 |
Radiation. Hospitals. Medicine of catastrophe. Growth and development. Examinations exercises
|
|
|
|
Radiation
51. The meaning of radioactivity, types of units for measuring.
Hospitals
70. Hygienic evaluation of hospital planing systems, and the locality in the city.
71. The hygienic needs for planing the department of internal diseases.
72. The hygienic needs for planing the department of surgical and gynaecological diseases.
73. The hygienic needs for planing the department of infectious diseases.
Medicine of catastrophe
74. Medicine of catastrophe. The main problems due to catastrophe.
75. The externals factors in relation with results of catastrophe.
76. The external factors and their influence on the result of catastrophe, on the health of population.
77. Classification of catastrophe and its main problems.
78. The catastrophe in the chemical industries. The toxic effects. of pollution on the health of populations.
79. The role of doctors in resolving the consequence of catastrophe.
80. The sanitary and hygienic measures to resolve the result of catastrophe.
81. The principles of resolving the housing problem. Purification of drinking water. Nutrition in the area of catastrophe.
82. Role of doctors in resolving the sanitary problems as a results of catastrophe.
52. The natural sources of radiation, the causes of increasing of radiation.
53. The types of radiation, physical characteristic, and measures of harmful level.
54. Closed sources ionising radiation, and protection methods.
55. Opened sources of ionising radiation, and protection methods.
56. The meaning of FDD, PD ionising radiation.
57. The methods of radioactive material dicantemenation.
Growth and development
58. The main signs of growth and development of children. The methods of assessment. Acceleration.
59. Prophylactics of the skeleton deformation of children.
60. Prophylactics respiratory diseases of children.
61. Prophylactics of cardiovascular diseases of children.
62. Prophylactics of gastrointestinal diseases of children.
63. Prophylactics of myopia of children.
64. Hygiene of school lessons.
65. Exhausting of school children, the aetiology, preventive methods of exhausting.
66. Medical supervision of the sports in the school.
67. Hygienic recommendation of kinder-garden planing.
68. Organisation of daily routine in kinder-gardens.
69. Hygienic recommendation of school planing.
EXAMINATIONS EXERCISES
1. Write your conclusion and recommendation about microclim-ate in the class. Temperature 25°c, alternative humidity 80%, the air velocity 0, 1 m/s. Solution;
a) The normal level of temperature in class is 18-20°
b) The normal level of humidity is 40-60%
c) The normal level of air velocity is 0, 2-0, 4 m/sec
That is mean, the temperature and the humidity higher than
the normal level and the air velocity is lower than normal level.
The class needs for artificial and natural ventilation, because
|
|
|
the microclimate effects the thermoregulation of the students body.
2. The light coefficient (Ic - ck) of the class on the ground flour is 1: 5, coefficient of the natural light (cnl - keo) on the last desk: 1, 1%. Your conclusion about the amount of the light in that class. Solution:
In the class the normal level of CK is 1: 4 - 1: 6. The level of KEO is not less than 1, 5%. Conclusion:
The amount of natural light in the class is normal. But the amount of the light on the last desk is lower than the normal level.
Recommendation:
We need to clean the windows and the colour of the wall must be having light colour.
3. Find out the number of lamps - EUF-15, in class which are used as prophylactic lamps for schoolchildren's. The daily dose equal 0, 5 biodose, area of the class 48m2, the exposure time 4 h. Solution: The formulas for finding the number of lamps are:
5, 4 x S x H T'
S - area of the room
( H - prophylactic dose (one biodose =5000 MER) EUFi5(Fi) - 340 MER T - exposure time in mounts
5, 4 x 48 x 2500 2698
F = -——————— = 2698wer, n = —— = 7, 8(8)/awos
240 340 v ' ^
4. The playing room in the kinder-garden, its area 50m2, the height of the ceiling is 3m, it need for air disinfection. How many bacte-riocide lamps BUF-15 you need for disinection of that room. Show the location of the lamps, and the time of disinfection, in the presence of the children. Solution:
For disinfection of one m3 of the air we need one wt. The capacity of the room is 3-50=150 m\ that means we need 150 wt, the power of one lamp BUF - 15 = 15 wt.
