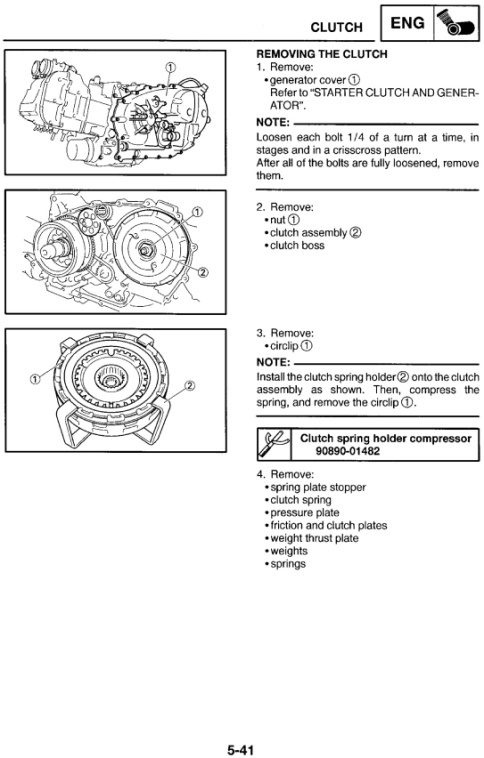
 |
Vehicle identification number
|
|
|
|
XP500
XP500A
VU5-AE1
SERVICE MANUAL
EAS00000
XP500/XP500A 2005
SERVICE MANUAL ©2004 by Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
First edition, September 2004 All rights reserved.
Any reproduction or unauthorized use without the written permission of Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
Is expressly prohibited.
EAS00002
NOTICE
This manual was produced by the Yamaha Motor Company, Ltd. primarily for use by Yamaha deal-ers and their qualified mechanics. It is not possible to include all the knowledge of a mechanic in one manual. Therefore, anyone who uses this book to perform maintenance and repairs on Yamaha vehicles should have a basic understanding of mechanics and the techniques to repair these types of vehicles. Repair and maintenance work attempted by anyone without this knowledge is likely to render the vehicle unsafe and unfit for use.
Yamaha Motor Company, Ltd. is continually striving to improve all of its models. Modifications and significant changes in specifications or procedures will be forwarded to all authorized Yamaha deal-ers and will appear in future editions of this manual where applicable.
NOTE:

Designs and specifications are subject to change without notice.

EAS00005
IMPORTANT MANUAL INFORMATION
Particularly important information is distinguished in this manual by the following.

The Safety Alert Symbol means ATTENTION! BECOME ALERT! YOUR
SAFETY IS INVOLVED!
 WARNING Failure to follow WARNING instructions could result in severe injury or death tothe scooter operator, a bystander or a person checking or repairing the scooter.
WARNING Failure to follow WARNING instructions could result in severe injury or death tothe scooter operator, a bystander or a person checking or repairing the scooter.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates special precautions that must be taken to avoid damage to the scooter.
NOTE: A NOTE provides key information to make procedures easier or clearer.
EAS00007
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended as a handy, easy-to-read reference book for the mechanic. Comprehensive explanations of all installation, removal, disassembly, assembly, repair and check procedures are laid out with the individual steps in sequential order.
1 The manual is divided into chapters. An abbreviation and symbol in the upper right corner of each page indicate the current chapter.
Refer to “SYMBOLS”.
2 Each chapter is divided into sections. The current section title is shown at the top of each page, except in Chapter 3 (“PERIODIC CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS”), where the sub-section title(s) appears.
3 Sub-section titles appear in smaller print than the section title.
4 To help identify parts and clarify procedure steps, there are exploded diagrams at the start of each removal and disassembly section.
5 Numbers are given in the order of the jobs in the exploded diagram. A circled number indicates a disassembly step.
|
|
|
6 Symbols indicate parts to be lubricated or replaced. Refer to “SYMBOLS”.
7 A job instruction chart accompanies the exploded diagram, providing the order of jobs, names of parts, notes in jobs, etc.
8 Jobs requiring more information (such as special tools and technical data) are described sequen-tially.
2 1 6

