 |
Indications for amniocentesis
|
|
|
|
• suspicion of chromosomal abnormalities;
• evaluation of lung maturity;
• evaluation of a degree of erithroblastosis fetalis;
• diagnosis of chorioamnionitis in labor;
• intrauterine diagnosis of chromosomal anomlies.
Amniocentesis can diagnose:
• In the 1st trimester of pregnancy - chromosomal abnormalities; up to 200 gene mutations and diseases of the fetus can be detected by amniocentesis;
• In the 2nd trimester - the severity of hemolytic disease, the degree of maturity of lung surfactants, the presence of intrauterine infections;
• Polyhydramnios (reduction of amniotic fluid is usually made with Amniocentesis);
Amniocentesis is carried out with the aim of:
• Medicinal termination of pregnancy in the 2nd trimester;
• puncture of the amniotic sac and taking of fluid to prepare the serum from embryonic tissues, at term 16 - 21 weeks, many diseases treated with the serum (so-called fetoterapiya);
• fetosurgery;
Contraindications for amniocentesis:
• in acute exacerbation of chronic diseases;
• suspected placental abruption;
• exacerbation of chronic inflammation;
• reproductive tract infections;
• uterine abnormalities and uterine pathology;
• risk of miscarriage;
• large tumors in the muscle layers of the uterus;
• problems with blood clotting;
• abnormal placental location.
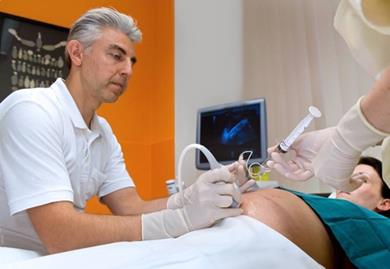
Fig. 102. The amniocentesis.
According to statistics, the reliability of the results of this study is about 99. 5% (Fig. 102). That is why it is so prized among doctors who prescribe it in the most dubious cases to avoid mistakes.
Self Test
1. Normally interspinous diameter is approximately:
A. 25-26 cm;
B. 27-28 cm;
C. 30-31 cm;
D. 19-21 cm.
2. Intertrochanteric diameter is normally:
A. 25- 26 cm;
B. 27-28 cm;
C. 30-31 cm;
D. 19-21 cm.
3. If a long axis of the fetus corresponds to the mother’s long axis, this is called
A. a longitudinal lie.
B. a transverse lie.
C. an oblique lie.
4. The maximum intensity of the F. H. S. is below the umbilicus in:
A. cephalic presentation
B. breech presentation
C. transverse lie of the fetus
5. The first grip helps to understand:
A. fetal presentation
B. fetal position
C. type of position
D. the fetal part, located in the fundus of the uterus
E. engagement of the presenting part
6. The 2nd grip can help to appreciate:
A. size of uterus
B. lie, position and type of position
C. the presenting part of the fetus.
D. ballotable head
E. engagement of the head
7. The 3rd grip is used to appreciate:
A. size of uterus,
B. position of the fetus,
C. presentation of the fetus,
D. fetal lie.
E. the fetal part, which is located in the fundus of uterus
Chapter 11. Diagnosis of pregnancy
The diagnosis of pregnancy is usually based on its anamnesis, complaints of patient, data of general and special obstetric examination, including those of additional methods of examination.
|
|
|
In the first trimester of pregnancy the diagnosis is based on complaints of pregnant and signs of pregnancy obtained on palpation, data of immunological tests, radioimmunoassay and sonography.
Commonly, all signs of pregnancy are subdivided into subjective and objective.
Subjective signs are questionable.
Objective signs of pregnancy are subdivided into probable and true (authentic).
Questionable signs of pregnancy
Questionable signs, as a rule, occur in early stages of pregnancy.
They include:
• Change of appetite, for example, dislike of fish, meat, and other foods. It is encountered in about 50% of cases, more often in the first pregnancy than in the subsequent one. It usually appears soon after the delayed menstruation and lasts beyond the 3rd month of gestation. Usually it does not affect the health state of mother.
• Changes of smell (aversion to perfume, tobacco, any other smells).
• Changes of the nervous system: quick fatigability, sleepiness, irritability, quick change of mood (instability of mood).
