5. What things do the speaker’s mention? Speak about them in groups of 3. Ex. 6 -7 are connected with a test: All about me. Is there something which terrifies you? Every student writes this task individually on a piece of paper. The teacher asks the students to name as many phobias as possible especially among teenagers. Optional Activity: Listening.
The students are given situations concerning phobias. Try to give some advice to avoid this fear. 1. How can you cope with fear of flying? Today, flying is both the fastest and easiest mode of transport between countries. But many of us are terrorized by the mere thought of boarding a plane. Why is that, and how do we deal with this anxiety?
2. A panic attack happens because of heightened anxiety. Anyone can have a panic attack, but it is also a hallmark symptom of panic disorder. It can lead to a rapid heartbeat, rapid breathing, sweating, shaking, and other symptoms. |
Student Book p. 108 Oxford English -English Dictionary
CD. 3. 25.
Pictures PPT
Teacher’s Book p. 130.
Writing Worksheet
| |||||||||
| Ending the lesson 6 min. |
Giving the home task. W. B. p. 74(a table) Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “ Six thinking hats ”: · Green: How can you use today's learning in different subjects? · Red: How do you feel about your work today? · White: What have you leant today? · Black: What were the weaknesses of your work? · Blue: How much progress have you made in this lesson? (Now I can, I still need to work on, I've improved in, Today I learnt... ) Yellow: What did you like about today's lesson? Slide (Homework) Slide " Six thinking hats" | ||||||||||
| Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? | Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’ learning? | Critical thinking | |||||||||
| Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners.
| Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner: · selects an appropriate answer. · completes the task. · uses appropriate subject-specific vocabulary while speaking. · discusses questions and answers the questions within the group. Observation/Feedback on the work/Peer-assessment | Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas | |||||||||
|
|
|