| GEN | SPEC | |||
| INFO | ||||
| CHK | CHAS | |||
| ADJ | ||||
| ENG | COOL | |||
| FI | ELEC | – | + | |
| TRBL | ||||
| SHTG | ||||
| A | B | |||
| C | D | |||
| T | ||||
| . | ||||
| R | ||||
| . | ||||
| E | F | G | ||
| H | I | J | ||
| E | G | M | ||
| K | L | M | ||
| B | LS | M | ||
| N | O | |||
| LT | New | |||
EAS00008
SYMBOLS
The following symbols are not relevant to every vehicle.
Symbols 1 to 9 indicate the subject of each chapter.
1 General information
2 Specifications
3 Periodic checks and adjustments
4 Chassis
5 Engine
6 Cooling system
7 Fuel injection system
8 Electrical system
9 Troubleshooting
Symbols 0 to G indicate the following.
0 Serviceable with engine mounted A Filling fluid
B Lubricant
C Special tool
D Tightening torque
E Wear limit, clearance
F Engine speed
G Electrical data
Symbols H to M in the exploded diagrams indicate the types of lubricants and lubrication points.
H Engine oil
I Gear oil
J Molybdenum-disulfide oil
K Wheel-bearing grease
L Lithium-soap- based grease
M Molybdenum-disulfide grease
Symbols N to O in the exploded diagrams indicate the following.
N Apply locking agent (LOCTITE®)
O Replace the part
EAS00012
TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION INFOGEN 1
SPECIFICATIONS
SPEC 2

| PERIODIC CHECKS AND | CHK ADJ 3 |
| ADJUSTMENTS |

CHASSIS
CHAS 4

ENGINE
ENG 5

COOLING SYSTEM
COOL 6
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
FI 7
– +
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
ELEC 8
TROUBLESHOOTING SHTGTRBL 9

INFOGEN 1
| GEN | ||||
| INFO | ||||
| CHAPTER 1 | ||||
| GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||
| SCOOTER IDENTIFICATION.......................................................................... | 1-1 | |||
| VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER..................................................... | 1-1 | |||
| MODEL LABEL.......................................................................................... | 1-1 | |||
| FEATURES...................................................................................................... | 1-2 | |||
| OUTLINE OF FI SYSTEM......................................................................... | 1-2 | |||
| FI SYSTEM................................................................................................ | 1-3 | |||
| OUTLINE OF ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (XP500A)........................... | 1-4 | |||
| INSTRUMENT FUNCTION..................................................................... | 1-15 | |||
| IMPORTANT INFORMATION....................................................................... | 1-19 | |||
| PREPARATION FOR REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY......................... | 1-19 | |||
| REPLACEMENT PARTS......................................................................... | 1-19 | |||
| GASKETS, OIL SEALS AND O-RINGS.................................................. | 1-19 | |||
| LOCK WASHERS/PLATES AND COTTER PINS................................... | 1-20 | |||
| BEARINGS AND OIL SEALS.................................................................. | 1-20 | |||
| CIRCLIPS................................................................................................ | 1-20 | |||
| CHECKING THE CONNECTIONS................................................................ | 1-21 | |||
| SPECIAL TOOLS.......................................................................................... | 1-22 |

|
|
|
 GEN
GEN
INFO
 GEN
GEN
SCOOTER IDENTIFICATION INFO
EAS00015
 GENERAL INFORMATION
GENERAL INFORMATION
SCOOTER IDENTIFICATION
EAS00017
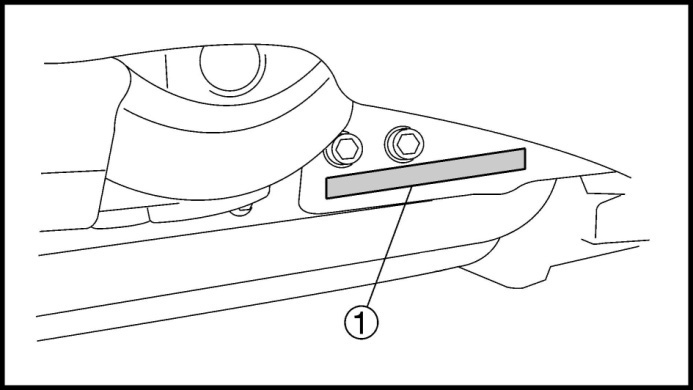
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The vehicle identification number 1 is stamped into the right side of the frame.
EAS00018
 MODEL LABEL
MODEL LABEL
The model label 2 is affixed to the storage box. This information will be needed to order spare parts.
1 - 1
FEATURES
EAS00019
FEATURES
EAS00896
OUTLINE OF FI SYSTEM
GEN

