 |
Intellectual property protection for game developers.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 1

As it was mentioned earlier, figure 1 illustrates the change in the share of innovative goods, work, and services in the total volume of goods shipped, work performed, and services delivered. The vertical axes shows the percentage share.
The second diagram reflects the level of innovation activity of organizations in percentage.
Fig. 2
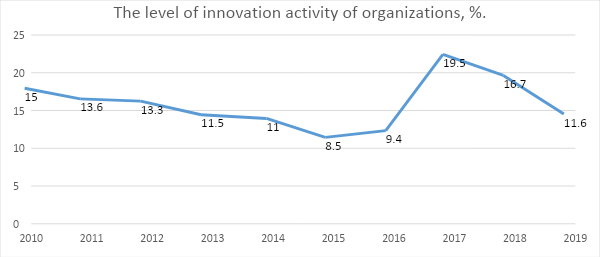
Both charts show the peak of production capacity in 2017 and the decline of innovation development over the next period. In 2018, the number of organizations followed a similar trend: there can be seen a slight drop by 11% (Fig. 2). By 2019, the dynamics increased sharply, namely, there was an increase by as much as 139%. Thus, in 2019, the number of organizations engaged in innovative activities was a high and reached the peak of 318 (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3

On the basis of the data analysis, it can be concluded that innovative development, which is measured in the specific number of innovative goods, work performed, and services delivered in Sverdlovsk region, as well as the level of innovative activity of organizations, declined. However, it should be noted that the Sverdlovsk Region also has a high development potential due to the growth in the number of organizations engaged in innovative activities, as well as due to the national programs implemented by the government in the territory of Sverdlovsk region.
List of references:
1. A. V. Babkin, M. V. Lychagin. Digitalization of economic systems: theory and practice. St. Petersburg, 2020. pp. 81-98.
2. A. V. Babkin, N. S. Alekseeva. Trends in the development of the digital economy based on the research of scientometric data // Economics and Management. 2019, No. 6 (164). pp. 16-25.
3. J. Rifkin. The Third Industrial Revolution: How Lateral Power is Transforming Energy, the Economy, and the World. 2011
4. O. V. Nikitenkova. The impact of digitalization on the world economy // World Economy, Smolensk State University (Smolensk), 2020. URL: https: //cyberleninka. ru/article/n/vliyanie-tsifrovizatsii-na-mirovuyu-ekonomiku/viewer
5. M. Mishustin. Speech at the forum " Digital Almaty: the digital future of the global economy". Almaty, 2020. URL: https: //youtu. be/iBVZFpPv8pU
6. Digital Economy – Official website of the Government of the Sverdlovsk Region URL: http: //midural. ru/community/100688/101009/
7. G. V. Dvas, Chief Scientific Secretary of the St. Petersburg Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Economics, Digitalization in the regional Economy (statistical aspects) URL: http: //www. gks. ru/publish/conf0918/dvas. pdf
8. Y. V. Gushchin, Director of the Department of Informatization and Communications of the Sverdlovsk Region. On the digital development of the economy of the Sverdlovsk region – the XIV All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference. Yekaterinburg, 2018.
URL: https: //мис. екатеринбург. рф/file/f6f49813a23a3bedc14e29942941e12a
|
|
|
УДК 347
Stolbov Egor Konstantinovich
Ural State Law University
Ekaterinburg, Russia
e-mail: eegor. freelance@gmail. com
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY PROTECTION FOR GAME DEVELOPERS.
Abstract: this article describes game developers’ legal risks related to intellectual property law. For example problems of indication of the author or rightholder, problems of legal transferring of IP rights and different kinds of treaties serving this purpose and protection of IP rights from unlawful actions.
Keywords: intellectual property, IP law, game development, exclusive rights.
Videogame industry is one of the most fast-growing industries in the world. Companies, such as Valve, EA, Blizzard earn millions of dollars from selling their games and in-app purchases. So, main assets of all videogame companies are games itself, consisting of code, graphics, music and other objects of IP(intellectual property). Moreover, these objects need legal protection and regulation to prevent their illegal use and entailing rightholder’s damages. That’s why protecting IP assets became very important.
A few words about what objects of Intellectual Property(IP) are. Objects of intellectual property are determined as products of creative work, as well as other equated to them. Rights on these objects can be personal, such as right for author’s name and being sold and exclusive rights, that can be alienated by treaty. Russian IP law also distinguishes complex IP law objects, which consist of many other objects (Gongalo, 2017: 385). For example, a video game can be considered as complex object, because it includes code, graphic objects, music, etc.
