 |
Biophysical profile scoring. AMNIOSCOPY
|
|
|
|
Biophysical profile scoring
| Biophysical Variable | Normal ( score = 2) | Abnormal (score = 0) |
| Amniotic fluid index | presence of pocket of fluid > 2 cm in vertical distance. | largest vertical pocket  2 cm 2 cm
|
| Fetal tone | 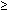 1 episode of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limb(s) or trunk (opening and closing of hand considered normal tone) 1 episode of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limb(s) or trunk (opening and closing of hand considered normal tone)
| Either slow extension with return to partial flexion or movement of limb in full extension or absent fetal movement |
| Gross body movements |  3 discrete body/limb movements in 30 min (episodes of active continuous movement considered as single movement) 3 discrete body/limb movements in 30 min (episodes of active continuous movement considered as single movement)
| 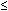 2 episodes of body/limb movements in 30 min 2 episodes of body/limb movements in 30 min
|
| Breathing movements | 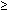 1 episode of 1 episode of 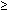 30 s in 30 min 30 s in 30 min
| Absent or no episode of 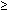 30 s in 30 min 30 s in 30 min
|
| Non-stress test. | 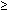 2 episodes of acceleration of 2 episodes of acceleration of  15 bpm and of 15 bpm and of  15 s associated with fetal movement in 20 min 15 s associated with fetal movement in 20 min
| < 2 episodes of acceleration of fetal heart rate or acceleration of < 15 bpm in 20 min |
A normal score is 10, or 8 in the absence of oligohydramnios. An equivocal score is 6, and abnormal scores are 0, 2, or 4. When the BPP identifies a compromised fetus, measures can be taken to intervene before progressive metabolic acidosis leads to fetal death.
AMNIOSCOPY
In 1962, E. Saling to determine the status of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth proposed method amnioscopy. The method consists in the examination of the lower pole of the ovum (fetal membranes, amniotic fluid and fetal presenting part) using a special endoscopic device (amnioscope).
Amnioscopy assesses the color and amount of amniotic fluid. Thus, the presence of meconium in fluids usually is a sign of fetal distress. As for diagnostics of the integrity of the membranes, it is easy to determine in vaginal examination, so there is no need to resort to amnioscopy. However, in order to study the nature of the membranes, this method has no equal. Amnioscopy makes it possible to diagnose the umbilical cord loops presentation and low attachment of the placenta.