• Morning sickness. It is encountered in about 50% of cases. It usually appears soon after the delayed menstruation and lasts beyond the 3rd month of pregnancy. Its intensity varies from nausea on getting up in the morning to loss of appetite or even vomiting. But usually it does not affect the general state of mother.
• Pigmentation of the skin. Pigmentation over the forehead and cheeks may appear at about 24th week of pregnancy and earlier. Pigmentation of the nipple and areolae, more marked in swarthy women, usually appears between the 6-8th week of pregnancy.
• Increase of fatty tissue, enlargement of abdomen and other signs may also occur.
• Frequency of micturition. It is quite a troublesome symptom appearing during the 8-12th week of pregnancy. It is due to: 1) pressure of the bulky uterus on the fundus of the bladder because of excessive anteverted position of the uterus; 2) congestion of the bladder mucous membrane, 3) stretching of the bladder base due to backward displacement of the cervix. All these irritate the bladder in pregnancy resulting in more frequent micturition. As the uterus becomes straight after the 12th week, these symptoms disappear.
• Breast discomfort. There is a feeling of fullness and a pricking sensation, evident since 6-8th week, especially in primigravidae.
All these signs are inconsistently present in pregnants. On the other hand, they may take place in non-pregnant women, and may be due to different diseases.
Probable sings of pregnancy
Usually they are encountered in early stage of pregnancy. They include the following:
• Cessation of menses (or amenorrhea). The abrupt cessation of spontaneous, cyclic and predictable menstruation is a strongly suggestive symptom of pregnancy. But amenorrhea can occur due to many diseases: gynecological, endocrine, changes of nutrition, emotional stress, etc.
• Breast changes. The breast signs are valuable only in primigravidae. The breast changes are evident at term of 6-8 weeks. There is enlargement of breasts with vascular engorgement evidenced by the delicate veins visible under the skin. The nipple and areola become more pigmented and prominent. Thick yellowish secret (foremilk) usually appears.
|
|
|
• Discolouration of the vestibule and anterior vaginal wall, visible at about 8th week of pregnancy. The color of the vestibule and cervix of the uterus becomes cyanotic due to local vascular congestion. However, it may also be caused by pelvic tumor, such as uterine fibroid.
• Changes of size, shape and consistence of the uterus. It should be borne in mind that the enlargement of uterus may be caused not only by pregnancy but also by tumors, and other diseases of the uterus, therefore these symptoms are not true signs of pregnancy.
The uterus is enlarged to the size of hen’s egg at 6th week, size of a cricket ball — at 8th week and size of a fetal head — by 12th week of gestation. The uterus becomes acutely anterverted between 6-8th week.
There are many signs of pregnancy based on the uterine size, consistency and shape.
• Piskacek’s sign. It is an asymmetrical enlargement of the uterus due to the lateral implantation of fertilized ovum. In such cases one half of the uterus is larger than another. As pregnancy advances, symmetry is restored.
• Hegar’s sign. It is present in two-thirds of cases. It can be manifested at term of 6-10 weeks, or a little earlier in multiparae. This sign is based on the fact that: 1) the upper part of the body of the uterus is enlarged by the growing ovum; 2) the lower part of the body is empty and extremely soft, and 3) the cervix is comparatively dense. Because of variation in consistency, on bimanual examination the abdominal and vaginal fingers seem to appose below the body of the uterus.
• Snegiryov’s sign. Regular and rhythmic uterine contractions can be elicited during bimanual examination as early as 4-8 weeks.
• Henter’s sign. It can be demonstrated in early weeks of pregnancy. It stands for expressed anteflexion of uterus due to softening of isthmus, and at the same time for the crest on the anterior wall of the uterus. But the crest is present not always.
• Haus-Gubarev’s sign. In early weeks of pregnancy the cervix of the uterus becomes very mobile, due to softening of the isthmus of the uterus.
True (authentic) signs of pregnancy
Usually they appear in the late stage of pregnancy.
They are:
• Palpation of the fetal parts.
• Evidently audible fetal heart sounds.
• Active movements of the fetus felt by examiner.
• Cardiography of the fetus.
• The US examination of the fetus, which evidently shows fetal parts, or fertilized ovum in the uterus.