In the process of protecting copyright and exclusive rights the problem of proving the right of authorship arises: is the subject really the copyright holder or the author? One of the ways to prove copyright is to indicate the name of the author on a copy of the work before publishing. For games it’s possible to put information about designers, programmers and company in the inner description or credits. There may also be written evidence, for example, various contracts, including an author's order with an act of acceptance and transfer of the result of work, e-mails and others.
So, if videogame company is sure that counterparty is a rightholder, it’s necessary to conclude a treaty for transferring exclusive rights. Type of treaty depends on who’s the partner. If it’s individual, who doesn’t work for company or legal entity it’s possible to conclude license agreement or make an agreement on the alienation of exclusive rights. License agreement assumes that the rightholder (licensor) of an exclusive right willgive an exclusive rights to the other party (licensee) for a time and within the established limits. There are two types of license agreements: a simple (non-exclusive) license, which is characterized by the fact that the offer is intended for indefinite persons. Another type of license is an exclusive license, which implies giving the licensee the right to use the result of intellectual activity while licensor can’t share it with other individuals or legal entities. For the whole acquirement of exclusive rights on any IP object it’s possible to make an agreement on the alienation under which author or rigtholder is obliged to transfer all exclusive rights on work to acquirer of exclusive rights. The exclusive rights to intellectual property objects are transferred by one party (rightholder) to the other party (acquirer) entirely. Both treaties have mandatory conditions: agreements must be in written form, specific object of treaty must be indicated, payments procedure must be indicated in the form of fixed one-time or periodic payments, percentage deductions from income (proceeds) or in another form, If the rules for concluding an agreement are observed, the exclusive right to the result of intellectual activity is transferred from the rightholder to the acquirer or from licensor to licensee. Violation of mandatory condition leads to invalidation of treaty, that entails financial risks to game developer.
|
|
|
If there is a need to create an IP object it’s possible to make a copyright contract, which can be signed with individuals, but it cannot be signed with legal entities. Under the terms of such an agreement, one party (the author) is ought to create a work stipulated by the agreement, upon the order of the other party (the customer) (Shcherbak, 2021: 136). The specific mandatory condition is term of creation of work. If produced IP object is transferred on condition of license, rules of license agreement are applied to this treaty, same if object transferred on condition of alienation.
In case with regulation relations between company and hired workers it’s possible to use construction of service work. In order for a work to be considered official in the employment contract, the obligation to create an intellectual property must be established - the exclusive right to it by default belongs to the employer. However, it’s important to use or publish work in three years, otherwise company will lose an exclusive rights on work.
If someone violated company’s IP rights it’s possible to protect them. Out-of-court ways to protect IP for a game developer include a direct appeal to a digital platform where content that violates rights is posted (Pozdnyakova, 2021: 13). Most of the major campaigns like Steam, Google Play and App Store provide such an opportunity to file a complaint electronically to remove illegal content. If appeal has no result or there is a need to recover damages, company can use judicial protection.
Copyright infringement cases are heard by the courts of general jurisdiction in the first instance, by the courts of appeal in the second instance and by the court of intellectual property rights in the third instance (Pozdnyakо, 2021: 124). Also, such cases are within the competence of arbitration courts with the participation of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. For example “Rovio Entertainment Corporation” sued individual entrepreneur for violating their trademark by selling toys that copied Rovio’s game characters without permission[3]. So, claim was satisfied and entrepreneur paid for every fact of violation of IP rights (Tolstoy, 2009: 279). On the one hand it’s unfair to punish with so great compensations for just selling toys, looking like game characters, but on the other hand, violations of IP law like this consequent damages for the creator of characters, because usually videogame companies sell different products, designed like characters from their games, moreover companies spend a lot of resources to create a character and make it famous and remarkable.
In conclusion it’s important to mention that protection of IP rights by game companies is necessary, making correct agreements with counterparties makes business clear and helps to avoid claims. It’s also needful to watch for violations of company’s IP rights, because it may lead to serious damages.
List of references:
1. Civil law: Textbook. In 2 volumes / Ed. B. M. Gongalo. T. 1. 2 ed. revised and additional - M.: Statut, 2017: 385
2. Intellectual property law: textbook and workshop for universities / E. A. Pozdnyakova [and others]; edited by E. A. Pozdnyakova. - 3rd ed., Rev. and add. - Moscow: Yurayt Publishing House, 2021: 13
|
|
|
3. Pozdnyakova, E. A. Copyright: textbook and workshop for universities / E. A. Pozdnyakova. - 3rd ed. - Moscow: Yurayt Publishing House, 2021: 124
4. Shcherbak, N. V. Copyright: textbook and workshop for universities / N. V. Shcherbak. - Moscow: Yurayt Publishing House, 2021: 136
5. Tolstoy, Yu. K. (2009). Civil law. Textbook T. 1. 7th ed. Prospekt: 279
|
|
|


