 |
Model: a) I fully agree with the statement.
|
|
|
|
Model: a) I fully agree with the statement.
b) I am afraid, I can’t agree with it.
1. The Senate is the main legislative body of the USA.
2. The Constitution of the USA sets forth the general process for making a bill into law.
3. The first step in the legislative process is voting.
4. In the House of Representatives, debate on most bills is unlimited.
5. All bill must pass both houses of the Congress before it goes to the President.
6. When receiving a bill from the Congress, the President has to sign it.
7. The Congress has no right to override the presidential veto.
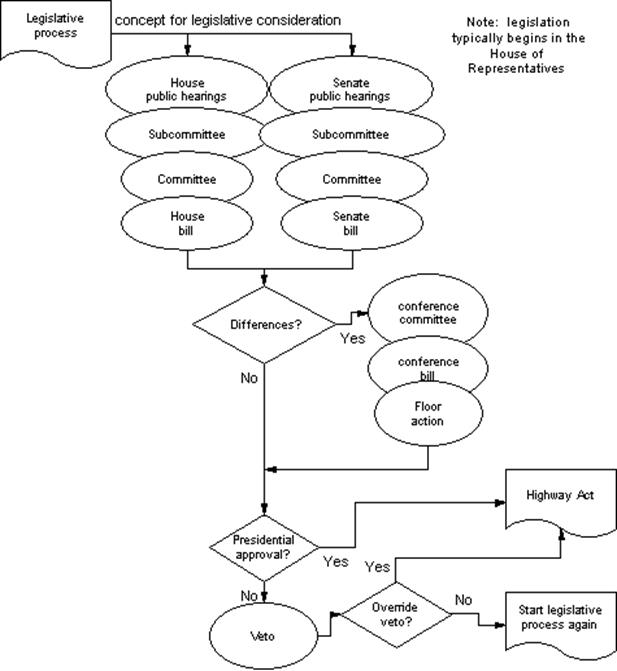
3. Изучите схему принятия закона в США. Сравните с информацией из текста 2. Найдите и опишите этапы законодательного процесса, которые не раскрыты в тексте 2.
public hearing - открытые слушания (meeting or session of a Senate, House, Joint, or Special Committee of Congress, usually open to the public, to obtain information and opinions on proposed legislation)
conference committee - комитет по согласованию расхождений, согласительный комитет
floor action - пленарная акция (once a bill reaches the floor, it can be debated and amended before coming to a vote)
highway act — основной (итоговый) проект закона
4. Посмотрите на картинки. Изучите законы, которые действуют в разных штатах США. LOONY* LAWS.



5. Ответьте на вопросы.
1. Can you figure out why each law has been passed?
2. What conditions in society might have led to its passing?
3. Are there laws today that may be considered loony in the future?
6. Напишите «безумный» закон или правило, которому необходимо следовать дома или в университете. Объясните, почему вы считаете его таковым. Спросите других студентов, что они думают о нем.
Note:
*loony: сумасшедший, безумный, бредовый
UNIT 3. The United Kingdom legislation
1. Прочитайте текст и ответьте на вопросы:
