|
Read the text and do the tasks below.
|
|
|
|
Reading.
Read the text and do the tasks below.
Everyone has heard of Sherlock Holmes. The author of all the Sherlock Holmes stories was Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Once Sir Arthur was in Paris. He was going from the railroad station to the hotel where he decided to spend the night. He arrived at the hotel, got out of the taxi and paid the taxi-driver.
'Thank you very much, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, ' said the taxi-driver smiling.
'Oh, do you know who I am? ' said Sir Arthur. He was very surprised.
'Well, sir, I read in the newspaper yesterday that you were coming to Paris from the south of France. The train on which you arrived came from the south of France. I also noticed that you hair was last cut by a barber in the south of France.
'Your clothes, and especially your hat, told me that you were English. I put all this together and realized at once that you were Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. '
'That is wonderful, ' said Sir Arthur. 'With so few facts you were really about to know me? '
'Of course, ' said the taxi-driver, 'your name is on both your travelling bags. That also helped'.
1. Finish the sentence. The text is about
A Sherlock Holmes in Paris.
В the famous detective Sherlock Holmes.
С the author of the Sherlock Holmes stories.
D the railroad station hotel.
2. Choose the true sentence.
A Sherlock Holmes spent the night at the hotel.
В Conan Doyle decided to spend the night in Paris.
С The taxi-driver did not recognize Conan Doyle.
D Conan Doyle came to Paris from the north of France.
3. Choose the false sentence.
A Conan Doyle was angry with the taxi-driver.
В Conan Doyle came to the hotel in a taxi.
С The taxi-driver thanked Conan Doyle smiling.
D The newspapers wrote about Conan Doyle's visit to Paris.
4. Choose the right answer: Why was Conan Doyle surprised?
A taxi-driver was rude to him.
В The taxi-driver did not like his clothes.
С The taxi-driver could not speak English.
D The taxi-driver knew his name.
5. Choose the appropriate word to complete the sentence: The taxi-driver was a ______ person.
A lazy Вquick-witted С strange D stupid
Short term lesson plan
| Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 58 | School: | |||||||||||||
| Date: | Teacher’s name: | |||||||||||||
| Class: 9 | Number present: | Number absent: | ||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Project: A poem | |||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to | 9. C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9. C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9. S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9. S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9. S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics
9. R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics | |||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives | All learners will be able to: · Identify the theme, new words and use them as the basis for discussion. · Demonstrate knowledge for rhyming patterns in poems and the ability to recite a poem. Transfer information from the given information into a graphic organizer. Most learners will be able to: · Select, compile, and synthesize information for an oral presentation · Provide a point of view in conversations and discussions; speak about poetry. Some learners will be able to: · Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills. · Compose poems in different languages. Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills. | |||||||||||||
|
Value links | Cooperation, respect each other's opinion, functional literacy. | |||||||||||||
|
Crosscurricular links | Literature, Social Science, Psychology, Information Technology, Art. | |||||||||||||
|
Previous learning | Talking about poems. | |||||||||||||
|
Useof ICT | Smart board for showing a presentation, getting additional information, playing the audio files. | |||||||||||||
|
Intercultural awareness | Students will be able to understand that people should like to read poems and try to compose their own works. | |||||||||||||
|
Health and Safety |
Breaks and physical activities used.
| |||||||||||||
|
Plan | ||||||||||||||
| Planned timings |
Planned activities |
Resources | ||||||||||||
| Beginning the lesson 6 min. | The lesson greeting.
The teacher begins the lesson with a sonnet of W. Shakespeare” Age and Youth”. The students see the portraits of well – known Kazakh, Russian, English, American and French poets. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Today we are having an unusual lesson – The lesson of Poetry. · Do you like poems? Have you ever composed poems? · About what is the sonnet? |
Slide (useful phrases)
Pictures PPT
The portraits of well – known Kazakh, Russian, English, American and French poets.
Writing Worksheet
| ||||||||||||
| Main Activities 15 min. 13 min. | In groups make a poster about the meaning of a poem by R. L. Stevenson. Follow the structure of answers. Ex. 1 – 3 p. 67. Two students will speak about the biography of R. L. Stevenson.
