 |
Ex. 22. Put general, alternative and special questions to the following sentences.
|
|
|
|
1. Such popular operating systems as MS-DOS and Windows were developed in the early 1980s and 1990s respectively.
2. The SAVE command is used to record a file on the hard disk.
3. Fast development of electronics began with the invention of transistor.
4. The car will be equipped with advanced audio signaling.
5. Communication satellites are being used now by all countries for television transmission.
6. This remote control needs four batteries to power it.
7. Universities and companies doing defense-related research were given access to the Internet in the 1970s.
8. Computers store information in the digital form.
9. The sharpness of the picture on the screen depends on the size and number of pixels.
10. I am trying to calculate how much paint we need.
11. The first electronic computer ENIAC was being developed at the Pennsylvania University from 1942 to 1946.
12. It is often stated that we use only 10 per cent of our brain.
Ex. 23. Memorize the following terms.
| 1. board– плата 2. bus – шина 3. register – регистр 4. clock – клок (генератор синхроимпульсов, тактовый генератор) 5. cycle – такт, цикл 6. adder – сумматор 7. memory – память, запоминающее устройство main memory – основная память, оперативное запоминающее устройство primary / secondary memory – первичная / вторичная память internal / external memory – внутренняя / внешняя память, внутреннее / внешнее запоминающее устройство nonvolatile / volatile memory – энергонезависимая / энергозависимая память memory location (=cell) – ячейка памяти запоминающего устройства RAM (R andom A ccess M emory) – оперативное запоминающее устройство, память с произвольным доступом ROM (R ead O nly M emory) – постоянное запоминающее устройство, память только для чтения write / read memory – память с возможностью чтения / записи 8. disk – диск CD-ROM (C ompact D isk R ead O nly M emory) – компакт-диск CD-R (C ompact D isc R ecordable) – компакт диск одноразовой записи CD-WORM (C ompact D isk W rite O nce/ R ead M any) – компакт-диск с однократной записью и многократным считыванием CD-RW (C ompact D isk R e w ritable) – [многократно] перезаписываемый компакт-диск; компакт-диск многоразовой записи с поддержкой стирания 9. light pen (stylus) – световое перо 10. hardcopy – документальная копия; бумажная копия 11. softcopy – недокументальная копия; электронная копия 12. output – выходные данные; вывод; результат вычислений 13. high definition – высокая четкость, высокое разрешение 14. voice recognition unit – устройство распознавания речи |
|
|
|
Ex. 24. Read and translate the text.
HARDWARE
What is hardware? Webster's dictionary gives us the following definition of this word: the mechanical, magnetic, electronic and electrical devices composing a computer system. A typical personal computer (See Figure 1) has components to display and print information (monitor and laser printer); to input commands and data (keyboard and mouse); to retrieve and store information (CD-ROM and disk drives); and to communicate with other computers (modem).
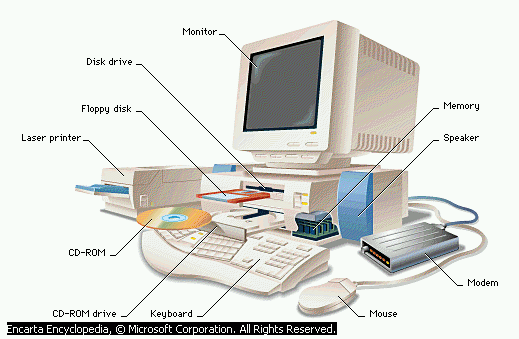
Figure 1
Personal Computer Components
Computers differ greatly in their internal organization, but every digital computer has a processor and internal/external memory. All units of the computer system are linked by a bus. (See Figure 2)The bus is a flat cable with numerous parallel wires. Each wire can move one bit, so the bus can transmit many bits along the cable at a time. For example, a 16-bit bus, with 16 parallel wires, allows the simultaneous transmission of 16 bits (2 bytes) of information from one component to another.

Figure 2
Computer System
The CPU consists of an arithmetic/logic unit, registers, control section, and internal bus. The internal bus connects the units of the CPU with each other and with external components of the system. For most computers, the main input device is a keyboard. Storage devices include external floppy disc drives and internal memory boards. Output devices are monitors and printers.
