 |
3. Переведите следующие слова и словосочетания из текста.
|
|
|
|
3. Переведите следующие слова и словосочетания из текста.
1. to create legislation
2. a law-making body
3. to have special powers
4. a dismissal of the Chairman
5. to bring a charge against the President
6. to adopt decrees on issues
7. to vote on draft laws
8. introduction of the law
9. approval of changes
10. to require
11. to reject a bill
12. to consider
13. to make amendments in bills
14. a chamber
15. to override the veto
16. conciliation commission
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты русским словам и словосочетаниям.
1. законодательная деятельность
2. законодательный орган
3. нижняя палата
4. верхняя палата
5. перечислять
6. постановление, указ
7. принимать закон
8. военный
9. одобрять
10. выборы
11. прийти к компромиссу
12. вето
13. назначение (на должность)
14. вносить поправки
15. разделение властей
5. Ответьте на вопросы по тексту.
- What is the main legislative body in Russia? What does it consist of?
- What powers of the State Duma are enumerated in the Constitution?
- What are the special powers of the Federal Council?
- How do the State Duma and the Federal Council meet?
- Which chamber of the Federal Assembly is more powerful? Why?
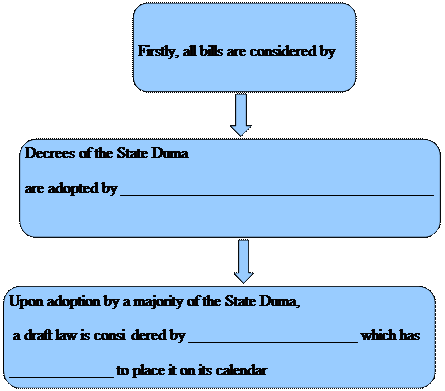
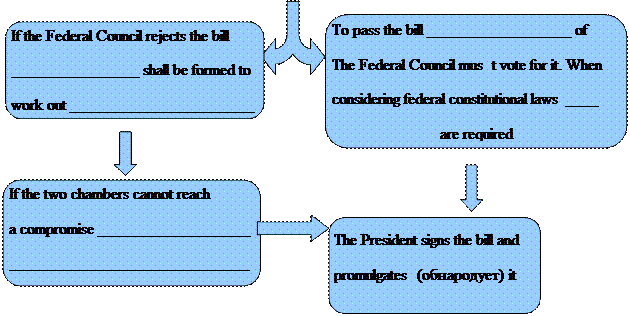
6. Используя текст, заполните схему, отражающую процесс принятия закона в России.
Draft laws may originate in either legislative chamber, or they may be introduced by the president, the Government, local legislatures and the Supreme Court, the Constitutional Court, or the Superior Court of Arbitration within their respective competences.
 | |||
 | |||
7. Используя текст 1 и схему упражнения 4, расскажите о законодательной власти в Российской Федерации.
8. Заполните пропуски словами и словосочетаниями в рамке.
| 1. bring charges against 2. elects 3. draft laws 4. the lower house 5. vetoed 6. issues 7. approve or reject 8. to override a presidential veto 9. the upper house 10. appoint or dismiss 11. appointment |
- The 628-member law-making body, termed the Federal Assembly, consists of two chambers, the 450-member State Duma (_______________) and the 178-member Federation Council (___________).
- The State Duma confirms the _______________ of the prime minister, although it does not have the power to confirm Government ministers.
- The two chambers of the legislature also have the power _________________________ of legislation.
- Upon the advice of the prime minister, the president can ___________________ Government members, including the deputy prime ministers.
- Under the 1993 constitution, if the president commits " grave crimes" or treason, the State Duma may _______________________ him with the parliament's upper house, the Federation Council.
- Several bills that the President had ____________ were taken up again by the new legislature.
- The Federation Council deals primarily with such ___________ as internal borders and decrees of the president establishing martial law or states of emergency etc.
- All _________________, even those proposed by the Federation Council, must first be considered by the State Duma.
- According to the 1993 constitution, the State Duma must decide within one week to ________________ a candidate once the president has placed that person's name in nomination.
- Each legislative chamber _____________ a chairman to control the internal procedures of the chamber.
|
|
|
9. Замените русские слова и выражения в скобках соответствующими английскими эквивалентами.
1. The State Duma (принимает постановления) on (вопросам) referred to its authority by the Constitution of the Russian Federation. Decrees of the State Duma are adopted by a majority of the total number of deputies of the State Duma, unless another procedure is envisaged by the Constitution. All (законопроекты) are first (одобряются) by the State Duma and are further debated and approved (or (отклоняются)) by the Federation Council.
2. The (Государственная Дума) in the Russian Federation is the lower house of the (Федерального Собрания) of Russia (legislature), the upper house being the (Совет Федераций) of Russia.
3. The president (назначает) the prime minister, and the Duma (голосует) whether to confirm the appointment. The president has wide legislative powers, including the (право вето) and decree. Decrees carry the force of law, but may not violate existing law. The Federal Assembly may (преодолеть президентское вето) by a two-thirds vote of each chamber.
4. (Законодательная деятельность) originates in the Duma and, if passed, is sent to the Federation Council. If the Federation Council approves the legislation or fails to examine it within fourteen days, the legislation is sent to the president to be signed.
5. When considering federal constitutional laws, three-fourths of the Council have to (проголосовать). If the Council vetoes a law passed by the State Duma, the two chambers are mandated to form a (согласительную комиссию) in order to (прийти к компромиссу) and make up a document, which would again go under vote by both houses.
6. The two houses of the Federal Assembly (заседают раздельно), with the State Duma residing in another part of Moscow. Sessions of the Federation Council are held in Moscow from January 25 to July 15 and from September 16 to December 31.
7. The State Duma has special powers enumerated by the Constitution of Russia. Among them there is the power to (выносить обвинение) against the President of the Russian Federation for his impeachment.
|
|
|
|
|
|