The number of the lamps = 150: 15 = 10 lamps. If children are present in the room we need a metallic screen on the lamp.
The location of the lamps near about the door and the windows. The time of disinfection not more than 2h, after that we must ventilate the room.
5. For prophylactic purposes for 40 healthy children, you have to use lamp PRK-7. The area of the hall = 180m2. Find out the number of children expossuring at one time, select the schedule of expossuring for 10 days. Solution:
To receive one biodose the distance from the lamp must be 3m, time of exposuring 3, 7 min (If the distance 2m the time must be 1, 6 min, if the distance 1m the time must be 0, 5 min).
To find out the number of children's exposuring at one time, use the formula 2; cR. 2-3, 14-3 = 18, 8, the distance between children's 0, 8- 1m, that mean at one time we can exposure 20 children's. The schedule for exposuring
| day | ||||||||||
| biodose | 0, 5 | 0, 5 | 1, 5 | 2, 5 | 3, 5 | 4, 5 |
6. The distance from radioactive iodine is 2m, its physical dose equal to 45 mkv/sec. Find out the physical dosage of this element if the distance 3m?
Solution:
You have to use the formula:
AT7 D - dose r - distance
|
|
|
7. After working 36 hours with radioactive element the exosuring dose of laboratory assistant is 03 roentgen. Your conclusion and recommendation about the condition on the work.
Solution:
The FDD for week (36 hours) must be 0, 1 ber
Iber =lrad =1, 14 roentgen
That mean 0, 3 roentgen 0, 342 ber.
He received 3 times more than the normal (FDD 0, 1)
Recommendation: he cannot work till 2, 5 weeks
8. Find out exposuring dose of doctor who worked with gamma iozining source, if the activity of that source is 5mg. eq. rad. He is working every day for 6h. The distance from the source is 40 cm. Solution:
To find out the dose you have to used the formula: 8, 4 x m x t
| r2 |
D =
D - dose m - activity t - time r - distance 9. Find out the distance from the radioactive source where the nurse is working for 6 h daily. The activity of the gamma source is 20 mg/equl/rad. Solution: use the formula: m xt
| r2 |
• = 120
m - activity t - time for one week r - distance
10. Find out the thickness of screen to reduce the intensity of gamma iozining for 100 times, if the thickens of lead 1, 8 cm it will be reduced 50% of the intensity. Solution.
To reduce the activity 4 times you have to use 2 layers, 8 times = 3 layers, 16 times = 4 layers, 32 times = 5 layers, 64 times = 6 layers, for 128 times = 7 layers.
That means, to reduce the activity of gamma iozinig for 100 times = 7 • 1, 8 = 12, 6 cm the screen thickness (use special table).
11. Write your conclusion about the quality of wells water, the J sample was taken in June, the soil around the well is polluted, i and the well with out roof. ^ ^^ miui U1 J1UC! 3M 1=> M t31Krf zi ibs The results of analysis ^ -.. • ri Ml • { 00V 21 ibw terfl moil test-nil, odour-nil, transparency - 25 cm, ammonia - 0, 3 mg/1, nitrate -50 mg/1, hardness - 6, 1 mg/1, iron - 0, 2 mg/1, fluoride - 0, 8 mg/1, chloride - 28, 6 mg/1, coli-titer - 0, 1 ml. . esrijofo
Conclusion . Xi, » uwiteUisrnrftcxjsi bn£ noisulonoo tuoY. £ [, yon The result of chemical and bacteriological analysis show a faecal pollution of the water. The concentrations of fluoride,. iron and
chloride are normal. •-.. ' Noido je^ni? 8{ - aisriqlug, F> gm 2£ - aJsuin
Recommendation -m
The well must be closed for repairing and to clean the area
around the well. Before consuming we have to get the analysis of the
water. 'pwo/ja alKvl& ns
12. Small village its population 258, they are using artesian water lo... well, the quantity of water equal 700 I/hour iol yThe result of analysis shows: colour - nil, odour - nil, transpar ency - more than 30 cm, hardness - 8, 8 mg/1, chloride - 135 mg/1, ammonia - 0, 1 mg/1, nitrate - 6, 2 mg/1, nitrite - 0, 001 mg/1, iron - 0, 6 mg/1, sulphate - 285 mg/1, fluoride - 0, 8 mg/1, coli-index - 4r orfT £
nGu Your conclusion and recommendation about sanitary situation of that well. ^ |Jstm IH s;? Jjjvy 1U im
Solution:
In relation to the state sanitary standards of 1996. The quantity of water per person in rural area about 50 I/day. Daily quantity of water from that well is 700 1 • 24 h = 16400 1 or 63, 5 I/person, that is means, the water enough for the village. The analysis shows high concentration of iron, that means the water cant be used for washing the clothes. 13. Your conclusion and recommendation about pipeline water.