Fig. 86. Amnioscope tubes
Amnioscopy (gr. Amnion — fetal membrane and scopeo — to view) – examination of the amniotic fluid in the lowest part of the amniotic sac by means of an endoscope introduced through the cervical canal (fig. 87, 88).
Amnioscopy allows to determine the violation of the fetus condition at different complications of pregnancy, to diagnose post-term pregnancy, detect abnormalities of placenta (low attachment of the placenta, placenta previa), to establish the presenting part of the fetus, to determine the integrity of the amniotic sac, to ascertain intrauterine fetal death. Using amnioscope and special scarifier you can pick up a drop of blood from predlagay part of the fetus to study its respiratory function (hypoxia diagnosis). Amnioscopy allows to take a drop of blood from the fetal presenting part with special scarifier to study its respiratory function (intrauterine fetal distress’ diagnosis).
|
|
|
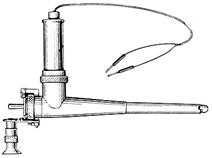
Fig. 87. Amnioscope
The indications for amnioscopy are:
1) suspected post-term pregnancy;
2) diagnostics of the fetus in pregnant women of high risk group (preeclampsia, complicated obstetric history, severe extragenital diseases, aged primiparas, violation of cardiac activity of the fetus);
3) determination of the integrity of the membranes;
4) clarifying the presenting part of the fetus;
5) diagnosis of fetal hemolytic disease (rhesus incompatibility);
6) suspected intrauterine fetal death;
7) diagnosis of the fetus condition in labor with with abnormalities of labor pains, prolonged labor (if membranes are entire);
8) identifying the cause of fetal distress in labor (presentation of umbilical cord loops);
9) Velamentous cord insertion, vasa previa.
Contraindications to amnioscopy:
1) colpitis, cervicitis, chorioamnionitis;
2) placenta previa, even if suspected.
The main condition for amnioscopy is the permeability of the cervical canal for a tube of minimal diameter. Many designs of amnioscopy are used currently. Most researchers use amnioscopy of conical shape. The nature of the light source and its location in amnioscope are of great importance. Lamp should give light without green components of the spectrum (to determine green coloured waters).
Amnioscope is a conical tube with a length of 20-25 cm, with centimetric graduations on the outer surface and obturator inside. The tube diameter is 12, 16, or 20 mm and more. Lighting device is connected to the tube (Fig 87). The forceps with a long handle are given to Amnioscope for grasping small tampons to clear a field of view from mucus, blood, etc., if necessary. The procedure of amnioscopy is simple and is as follows. Expectant mother is placed on the examination table. Firstly the treatment of external genital organs and vagina is made, then vaginal examination. Some authors recommend inspection of the cervix with specula. Dirty, greenish mucus plug of the cervical canal in most cases indicates the presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid.
The shape of the cervix, its length, position, patency of the cervical canal are evaluated in vaginal exam, which in turn allows to choose the appropriate diameter of the tip of amnioscopy and procedure of amnioscopic examination.
There are two fundamentally different ways of introducing of amnioscope into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal: under the control of specula without the grasping of the cervix with bullet forceps and under the control of the fingers, introduced into the vagina. If there is the mucous plug, it should be removed with a special tool from the field of vision, as it mimics the milky color of the amniotic fluid.
Fetal condition assessment using amnioscopy, produced at the end of pregnancy (mainly from the 36th week. ) dynamically (every two days) and in labor, while the BOW is entire.
Amniocentesis and amniotomy may be carefully (without complications) made during amnioscopy.
Amnioscopy — simple, quite effective and, when done correctly, safe manipulation (Fig. 88).
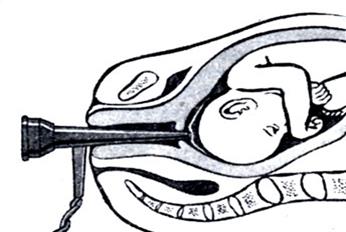
Fig. 88. Amnioscopy in pregnancy
The preparation and technique of amnioscopy.
|
|
|
With the patient in the lithotomy position and without premedication the perineum should be swabbed with antiseptic solution. Then vaginal examination performed to determine the shape of the cervix, its position and patency of the cervical canal, (dilatation by fingers may be done, if necessary).
Then amnioscope tube with obturator is introduced into the cervical canal (Fig. 89). Manipulation can be performed under the control of specula, without the grasping of the cervix with bullet forceps, or under the control of the fingers, introduced into the vagina. After passing the internal uterine os amnioscope should be pushed in the direction of the sacral hollow. Then the obturator removed, the illuminator is attached, and the tube of amnioscope installed in a horizontal position, so that the presenting part of the fetus appears in a field of view of amnioscope, and serves as a reflective surface when the amniotic fluid are investigated. If the mucous plug of the cervical canal closes the field of view, it is removed with cotton buds.
At first the condition of membranes (intact or not), the presence or absence of vascular pattern on the shells are assessed. After this, the attention is concentrated on the determination of the color of amniotic fluid (bright, opalescent, meconium containing, yellow, brown). Estimate the number of Vernix caseosa (absence of vernix, moderate amount, a lot). It is important to establish the degree of detachment of membranes of the lower pole of the amniotic sac (0-1 cm, 2-3 cm, 4 cm and more).
The presenting part of the fetus (head, buttocks) determine in amnioscopy, as well as the umbilical cord loops and small parts of the fetus (hand, legs). The greatest diagnostic value is the color of amniotic fluid. It was found that certain types of obstetric pathology has characterized by the color of the liquid (Fig. 89). So, for post-term pregnancy green color is typical, for RH-incompartibility — yellow, for intrauterine fetal death — dark brown. Expressed vascular pattern on the shells usually indicates a low location of the placenta. In cases of suspected fetal suffering in late pregnancy it is recommended to performe amnioscopy an interval of 2 days.
Green staining of amniotic fluid indicates a threatening of the fetus, but not an absolute indication for emergent surgical intervention. In such cases, the labor should be managed under monitor control. In labor, the making amnioscopy is especially important.
Amnioscopy during childbirth in women with a high risk is justified. Upon detection of meconium amniotomy and, if possible, blood sampling from presenting part of the fetus to determine acid-base status and to conduct intensive monitoring of the fetus during childbirth is required. With prolonged first stage of labor a repetitive amnioscopy indicated for women with intact bag of water. Positive result of amnioscopy contributes to the correct choice of management of the patient in labor.
Possible complications in amnioscopy are as follows: rupture of membranes, bleeding (damage to the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, separation of the placenta), infection of recently confined woman and new-born.
At low attachment of the placenta vascular pattern on the fetal membranes, membranes usually dense, with reduced transparency, reveal with the help of amnioscopy. In case of placenta previa placental tissue is visible at amnioscopy.
In the case of suspected placenta previa, amnioscopy must be made in the hospital with a prepared operating room. Amnioscope tube is introduced into the cervical canal under the control of the specula (without digital examination), the tube is driven into the internal os of the uterus after removal of the obturator, but without contact with the placental tissue.
Parameters of a good fetal condition in Amniscopy are as follows:
- the color of amniotic fluid is light, milky;
- the number of Vernix caseosa is moderate, with lively (quick) particles;
|
|
|
- rise of ability of membranes to be detached closer to the term of labor;
Parameters of unfavorable fetus’ condition in Amnioscopy are as follows:
- green color of amniotic fluid because of the presence of meconium;
- the amount of amniotic fluid is significantly less,
- the thickening of fluid ( as a result of placental insufficiency because complications of pregnancy).
Dirty amniotic fluid, looking like a “meat garbage”, slow, intensive colored particles of vernix caseosa, are ususal evidence of intrauterine fetal death.
In case of Rh-incompatibility in pregnancy, the characteristic signs in amnioscopy are: icteric color of fluid, which is the evidence of severe degree of fetal hemolytic diseases.
Amnioscopy is effective in diagnosis of post term pregnancy. It is characterized with thick,
In this case the amount of fluid is significantly less, then normal, scanty fluid of green color, lack or absence of Vernix caseosa, easy exfoliation of membranes from the uterine wall. The labor delivery should be careful.
Amnioscopic parameters, reflecting intrauterine fetal condition before labor, help to determine the most effective and appropriative management and mode of delivery.

а) Light amniotic fluid

b). Light amniotic fluid with hears on the fetal head

c) Icteric color of amniotic fluid in hemolytic disease of the fetus.
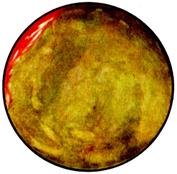
d) Green amniotic fluid in post-term pregnancy.

e) Dark-green color of amniotic fluid in post term pregnancy and severe fetal distress.

f) Placental margin in placenta previa.
Fig. 89. Amniotic fluid color
|
|
|