(1) The Central Processing Unit
The CPU is a main part of any digital computer. In addition to performing arithmetic and logic operations on data, it coordinates and controls the activities of other units of the computer system. It determines which operations should be carried out and in what order.
The CPU is a single chip device containing millions of tiny, interconnected electrical components. Mainframe and supercomputer CPUs sometimes consist of several linked microchips, called microprocessors, each of which performs a specific task, but most other computers require only a single microprocessor as a CPU.
Most CPUs have two functional sections: the arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) and the control unit (CU).
• The ALU is that part of the computer in which the four basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and certain logic operations (such as the comparing of data and the selection of the required problem-solving procedure) are performed.
• The CU times and regulates the whole computer system. It obtains instructions from the program stored in main memory, interprets the instructions, and transmits signals that cause other units of the system to execute them. The CU has the following components: a counter that selects and retrieves the instructions from memory; a register that temporarily holds the instructions while they are being processed; and a decoder that takes the coded instruction and breaks it down into individual commands necessary to carry it out. A very fast clock times and regulates all the operations performed by a CPU. Every tick, or cycle, of the clock causes each part of the CPU to begin its next operation and to stay synchronized with the other parts. The faster the CPU's clock, the faster the computer can perform its tasks. The clock speed is measured in hertz (Hz). Today's desktop computers have CPUs with 1 to 4 GHz (gigahertz) clocks. The fastest desktop computers therefore have CPU clocks that tick 4 billion times per second. A CPU can perform a very simple operation, such as copying a value from one register to another, in only one or two clock cycles. The most complicated operations, such as dividing one value by another, can require dozens1 of clock cycles.
|
|
|
The basic operation of the CPU is analogous to a computation carried out by a person using an arithmetic calculator, as illustrated in Figure 3. The control unit corresponds to the human brain and the memory to a notebook that stores the program, initial data, and intermediate and final computational results.
Figure 3
(2) Storage Devices
Computer memory is a physical device that is used to store such information as data or programs on a temporary or permanent basis. Most digital computer systems have two levels of memory – the main (or internal) memory and secondary (or external) memory.
Internal Memory
The main memoryis the systems component of the computer, which holds data and instructions required for ongoing process. It receives this information from an input device or a secondary storage unit. The more memory you have in your computer, the more operations you can perform, i.e. the faster it works.
There are two types of main memory: RAM and ROM.
Read-only memory (ROM) is built into the computer and cannot be changed. It contains information and software (such as the operating system) that controls the computer's actions from start up to shut down. ROM is called nonvolatile memory because the memory chips do not lose their information when power to the computer is turned off.
Random-access memory (RAM) is used to store the information and instructions temporarily while data is being processing. RAM is also known as volatile memory because the information within the computer chips is lost when power to the computer is turned off. This kind of internal memory is also called read/write memory. Today's memory chips can each store up to 512 MB of data; a set of 16 chips on a RAM module can store up to 1 GB of data.
External Memory
Secondary storage units are used for long-term storing data and instructions. They can store considerably more information than a main memory can but operate at slower speeds.
The most common form of secondary storage is magnetic disk. Magnetic disks are flat, circular plates coated with a magnetic material that contains all the data stored on the disk. There are two types: hard disks, which are made of aluminum, glass or ceramic and are physically rigid; and floppy disks, which are made of plastic and are flexible. Hard disk is a permanent part of the computer. It can store from 20 megabytes to 2 gigabytes of information and retrieve that information very quickly. Floppy disks have a much smaller capacity of only 2 to 3 megabytes.
Another form of external memory is the optical disk, which uses optical rather than electrical means for reading and writing. The standard compact disc was introduced in 1982 for digital audio reproduction. But, because any type of information can be represented digitally, the computer industry began to use the standard CD as an inexpensive storage-and-distribution medium for large computer programs, graphics and databases.