Immunological test of pregnancy
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) released from the syncytiotrophoblast has got antigenic properties. Its presence either in the serum or urine can be detected by means of immunological antigen — antibody reaction. The test should be performed at least 8 days or preferably 14 days following the missed period. The test is not reliable after 12 weeks of pregnancy. When the urine, containing HCG, is added to HCG antiserum, the HCG will combine with its antibody and neutralize it. If the HCG coated red cells (or latex particles) are then added, no agglutination occurs. In place of uniform precipitation one can find a ring-shaped one. This is a positive test for the presence of HCG in the urine and hence pregnancy. If the urine does not contain HCG to which HCG-antiserum is added, the antibody will remain available to agglutinate with the added HCG coated particles. Thus there will be visible agglutination (for example, uniform presipitation) and the test is negative for the diagnosis of pregnancy.
More modern and simple for application tests are used nowadays, for example BB-test. This test gives a result at a low level of HCG in urine — about 10 IU HCG/L.
Radioimmunoassay
This is a more sensitive method and can be employed to detect the presence of HCG in the serum as early as 7-10 days following fertilization.
Sonography
The characteristic small white gestational ring is evident as early as 5th week of pregnancy. It is possible to find gestational ring in term of 3 weeks of pregnancy using vaginal sonography. Real time scanner can detect the uniform cardiac motions in term of 7 weeks. Fetal movements are also detected beginning with the 12th week. Instead, employing the Doppler effect of ultrasound, one can pick up the fetal heart rate reliably by the 10th week.
|
|
|
In the first trimester of pregnancy the diagnosis is based on the questionable and probable signs of pregnancy, immunological tests of pregnancy, ultrasound examination (sonography).
In the second trimester of pregnancy (13 –28 weeks) the diagnosis is based on the subjective symptoms (nausea, vomiting, frequency of micturition, amenorrhea). It is necessary to diagnose the fact of pregnancy, its term, and complications if any, in the 2nd trimester of gestation.
The following signs usually help to diagnose pregnancy in this term.
• Quickening. It means fetal movements which can be felt by a pregnant woman first. Quickening is usually felt about the 20th week in nullipara, and about two weeks earlier in multipara. Its appearance is a useful guide to calculate the expected date of delivery. Thus, in primigravida quickening occurs by the 20th week and in multipara — by the 18th week of pregnancy.
• The progressive enlargement of uterus. At the end of the 4th obstetrical month (16 weeks) one can find the fundus of the uterus in the middle between the symphysis pubis and the umbilicus, 8 cm above the the pubis. At the end of the 5th month (20 weeks) the fundus of the uterus can be found 11-12 cm above the pubis, or 4 cm below the umbilicus. At the end of the 6th month (24 weeks) the fundus of the uterus is at the level of umbilicus, or 22-24 cm above the pubis. At the end of the 7th month (28 weeks) it is about 3-4 cm above the umbilicus.
It should be borne in mind that one obstetrical month comprises 4 weeks.
• Fetal parts and its movement, which can be found during external palpation, are true signs of pregnancy and a decisive factor in making the diagnosis.
• Auscultation of distinct fetal heart sounds may be done using obstetrical phonendoscope. Fetal heart sounds may be heard in term of 18-20 weeks of gestation, if the patient has no obesity.
• Vaginal examination helps to ascertain the enlarged uterus, softened cervix. One can find even the presenting part of the fetus, ballotable head.
• Additional methods of examination are usually used for diagnosis in this term of pregnancy.
In the third trimester of pregnancy (28-40 weeks) the diagnosis is based on the authentic signs of pregnancy.
The dates of the last period, quickening, height of the uterus are useful for determination of the term. The height of the uterus is usually measured with a tape-measure from the pubis to the fundus of the uterus. The circumference of the abdomen is also of importance. At the end of the 8th month (32 weeks) the fundus of the uterus is in the middle between the umbilicus and sternum, the umbilicus is flattened; the abdominal circumference is about 80-85 cm. At the end of the 9th month (36 weeks) the fundus of the uterus is on the line of ribs, the abdominal circumference is about 90 cm. The umbilicus is absolutely flat. At the end of the 10th month (40 weeks) the fundus of the uterus is in the middle between the umbilicus and sternum, as it was in the period of 32 weeks, the abdominal circumference — 95-100 cm. The head of the fetus is usually pressed to the pelvic brim in nulliparae, and ballotable in multiparae.
|
|
|


