 |
Indicate the the results. Determine the titer of the reactions (the highest dilution where positive reaction can be observed) and write down conclusion.
|
|
|
|
Indicate the the results. Determine the titer of the reactions (the highest dilution where positive reaction can be observed) and write down conclusion.
1 2 3 4 5







1/100 1/200 1/400 1/800 1/1600 Serum control Antigen control







Conclusion: __________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Precipitation reactions
When a soluble antigen combines with specific antibody, the antigen-antibody complex forms an insoluble precipitate (antigen and antibody have to be present in optimal or equivalent proportion). Precipitation results when a large lattice is formed consisting of alternating antigen and antibody molecules. Precipitation test may be run in liquid or gel.
2. 1. Ring test (Ascoli’s test). Detect the presence of Bacillus anthracis thermostable antigen in boiled tissue extract by ring precipitation test with diagnostic anthrax antiserum.
Ring test procedure. Run in 3 tubes: 1st-experimental, 2nd- antiserum control, 3rd- antigen control.
(1) Using pipette add 0. 3-0. 5 ml of undiluted serum in 1st and 2nd narrow tubes.
(2) Add saline solution into the 3rd tube for antigen control.
(3) Layer the equal volume of antigen solution over a column of antiserum in the 1st tube.
(4) Layer the equal volume of saline solution over a column of antiserum in the 2nd tubes.
(5) Layer the equal volume of antigen solution over a column of saline solution in the 3rd tubes.
(6) Wait 1-5 min and read the results. A precipitate forms at the junction of the two liquids.
Draw the results of the experiment.



1 2 3
Ring precipitation test.
1 – antiserum control; 2 – antigen control; 3- experimental tube.
2. 2. Discribe the result of the precipitation in gel (double radial immunodiffusion) test performed for toxigenicity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae (Elek test).
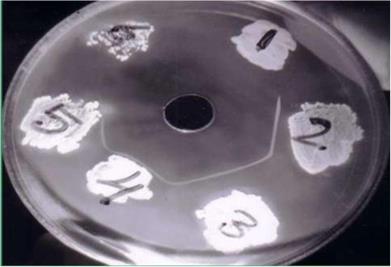
Conclusion: _______________________________________________________________
3. Complement Fixation test (CFT) to examine the presence of the specific antibodies in patients’ blood serum.
CFT is a complex procedure consisting of two steps and five reagents combined in two systems:
I system: (1) antigen; (2) antibody; (3) complement;
|
|
|
II system: (4) sheep erythrocytes; and (5) amboceptor (rabbit antibody to sheep erythrocytes).
All reagents have to be separately standardized.
(1) Prepare separately the first system in three tubes and the second system in one tube:
Table 1.
Complement fixation test procedure
| Reagents/ tubes | Patient serum (1: 5) | Saline solution (control tubes) | Antigen | Comple- ment | Hemolytic serum | Sheep erythrocytes (3% mixture) |
| 1st (test tube) | 0. 5 ml | - | 0. 5 ml | 0. 5 ml | - | - |
| 2nd (serum control tube) | 0. 5 ml | 0. 5 ml | - | 0. 5 ml | - | - |
| 3rd (antigen control tube) | - | 0. 5 ml | 0. 5 ml | 0. 5 ml | - | - |
| 4th (hemolytic system) | - | - | - | - | 2 ml | 2 ml |
(2) Incubate all tubes for 30 min at 37°C;
(3) Add 1 ml of hemolytic system from the 4th tube into each of the first three tubes;
(4) Incubate all tubes for 30 min at 37°C;
(5) Read the results.
· Lyses of erythrocytes indicates that complement was not fixed in the first step because the absence of antibodies - negative reaction.
· Absence of erythrocyte lyses indicates that the complement was fixed and used up in the first step, and therefore, patient’s serum contains antibody.
3. Draw a mechanism of the interactions between reagents in positive and negative reaction in test tubes.
Positive reaction Negative reaction
 
|
Mechanism of the complement fixation test.
4. Examine the results of CFT, demonstrating positive, negative and intermediate reactions, explain the mechanism of the intermediate reactions and draw samples, indicating he presence of hemolyses and sedimentation of erythrocytes. Indicate positive, negative and intermediate CFT results.




|
|
|