Find rhyming words: Speak about the patterns od rhyming words: ABAB CDCD EFEF AABBCCDD Ex. 3 – 4 p. 67 A Contest of poems devoted to love Students prepared poems in different languages with a presentation of a poet. After the reciting of a poem, they ask the group the meaning of it. | Student Book p. 67 CD2. 21
Writing Worksheet
Whiteboard
| ||||||||||||
| Ending the lesson 6 min. |
Giving the home task. W. B. p. 45 A project: a poem Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “ Six thinking hats ”: · Green: How can you use today's learning in different subjects? · Red: How do you feel about your work today? · White: What have you leant today? · Black: What were the weaknesses of your work? · Blue: How much progress have you made in this lesson? (Now I can, I still need to work on, I've improved in, Today I learnt... ) Yellow: What did you like about today's lesson? Slide (Homework) Slide " Six thinking hats" | |||||||||||||
| Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? | Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’learning? | Critical thinking | ||||||||||||
| Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. | Assessment criteria: 7. Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. 8. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. 9. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner: · selects an appropriate answer. · completes the task. · uses appropriate subject-specific vocabulary while speaking. · discusses questions and answers the questions within the group. · Observation · Feedback on the work · Peer-assessment | Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas | ||||||||||||
Age and Youth by William Shakespeare
Crabbed age and youth
Cannot live together;
Youth is full of pleasure
Age is full of care;
Youth like summer morn;
Age like winter weather;
Youth like summer brave;
Age like winter bare.
Youth is full of sport;
Age's breath is short;
Youth is hot and bold
Age is weak and cold;
Youth, I do adore thee!


Short term lesson plan
| Unit of a long term plan Unit 6 Tradition and language Lesson plan 59 | School: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date: | Teacher’s name: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: 9 | Number present: | Number absent: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Relationships. Talking about traditional stories. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to | 9. C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9. C2 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 9. C3 respect differing points of view 9. C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 9. W8 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topic 9. S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9. S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives | All learners will be able to: · Identify the theme, new words and use them as the basis for discussion. · Demonstrate knowledge for usage of the Present Perfect + for and since. Transfer information from the given information into a graphic organizer. Most learners will be able to: · Select, compile, and synthesize information for an oral presentation · Provide a point of view in conversations and discussions; speak about traditions and customs.
Some learners will be able to: · Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills. Make a presentation about traditions of Kazakhstan. Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Value links | Cooperation, respect each other's opinion, support, functional literacy. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Crosscurricular links | Culture, Art, Social Science, Psychology, Information Technology, Geography. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Previous learning | Talking about traditional stories. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Useof ICT | Smart board for showing a presentation, getting additional information, playing the audio files. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Intercultural awareness | Students will be able to understand that people should know and respect traditions and customs of their country and the country the language of which they learn. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Health and Safety | Breaks and physical activities used. Everyday classroom precautions will ensure that safety measures are provided to prevent the exposure of electrical power cords.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Planned timings |
Planned activities |
Resources | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginningof the lesson 7 min. |
The lesson greeting.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. · When you hear the words " tradition" and " customs" what associations do you have? What traditions and customs do people have? Do people try to keep traditions alive? · Look at the photo and guess the traditions:
Thanksgiving (fourth Thursday in November) Toy dastarkhan Betashar Maslenitsa
Britain is full of culture and traditions which have been around for hundreds of years. British customs and traditions are famous all over the world. When people think of Britain they often think of people drinking tea, eating fish and chips and wearing bowler hats, but there is more to Britain than just those things. Poppy Day or Remembrance Day
In groups speak about these traditions. |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT
Student Book p. 68
Writing Worksheet
Pictures PPT
Writing Worksheet
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main Activities 15 min. 12 min | READING TASK: Match the facts with people and countries. Don’t forget to underline new words and be able to say their meanings. Answer: free Ex. 1 - 2 p. 68 How do people keep the traditions alive? Do traditional stories travel from one country to another? While reading the text write down word – combinations:
Which of the traditional stories did you like best of all? Explain: “Remember the ant”.