1. What is the legislative body in the UK? What does it consist of?
2. What are the steps in the legislative process?
3. What are the sources of bills? Who can introduce the legislation?
TEXT 3
The United Kingdom legislation
|
|
|
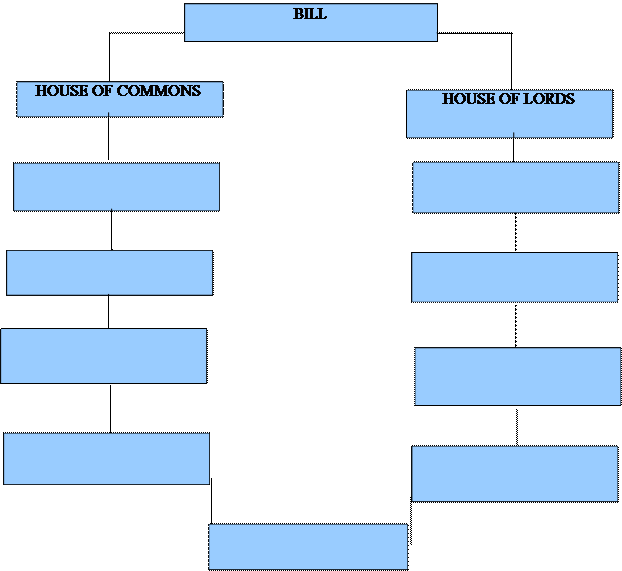
In Great Britain laws are made in Parliament at Westminster. The British Parliament consists of the monarch, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. Their work is similar: making laws (legislation), checking the work of the government (scrutiny), and debating current issues. The House of Lords is composed of life peers and hereditary peers. The House of Common is composed of Members of Parliament (Mps).
The idea for a new law can come from a variety of sources: bills may be introduced by any member of either House (a " Private Member's Bill" ), a Minister of the Crown (a " Government Bill" ), by the general public (" Public Bills" ), by an individual or small group of individuals (a " Private Bill" ).
First reading is the first stage of a Bill’s passage through the House of Commons - usually a formality, it takes place without debate. The short title of the Bill is read out and then the Bill is printed. The Bill is published as a House of Commons paper for the first time.
The next stage is second reading, the first opportunity for MPs to debate the general principles and themes of the Bill.
Once second reading is completed the Bill proceeds to committee stage. Committee stage is where detailed examination of the Bill takes placel, clause by clause, determining the intent and impact of the bill’s language. This is therefore often considered the most important step in the parliamentary process for researchers aiming to determine legislative intent. It is at this stage that amendments are made. If the Bill has been amended the Bill is reprinted before its next stage.
Once committee stage is finished, the Bill returns to the floor of the House of Commons for its report stage, where the amended Bill can be debated and further amendments proposed. All MPs can suggest amendments to the Bill or new clauses (parts) they think should be added.
Report stage is normally followed immediately by debate on the Bill's third reading. Committee stage is where detailed examination of the Bill takes place, clause by clause, determining the intent and impact of the bill’s language. Amendments (proposals for change) cannot be made to a Bill at third reading in the Commons.
The process in the House of Lords is very similar to the process in the House of Commons. The bill will have a pro forma first reading, then a second reading. After the second reading the bill will normally be referred to a Committee of the Whole House. The bill then passes through a consideration stage and a third reading. In the House of Lords amendments may be made in the Committee of the Whole House, the consideration stage, and the third reading (this is different from the House of Commons where no amendments can be made in the third reading).
If the Bill started in the Commons it goes to the House of Lords for its first reading. If the Bill started in the Lords it returns to the House of Lords for consideration of any amendments the Commons has made. Both Houses must agree on the exact wording of the Bill. A Bill may go back and forth between each House (‘Ping Pong’) until both Houses reach agreement.
When a Bill has completed all its parliamentary stages in both Houses, it must have Royal Assent before it can become an Act of Parliament (law). Royal Assent is the Monarch's agreement to make the Bill into an Act and is a formality. When Royal Assent has been given to a Bill, the announcement is usually made in both Houses by the Lord Speaker in the Lords and the Speaker in the Commons.
|
|
|
2. Закончите предложения согласно содержанию текста и переведите их на русский язык.
1. The British Parliament consists of ____________________.
2. During the first reading the short title of the Bill _____________.
- The second reading is the first opportunity __________________.
4. Committee stage is _______________________________.
5. Once committee stage is finished, the Bill returns to the floor of the House of Commons for its report stage, where __________________________.
6. Report stage is followed by ________________________.
- The process in the House of Lords is ________________.
8. Royal Assent is _________________________________.
9. When Royal Assent has been given to a Bill, __________.
3. Просмотрите текст 3 и заполните таблицу, отражающую этапы принятия закона в Великобритании.
 |
|
|
|


