 |
Topic: Cell cooperation in humoral immune responses. Antibodies structure and function. Monoclonal antibodies.
|
|
|
|
Teacher’s signature __________________
Date__________________
CLASS 6
Topic: Cell cooperation in humoral immune responses. Antibodies structure and function. Monoclonal antibodies.
Questions to be discussed:
- Cells involved in the immune response: morphology, lineage, and function.
- B-lymphocytes: stages of differentiation, main surface receptors, function.
- Т-lymphocytes, stages of differentiation, subpopulations, main surface receptors, function.
- Cellular communication through direct cell-to-cell (receptor) and with cytokines (mediator) interaction in humoral immune response.
- Immunoglobulin (Ig): structure, classes of Ig, properties.
- Effector functions of the antibodies.
- Genetic regulation of the antibody production.
- Primary and secondary immune responses. Immunological memory.
- T-independent immune response.
- Monoclonal antibodies, production, application in treatment and diagnosis.
Practical tasks:
1. Draw a scheme of receptor and mediator cells cooperation in humoral immune response.
| T-dependent T-independent |
2. Draw a scheme of the human immunoglobulin G basic structure. Label the components of the antibody molecule.
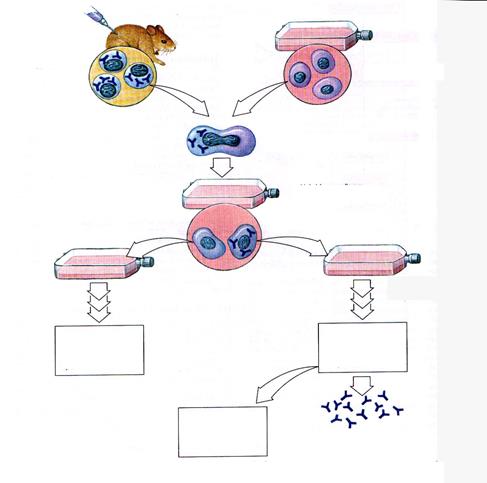
3. Draw a scheme of monoclonal antibodies production.
Teacher’s signature __________________
Date__________________
CLASS 7
Topic: Cells cooperation in cellular immune response development. Anti-tumor immunity. Immunity in transplantation.
Questions to be discussed:
1. Cells involved in generation of cell-mediated immune responses: main surface receptors, function, lymphokines and monokines.
2. Receptor and humoral cell-cooperation in cell-mediated immune response.
3. Effector function of T cytotoxic lymphocytes.
4. Effector function of Th1 DH lymphocytes.
5. Classification of tumor antigens basing on the pattern of expression (tumor specific Ag and tumor associated Ag).
6. General features of anti-tumor immunity.
|
|
|
7. Types of transplantation. Immunity in transplantation.
Practical tasks:
1. Draw a scheme of cells receptor and mediator interactions in cell mediated immune response.
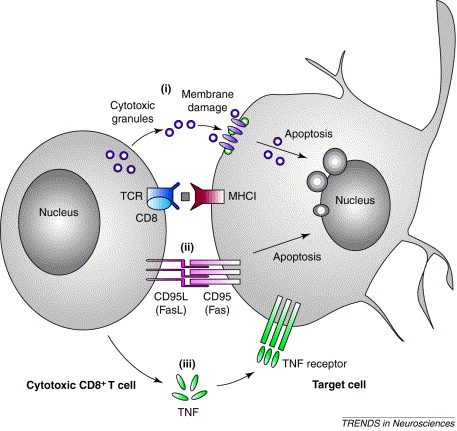
2. Describe the target cell recognition and their killing by T CTL cell.
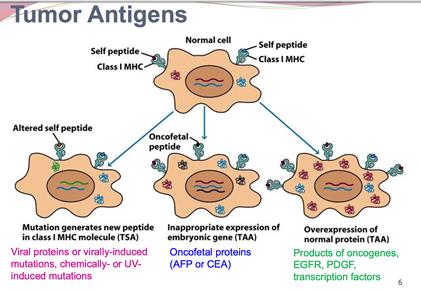
3. Study classification of tumor antigens based on the molecular structure, and source of antigens. Give examples of tumor antigens from each group:
- oncofetal (typically only expressed in fetal tissues and in cancerous somatic cells),
-oncoviral (encoded by tumorgenic transforming viruses),
overexpressed/ accumulated (expressed by both normal and neoplastic tissue, with the level of expression highly elevated in neoplasia),
cancer-testis (expressed only by cancer cells and adult reproductive tissues such as testis and placenta),
lineage-restricted (expressed largely by a single cancer histotype),
mutated (only expressed by cancer as a result of genetic mutation or alteration in transcription),
posttranslationally altered (tumor-associated alterati alterations in glycosylation, etc. )
4. Study classification of tumor antigens based on specificity..

4. Describe the main mechanisms of the anti-tumor immunity.

Teacher’s signature __________________
Date__________________
CLASS 8
Control class for the topic” Basic Immunology” -classes 1-7.
I. Draw a diagram of the important cell receptors (TLR, CD4, CD8, CD3, MHC-I, MHC-II, BCR, TCR), cells of immune system (T cells, B cells, Macrophages, Dendritic cells, NK cells), or schemes of these cells cooperation in immune response development.
II. Oral answer.
Questions for oral answer:
1. Immunity. Types and forms of immunity. Characteristic of innate and acquired defense mechanisms.
2. Factors of Innate immunity, their characteristic features.
3. Inflammation as a protective reaction against infection. Stages of inflammation.
4. Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) – “non-self’, and damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) – “Damaged self”, their characteristic, examples.
5. Pattern recognition receptors (PRR), their categories (surface, endosomal, soluble).
6. Phagocytosis. Phagocytes. Stages of phagocytosis. Mechanism of killing. Complete and incomplete phagocytosis.
7. NK cells, characteristic, mechanism of target recognition and killing.
8. Complement system, its components. Classical, alternative and lectin activation pathways. Biological effects of complement.
9. Interferons, their classification and functions. Mechanism of anti-viral activity. The way of production. Application.
10. Cells of the immune system: immunocompetent, antigen-presenting, antigen-nonspecific.
11. Antigens, their characteristic and main properties. Complete and incomplete antigens. Bacterial and viral antigens. Group-specific, and type-specific antigens of microbs.
12. Human antigens. Genetic organization of the Major Histocompatibility complex (MHC). Class I and class II MHC antigens, structure and function. Significance in immune response development.
|
|
|
13. Cluster of differentiation – CD molecules, their identification. Human leukocyte markers.
14. B-lymphocytes: stages of differentiation, characteristic features, functions. BCR, structure and function.
15. T lymphocytes: populations and subpopulations of T lymphocytes, characteristic and function. Surface markers and receptors.
16. T lymphocytes: structure and function of TCR. Differences in a function of α /β and γ /δ TCR types.
17. Characteristic of Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes. CD markers, interleukins, function. Regulatory T lymphocytes (Treg), their characteristic, surface markers, function.
18. Exogenous and endogenous antigen processing and presentation.
19. Antibody (Igs). Classes of immunoglobulins, their differences in structure and function.
20. Humoral immune response. Cooperation of antigen-presenting cells, T and B cells by receptors and cytokines (mediators). T-dependent and T-independent immune responses.
21. Primary and secondary immune responses. Immunological memory.
22. Cells involved in generation of cell-mediated immune responses: main surface receptors, function, lymphokines and monokines.
23. Receptor and humoral cell-cooperation in cell-mediated immune response.
24. Effector function of T cytotoxic lymphocytes.
25. Effector function of Th1 DH lymphocytes.
26. Mechanism of anti-tumor immunity development.
27. Immunity in transplantation.
|
|
|