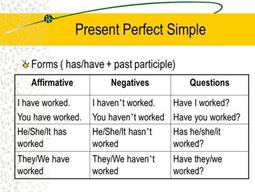
THE INTRODUCTION OF GRAMMAR. Present Perfect. Ex. 4 - 5 p. 69 Sentence completion task with adverbs:
The teacher asks Sts. to listen to the song " Brighton in the rain" and put down the verbs and underline the position of adverbs in the Present Perfect.
Brighton in the Rain Fill in the gaps and complete the song lyrics with the Present Perfect Tense of the verbs listed below. (verbs may be used more than once). Listen to the song and check your answer
I’ve never (1) _ _ _ _ to Athens and I’ve never (2) _ _ _ _ to Rome. I've only (3) _ _ _ _ the Pyramids in picture books at home. I've never (4) _ _ _ _ _ _ across the sea or (5) _ _ _ _ inside a plane. I've always (6) _ _ _ _ _ my holidays in Brighton in the rain. I've never (7) _ _ _ _ _ foreign food or (8) _ _ _ _ in a foreign bar. I've never (9) _ _ _ _ _ _ a foreign girl or (10) _ _ _ _ _ _ a foreign car. I've never (11) _ _ _ to find my way in a country I don’t know. I've always (12) _ _ _ _ _ just where I am and where I’ll never go. I've (13) _ _ _ _ travel books by writers who have (14) _ _ _ _ to Pakistan. I’ve (15) _ _ _ _ _ people telling stories of adventures in Iran. I’ve (16) _ _ _ _ _ _ _ TV documentaries about China and Brazil. But I've never (17) _ _ _ _ abroad myself. It’s making me feel ill. I've (18) _ _ _ _ _ _ _ several languages like Hindi and Malay. I've (19) _ _ _ _ _ _ lots of useful sentences I’ve never (20) _ _ _ _ able to say. The furthest place I’ve ever (21) _ _ _ _ was to the Isle of Man, and that was full of tourists from Korea and Japan. |
Student Book p. 68
Student Book p. 68
Writing Worksheet A Table
Student Book p. 68
Student Book p. 69
A Table
A song“ Brighton in the Rain”.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending the lesson 6 min. |
Homework: W. B. p. 46, Ex. 5 – 6 p. 69 St. B. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “ Six thinking hats ”: · Green: How can you use today's learning in different subjects? · Red: How do you feel about your work today? · White: What have you leant today? · Black: What were the weaknesses of your work? · Blue: How much progress have you made in this lesson? (Now I can, I still need to work on, I've improved in, Today I learnt... ) Yellow: What did you like about today's lesson? Slide (Homework) Slide " Six thinking hats" | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? | Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’learning? | Critical thinking | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. | Assessment criteria: 10. Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. 11. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. 12. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner: · selects an appropriate answer. · completes the task. · uses appropriate subject-specific vocabulary while speaking. · discusses questions and answers the questions within the group. · Observation · Feedback on the work · Peer-assessment | Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Peer-assessment.
Rubric
| Category | Excellent 4 pts | Good 3 pts | Fair 2 pts | Poor 1 pts |
| Fluency | Author demonstrates normal pace, not too fast, not to slow. | Author demonstrates adequate normal pace, not too fast, not to slow. | Author demonstrates some normal pace, not too fast, not to slow. | Author demonstrates little normal pace, not too fast, not to slow. |
| Spelling and Grammar | There are no spelling, punctuation, or grammar errors. | There are 1-2 spelling, punctuation, or grammar errors. | There are 3-4 spelling, punctuation, or grammar errors. | There are more than 4 spellings, punctuation, or grammar errors. |
| Presentation/ Memorization | Dialogue is well organized and flows like a natural conversation. | Dialogue is fairly well organized and mostly flows like a natural conversation. | Dialogue is slightly confusing and somewhat flows like a natural conversation. | Dialogue is hard to follow and doesn't flow like a natural conversation. |
| Pronunciation/ Expression | No pronunciation errors are noted. Conversation is recited with appropriate expression. | There are 1-2 errors in pronunciation. Conversation is recited with mostly appropriate expression. | There are 3-4 pronunciation errors. Conversation is recited with somewhat appropriate expression. | There are 5 or more pronunciation errors. Appropriate expression not used. |
|
|
|
|
|
|