|
|
|
The results of analysis shows: test - nil, odour - nil, transparency -30 cm, hardness - 6, 5 mg/1, ammonia - 0, 1 mg/1, nitrite -0, 005 mg/1, nitrate - 25 mg/1, sulphate - 185 mg/1, chloride - 28 mg/1, fluoride - 2 mg/1, coli-index - 2.
i: Solution: -: ifa ^'initcp: k,; i bsaoio iitl jiiuru I'yy jni" In relation to the state sanitary standards for 1996, the results of analysis shows:
1. The physical and chemical signs are normal.
2. High concentration of ammonia, nitrite and nitrate because of
-> faecal pollution of water. It is dangerous for health specially for
- children because of Metahemoglubinemia. " • nfn; ? -iofo - vons
3. High concentration of fluoride may cause flurosis. ' cinomms
4. The water need for dismfectionT-05; ft -^ — -•••?! ni^, 1'qm
14. Find out the amount of 25% bleaching powder for chloranation 3m3 of water in rural area.
Solutlon: \. In rural if the water with out analysis you must use hyperchloranation method. 2. The dosage of active chlorine is 20-25 mg/1. that mean for 3000 1 of water (one m3 = 1000 1) 3000 • 25 mg = 75000 mg or 75 g of active chlorine.
3. The amount of bleaching powder 100-25 X -75
X = 300 mg of bleaching powder.
15. Estimate the growth and development of 10 year old girl, living in Moscow. Somatometrical signs: height - 133 cm, weight -26, 5 kg, chest circumference - 62 cm.
Solution:
For assessment we need special standard for growth and development of Moscow children's table of regression scale.
| Signs | M | differ. | Standard deviation | |
| Height | 133 cm | 133, 7 cm | -4, 3 | -0, 6 |
| Weigh | 26, 5 kg | 32, 4 kg | -5, 9 | -0, 9 |
| Chest circumference | 62cm | 65, 9 cm | -3, 7 | -0, 7 |
| +15 +26 |
| M |
| -26 -15 |
Conclusion:
The signs of growth and development for girl 10 years old lower median minus one standard deviation.
16. Your conclusion about the group of kinder-garden planing.
Conclusion:
1. There must be good isolating groups in kinder-garden, agents spreading of infection
2. In every group there must be: a) Reception room, b) Dining room, c) Bedroom, d) Playing room, and toilet.
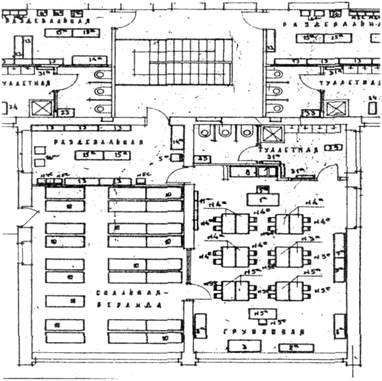
17. Your conclusion about the general plan of the hospital.
Solution:
You have to answer the following questions:
1. The system of hospital planing
2. How many zones in the area of the hospital
3. Is there enough entrance
140
Conclusion:
The plan of the hospital is a compound system. All departments in the main building.
The building of the infections diseases near the main building. There is enough area for green zone.
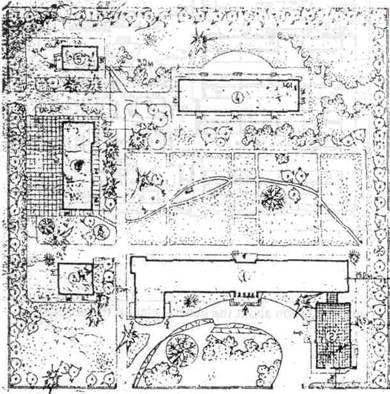
In the area there are:
a) Zone of main building( departments)
b) Zone of infection diseases department
c) Zone of morgue
d) Green zone
e) Thrifty zone
There are 3 entrance, one to the main building; another to the morgue and department of infectious diseases.