INFO
The main function of a fuel supply system is to provide fuel to the combustion chamber at the opti-mum air-fuel ratio in accordance with the engine operating conditions. In a conventional carburetor system, the air-fuel ratio of the mixture that is supplied to the combustion chamber is created by the volume of the intake air and the fuel that is metered by the jet used in the respective chamber. Despite the same volume of intake air, the fuel volume requirement varies with the engine operating conditions, such as acceleration, deceleration, or operation under a heavy load. Carburetors that meter the fuel through the use of jets have been provided with various auxiliary devices, so that an optimum air-fuel ratio can be achieved to accommodate the constant changes in the operating con-ditions of the engine.
As the requirements for engines to deliver more performance and cleaner exhaust gases increase, it becomes necessary to control the air-fuel ratio in a more precise and finely tuned manner. To accommodate this need, this model has adopted an electronically controlled fuel injection (FI) sys-tem in place of a conventional carburetor system. This system can achieve an optimum air-fuel ratio required by the engine at all times by using a microprocessor that regulates the fuel injection volume according to the engine operating conditions detected by various sensors.
|
|
|
Adoption of the FI system has resulted in a highly precise fuel supply, improved engine response, better fuel economy, and reduced exhaust emissions.

| A | B C | ||||
| D | |||||
| I | H | G | F | E |
| 1 Ignition coil | 8 Intake air pressure sensor | F O2 sensor | ||
| 2 Air filter case | 9 Throttle position sensor | G Crankshaft position sensor | ||
| 3 Intake air temperature sensor | 0 Fuel injector | H Coolant temperature sensor | ||
| 4 Fuel injection system relay | A Fuel tank | I Spark plug | ||
| 5 Lean angle cut-off switch | B Fuel delivery hose | |||
| 6 Engine trouble warning light | C Fuel pump | |||
| 7 ECU (engine) | D Battery | |||
| E Catalyst |
1 - 2
FEATURES
EAS00897
FI SYSTEM
GEN

