 |
Necessity of confirmation of normal course of uterine pregnancy by ultrasound.
|
|
|
|
Necessity of confirmation of normal course of uterine pregnancy by ultrasound.
The detection of the ovum in the uterus by ultrasound is possible from 30 – 31st day, ie, 4 weeks and 3 days, after the 1st day of the last normal menstrual period in the form of a round echonegative formation 2-4 mm in size, surrounded by a hyperechoic chorion against the background of the thickened endometrium of increased echogenicity (Fig. 43).
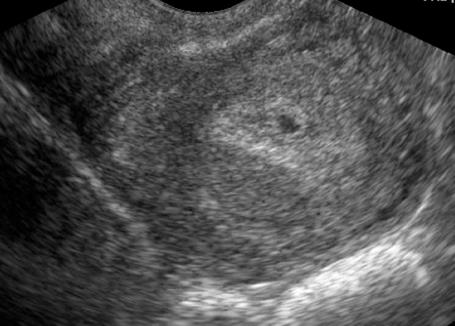

Fig. 43. The arrow points to the fertilized egg.
Yolk sac is visualized with 5. 5 weeks of pregnancy (with an average inner diameter of the gestational SAC (GS) ~ 10 mm)
• Yolk SAC diameter ≤ 6 mm (Fig. 44);
• The number of yolk bags corresponds to the number of embryos;
• Spontaneous regression of the yolk sac occurs to the 12-14 week;
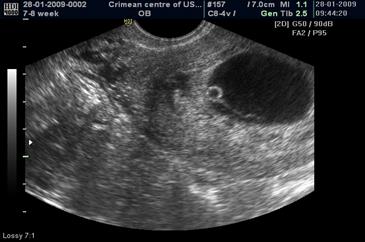
Fig. 44. Yolk sac.
The embryo is visualized when gestational SAC reaches ~ 15 mm, the stage of " diamond ring" (Fig. 45)
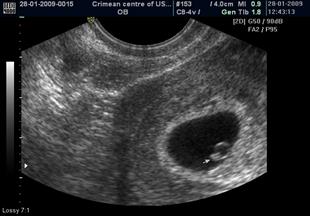
Fig. 45. The arrow points to the embryo.
The registration of cardiac activity of the embryo is possible from 4-6 mm of the Crown-rump length (CRL) (Fig. 46).
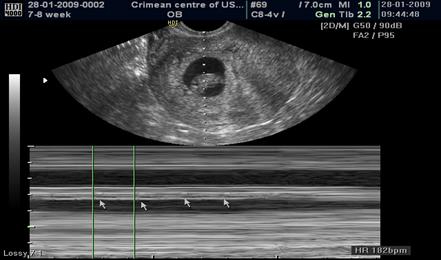
Fig. 46. The heart rate of the embryo at 7-8 weeks of pregnancy is 182 beats per minute.
The amnion visualization is worse because its covering is thinner then yolk sac.
With the further development of pregnancy and growing of the yolk sac the amniotic cavity increases in size. Full convergence of the amniotic and chorionic membranes leaves occurs in the term from 14 to 18 weeks of pregnancy. Chorion has an annular shape before 6 weeks, ultrasound examination shows a clear inner contour and 'gritty' outer, with high echogenicity. Colour flow mapping (CFM) and Power Doppler can identify single color loci – areas of established intervillous bloodstream.
Prognostic criteria for ongoing pregnancy:
• Presence of heart beats in embryo of 6 mm or more in size;
• Correspondence of the size of the embryo the size of the ovum;
• The dynamical growth of the - 0. 8-1. 0 mm per day.
Sonographic signs of Missed abortion
•at 5-6 weeks: the discrepancy between the size of the ovum and estimated term of pregnancy (according to the 1st day of LNMP), yolk sac and embryo are not visualized;
• The diagnosis of missed abortion at 5-6 weeks should be confirmed by at least two experts. If case of lack of confidence in the results of the ultrasound, it need to be repeated after 3-7 days, in parallel to measure the level of HCG;
• at 7-8 weeks: the absence of fetal heart rate, the discrepancy between the size of the ovum and estimated term of pregnancy, the embryo is visualized in the form of an undifferentiated hyperechogenic mass; ovum contours are blurred with deformation. The increase of echogenicity of the yolk sac and absence of trophoblastic blood flow in Color flow mapping (CFM) confirms missed abortion.
Sonographic signs of incomplete abortion
• Previously visualized embryo is not determined in the uterus;
|
|
|
• the uterus cavity (and cervix) expanded by more than 15 mm;
• internal contours of the uterus are blurred and uneven;
• uterine content presented as heterogeneous echo structure, in separate parts of the uterine cavity and cervical canal some vascularization is determined in Color flow mapping (CFM).
Suspected ectopic pregnancy
When the serum level of beta human chorionic gonadotropin (β -hCG) is higher than 1500 mIU/mL, the level known as the discriminatory zone, transvaginal ultrasonographic findings of an intrauterine pregnancy should be present (gestational sac visualized in the uterus). If the fertilized egg is not determined in the uterine cavity, and there is excess fluid in a Duglas pouch with a positive HCG test, it is necessary to conduct a thorough assessment of the region of the appendages, of the cervix, the interstitial zone of the myometrium of the uterus and pelvic cavity to exclude ectopic location of the ovum (Fig. 47, 48).

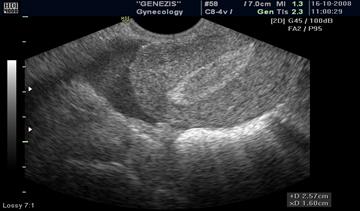
Fig. 47. An excess fluid (arrow) in a Duglas pouch in ectopic pregnancy.
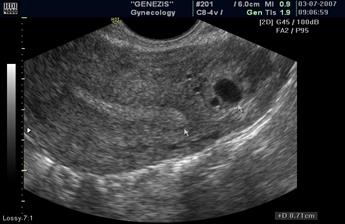
Fig. 48. The arrow indicates atypically located ovum (in the interstitial part of fallopian tube) - interstitial ectopic pregnancy
|
|
|