The sanitary recommendations says that for morgue must be individual entrance.
|
|
|
18. Your recommendation about the balanced daily diet for 37 years old worker in the factory:
| Calorie | 3200 unit | calcium | 500 mg |
| Proteins | 90g | Phosphorus | 1800 mg |
| Animal proteins | 30g | Vit. A | l, 5mg |
| Fats | 80g | Vit. bi | 2mg |
| Vegetables fats | 20 g | Vit. B2 | 1, 6 mg |
| Carbohydrate | 600g | Vit. C | 70 mg |
Solution:
You have to use the table of physiological standards of nutrition for populations. This man belong to the 4th professional group. The amount of calorie must be 3600 Kcl, the amount of protein must be 102 g, animal proteins must be 56g, (50%), the amount of fats must be 25 % of fats.
The amount of carbohydrate more than normal daily intake (528g), the relation between Prot, fat, carb. is 1: 0, 9: 7, 5. In normal must be 1: 1, 2: 5. Calcium not enough (N- 800 mg), Phosphorus high
than normal (N-1200 mg). The relation between Ca and P is 1: 3, 5, in normal 1: 1, 5. The daily intake of vitamins A, bi, B2 is enough, but vitamin C not enough (N- 150 mg).
Recommendation:
He needs for correction the daily diet, he can add milk products, as a source of calcium, vegetable and fruits as a source of vitamin C.
19. Your conclusion about the sample of milk
Results of analysis:
| Colour | White yellowish |
| Test | Standard |
| Odour | Standard |
| Fats | 3, 2% |
| Specific gravity | 1, 032 |
| Acidity | 21° |
| Reductase test | 7 hours |
| Number of bacteria | 25000 /ml |
| Coli- liter | 3ml |
Solution:
You have to use the sanitary standard for 1979
The normal sp. gravity 1, 028 - 1, 034
Fats - 3, 2%.
The signs of fresh milk:
Acidity not more than 22°
Reductase test - not less than 5, 5 hours
The number of bacteria - up to 5000/ml
Coli-titer - 3 ml
The milk must be preserve in 8° for not than 48 hours
ESSAY /. Deficiency of food and its problems.
a) The problem of nutrition in different countries
b) Evaluate the quality and the quantity of foods
c) Your recommendations
//. The problem of drinking water in rural area
a) The problem of drinking eater in different countries
b) Evaluate the quality of the quality of water in rural area
c) The way to resolving these problems ///. Health problems of children's
a) Growth and development of children's In different countries
b), Health problem of children's in deferent countries
c) Signs and methods of assessment of growth and development
IV. Prevention of infections disease in kinder-gardens
a) The infections diseases of children's in different countries
b) The isolation principles in kinder- gardens
c)Insecticides, the preventive measures
V. The occupational diseases in rural area
a) There effect on health
b) Preventive measures against chemical poising
VI. Food poising in big dies
a) Classification of food poising
b) Particular feature of food poising in deferent countries
c) Preventive measures
VII. Safety of drinking water
a) The problems of drinking water in developing countries
b) The effect of chemical content of water on health
c) Significant of epidemiological signs of water
VIII. The environmental and ecological problems in cities
a) The problem of ecology of the cites in deferent countries
b) The health problem in relation to ecology
c) Preventive measures
IX. Acceleration as hygienic and social problem
a) The meaning of acceleration
b) The future of acceleration in different countries
c) The causes of acceleration
X. The hygienic of housing in rural area
a) The problem of habitation in rural area in deferent countries
b) The effect of sanitary situation in house on the family health,
c) The role of pet animals and insects
XI. The problem of occupational hygiene in developing countries
a) Occupational diseases
b) The health problems of workers in deferent countries
XII. Computer and health
a) The effect of computer on the health of operators
b) The preventive measures and recommendations
|
|
|


