 |
Topic: Immune response against bacteria and fungi. Diagnostic serological reactions: Complement fixation test (CFT).
|
|
|
|
Date__________________
CLASS 9
Topic: Immune response against bacteria and fungi. Diagnostic serological reactions: Complement fixation test (CFT).
Questions to be discussed:
1. Characteristic features of bacteria. Mechanisms of anti-bacterial immunity.
2. Characteristic features of fungi as causative agents of infections. Anti-fungal immunity.
3. Agglutination reactions. Mechanism of agglutination reactions.
4. Components of agglutination tests (agglutinating sera, diagnostic antigens for agglutination).
5. Modifications of agglutination tests (slide and tube agglutination tests, indirect agglutination tests).
6. Precipitation reactions. Components of the reaction. Mechanism of precipitation.
7. Modifications of precipitation tests (ring & gel precipitation tests, immunoelectrophoresis).
8. Complement fixation test, reagents and mechanism.
Practical tasks:
1. Fill in a table of protective mechanisms of anti- bacterial and anti-fungal immunity.
| Type of microbe/ surface antigens | Innate immunity factors | Acquired immunity factors | Mechanisms of immune escape |
| Bacteria | |||
| Fungi |
1. Agglutination reactions
When a particulate polyvalent antigen is mixed with an antibody, the particles are clumped or agglutinated after several minutes. Agglutination is usually visible by naked eye but may be observed under the microscope for better reading of the result. This type of reaction is more sensitive for the detection of antibody than for antigen. Agglutination tests may be run on a slide and in tubes.
1. 1. Serotyping by the slide agglutination test. Using a set of monovalent sera against salmonella O, Vi and H antigens examine the antigenic structure of Salmonella, draw the result, and identify the culture species from the diagnostic table 1.
Slide agglutination test procedure.
(1) Place a drop of diagnostic antiserum and a drop of saline solution (negative control) on the top of flamed glass slide.
(2) Half-open a petri dish with your left hand and peak the loopful of culture from the surface of the plate by sterile bacterial loop.
(3) Spread specimen in a drop of serum to get smooth, uniform suspension.
(4) Sterilize the loop and spread a new loopful of culture in saline solution.
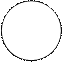
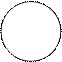
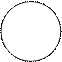
(5) Read the test. If positive, you will see clumping of bacteria and the clearing of the liquid. If negative, the drop remains turbid.
| Sera against Salmonella Ag | О - 9 | О - 12 | Vi | Hd | Hgm | 0, 85% NaCl (control) |
| Presence of agglutination | 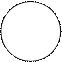
| 
| 
| 
| 
| 
|
Results of Salmonella pure culture serotyping by the slide agglutination with monovalent anti-sera.
Conclusion: Culture of Salmonella isolated from the patient and serotyped by slide agglutination
|
|
|
test belongs to ______________________________.
Table 1.
Salmonella classification based on antigenic structure
|
Serogroup/ serovar |
О-antigen |
Н-antigen | |
| phase -1 | phase-2 | ||
| Serogroup А S. paratyphi A | 1, 2, 12 | a | (1, 5) |
| Serogroup B S. schottmuеlleri S. typhimurium | 1, 4, (5), 12 1, 4 (5), 12 | b i | 1, 2 1, 2 |
| Serogroup C S. cholerаesuis | 6, 7 | c | 1, 5 |
| Serogroup D S. typhi S. enteriditis S. dublin S. moscow | 9, 12, Vi 1, 9, 12 1, 9, 12 9, 12 | d g, m g, p b, g | - (1, 7) - - |
1. 2 Tube agglutination quantitative test. Determine antibody titer in patient blood sera in typhoid fever case by the quantitative tube agglutination test (Widal test). Test is performed with pair sera taken at the beginning of the disease and 10-14 days after to monitor the changing of the specific antibody titer.
Tube agglutination test procedure.
(1) Prepare 2-fold dilutions of patient’s serum in saline solution (from 1: 100 to 1: 1600).
(2) Add fixed volume of standard particulate O-antigen in each tube.
(3) Prepare two control tubes: serum control (serum dilution without Ag) and Ag control (antigen diluted in saline solution without serum).
(4) Incubate for 2h at 37 º С, and 18-20 h at room temperature.
(5) Detect the appearance of tight, compact deposit.
|
|
|