CDs, whose data can be read but not changed, are called CD-ROMs. They are used to distribute relatively static data, for example in encyclopedias and other reference works, and their large capacity makes them ideal for combinations of text with audio and graphics or other multimedia formats. Each disc can usually hold about 700 megabytes of data; the largest ones can store 1.5 gigabytes of information, which is equal to about 700,000 pages of printed material.
|
|
|
 In 1991, the CD-R (recordable) format was introduced. This variation of CD-ROM allows a user to write information on each disk only once, with subsequent erasure impossible. Such CDs are also known as WORM discs, for “Write Once Read Many”.
In 1991, the CD-R (recordable) format was introduced. This variation of CD-ROM allows a user to write information on each disk only once, with subsequent erasure impossible. Such CDs are also known as WORM discs, for “Write Once Read Many”.
A rewritable version, CD-RW, was introduced in 1997. (See Figure 4)
Figure 4
Compact Discs
A new type of discs – digital videodisc (DVD) – was developed by Philips and Sony in 1995. It looks and works like a CD-ROM but can store more than 15 times as much information. Single-sided disc2 can store up to 4.7 gigabytes of data such as high-definition digital video files. A DVD has the same dimensions as a standard CD but cannot be read by a standard CD player, though a DVD player can read standard CDs. Beginning in the late 1990s, various writable and rewritable DVD formats were introduced.
Flash memory is another electronic storage unit. Since its invention in the late 1980s (by Intel and Toshiba), it has become standard for portable devices such as digital cameras, cellular telephones, PDAs, MP3 players, and video-game machines. In the early 21st century, flash memory devices that could fit on a key ring and had storage capacities of up to 1 GB (and later more) began to serve as portable hard drives.
(3) Input Devices
Input hardware consists of external devices – i.e. components outside of the computer's CPU – that are used to enter information and instructions into a computer for storage or processing. The purpose of an input device is to convert incoming data into binary code (i.e. combinations of 0s and 1s) understandable to a digital computer. The most common input devices are a keyboard and a mouse.
A keyboard is a device with buttons or keys that a user presses to enter text, commands, numbers, or other data into a computer. The most used English-language keyboard is called QWERTY. (It was created by an American inventor and printer Christopher Sholes in the late 1860s.) QWERTY is not a word. It is the first six letters in the top alphabet row on a keyboard. That combination of letters is often used to name the standard keyboard in contrast to other keyboards. The minimum number of keys on a board is 44 but modern keyboards may have more than 100 buttons.
A mouse is a mechanical or optical hand-held device. It has two/three buttons and a stroll wheel on the top as well as a rolling ball or an optical sensor in its base. To move the cursor on the display screen, the user moves the mouse around on a flat surface. When the cursor reaches the required location, the user presses the right or left button on the mouse once or twice. Clicking the button, the user can select operations, activate commands, create or change images on the screen.
A trackball, joystick, light pen, and laser scanner also refer to input devices.
 A trackball is an inverted mouse. (See Figure 5)The only functional difference between a mechanical mouse and a trackball is in how the ball is moved. With a mouse, the ball is rolled by moving the whole unit over a desktop or other surface. With a trackball, the user rotates the ball itself while the unit is stationary. One of the main advantages of a trackball is that it takes little desktop surface. Figure 5
A trackball is an inverted mouse. (See Figure 5)The only functional difference between a mechanical mouse and a trackball is in how the ball is moved. With a mouse, the ball is rolled by moving the whole unit over a desktop or other surface. With a trackball, the user rotates the ball itself while the unit is stationary. One of the main advantages of a trackball is that it takes little desktop surface. Figure 5
|
|
|
Trackball
A joystick is a pointing device used primarily for playing computer video games. A joystick usually has a square or rectangular plastic base to which is attached a vertical lever. Control buttons are located on the base and sometimes on top of the lever. The lever can be moved in multiple directions to control the movement of a cursor or other graphical object on the screen.
A light pen (or stylus) is a device like an ordinary pen that can be used to write text or draw an image directly on a special screen or to select information on the screen by pressing the light pen against the surface of the screen. Light pens are often used in computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacture (CAD and CAM) technology.