INFO
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel injector via the fuel filter. The pressure regulator (in the fuel pump) maintains the fuel pressure that is applied to the fuel injector at 240 ~ 260 kPa (2.40 ~ 2.60 kg/cm2, 34.1 ~ 37.0 psi) higher than the intake manifold pressure. Accordingly, when the ener-gizing signal from the ECU (engine) energizes the fuel injector, the fuel passage opens, causing the fuel to be injected into the intake manifold only during the time the passage remains open. There-fore, the longer the length of time the fuel injector is energized (injection duration), the greater the volume of fuel that is supplied. Conversely, the shorter the length of time the fuel injector is ener-gized (injection duration), the lesser the volume of fuel that is supplied.
The injection duration and the injection timing are controlled by the ECU (engine). Signals that are input from the throttle position sensor, crankshaft position sensor, intake air pressure sensor, intake air temperature sensor, coolant temperature sensor, and O2 sensor enable the ECU (engine) to determine the injection duration. The injection timing is determined through the signals from the crankshaft position sensor. As a result, the volume of fuel that is required by the engine can be sup-plied at all times in accordance with the driving conditions.
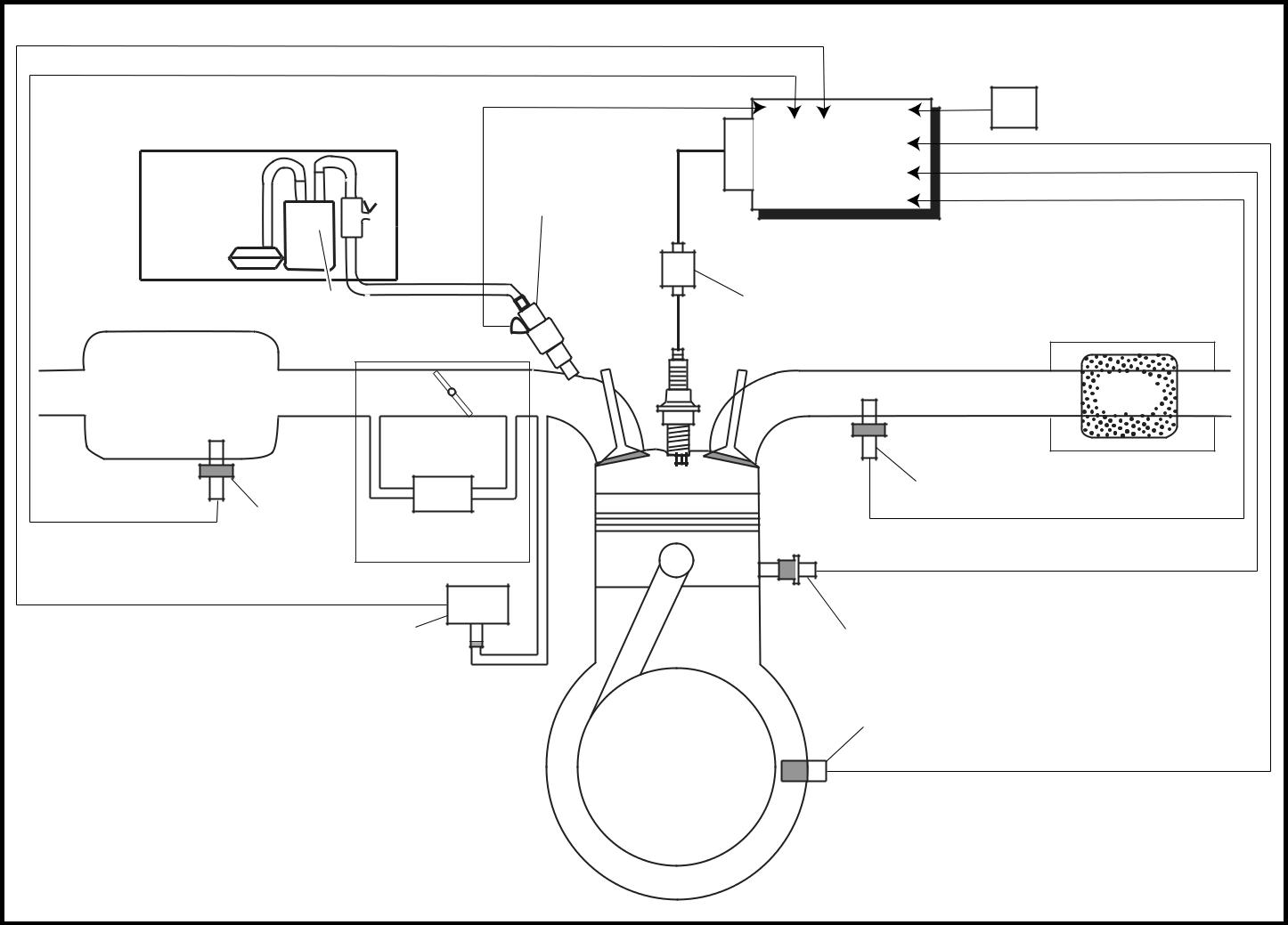
C
К
И
| B | ||
| Й | ||
| A | ||
Illustration is for reference only.
| 1 Fuel pump | 9 Intake air pressure sensor | И Fuel system |
| 2 Fuel injector | 0 Throttle body | Й Air system |
| 3 Ignition coil | A Intake air temperature sensor | К Control system |
| 4 ECU (engine) | B Air filter case | |
| 5 Catalyst | C Throttle position sensor | |
| 6 O2 sensor | ||
| 7 Coolant temperature sensor | ||
| 8 Crankshaft position sensor |
1 - 3
|
|
|
FEATURES
|
|
|