An optical scanner is used to enter graphics as well as typeset characters.This device reads images such as a picture or text on a printed page and translates them into binary numbers that the CPU can use. For example, a photograph can be scanned into a computer and then included in a text document created on that computer.
A microphone and a voice recognition unit can be also used to feed data into the computer. A microphone is a device converting sound into signals that can then be stored, manipulated, and reproduced by the computer. A voice recognition module is a device that converts spoken words into information that the computer can recognize and process.
(4) Output Devices
External devices that enable the user to see or hear the results of the computer's data processing are known as output devices. The results are output in either hardcopy or softcopy form. Hardcopy output can be held in your hand, such as paper with text (word or numbers) or graphics printed on it. Softcopy output is displayed on a monitor.
Monitor is a component with a video display or screen for viewing computer data, television programs, etc. Displays usually take one of two forms: a video screen with a cathode ray tube (CRT) or a video screen with a liquid crystal display (LCD).A CRT-based screen, or monitor, is similar to a television set.An LCD-based screen displays visual information on a flatter and smaller screen than a CRT-based video monitor. LCDs are often used in laptop computers.
Printers produce hard copy – a printed version of information stored in one of the computer's memory systems. Color ink-jet and black-and-white laser printers are the most common, though the decreasing cost of color laser printers has increased their use outside of the publishing industry3.
Most PCs also have audio speakers. These allow the user to hear sounds, such as music or spoken words that the computer generates.
A modem is an I/O device that connects a computer to a telephone line or cable television network and allows information to be transmitted to or received from another computer.
The digital signal sent from one computer is converted by the modem into an analog signal, which is then transmitted by telephone lines or television cables to the receiving modem, which converts the signal back into a digital signal that the receiving computer can understand.
Notes: 1dozens – множество;
2single-sided disk – односторонний диск (с записью на одной стороне);
3publishing industry – издательское дело;
EXERCISES
Ex. 25. Search the text for the equivalents of the following phrases:
1. 16-разрядная шина;
2. одновременная передача 16 битов информации;
3. устройство, выполненное в виде одной микросхемы;
4. каждый выполняет определённую задачу;
5. промежуточные результаты вычислений;
6. четыре основные арифметические действия;
7. определённые логические операции;
8. выбор процедуры, необходимой для решения задачи;
9. синхронизировать все операции ЦПУ;
10. четыре миллиарда раз в секунду;
11. копирование значения из одного регистра в другой;
12. хранить данные временно или постоянно;
13. данные, необходимые для процесса, происходящего в настоящий момент;
14. информация не сохраняется, когда прекращается подача электроэнергии;
|
|
|
15. временно хранить информацию, пока идёт процесс обработки данных;
16. плоская круглая пластина, покрытая магнитным материалом;
17. оптические средства для считывания и записи;
18. воспроизведение цифровой звукозаписи;
19. любая информация может быть представлена в цифровой форме;
20. недорогой носитель для распространения и хранения информации;
21. справочник;
22. цифровое видеоизображение высокой четкости;
23. самое распространённое устройство ввода;
24. шесть букв в верхнем ряду клавиатуры;
25. светочувствительный датчик;
26. устройство, похожее на обычную ручку;
27. сигналы, которые компьютер может сохранять, обрабатывать и воспроизводить;
28. преобразовывать произнесённые слова в информацию, которую компьютер может распознать.
Ex. 26. Answer the questions:
1. What is the Webster's dictionary definition of the hardware?
2. What groups of hardware could be defined?
3. What is the main part of any computer?
4. How many microprocessors does a PC have? What about mainframes and supercomputers?
5. What two sections do most CPUs have? What are their functions?
6. There are two types of storage devices used in a PC, aren't there? What are they?
7. What can you say about the main memory?
8. What secondary storage devices do you know? Say a few words about each of them.
9. Can a user record his or her data on a CD-R?
10. What kind of storage hardware can contain more information: CD-ROM, RAM or ROM?
11. What is input hardware?
12. What are the examples of input hardware?
13. What is a mouse designed for?
14. What is a light pen?
15. What output devices do you know? What are they used for?
16. What is a modem used for?
17. Can a PC-user communicate with other people without a modem?
|
|
|


