 |
Topic: Immunological reactions with labeled reagents (RIA, IF, ELISA, Western Blot), their application. Immunity status of the human body.
|
|
|
|
Teacher’s signature __________________
Date__________________
CLASS 10
Topic: Immune response against viruses. Characteristic features of immune response against protozoa and helminthes. Diagnostic serological reactions: Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test, Neutralizing (Nt) test.
Questions to be discussed:
1. Mechanism of anti-viral immune response.
2. Characteristic features of anti-protozoal immunity.
3. Characteristic features of anti-helminthes immunity.
4. Serological reactions used for virus identification and anti-viral immunity evaluation (Nt test, HI test).
Practical tasks:
1. Fill in a table of protective mechanisms of anti- bacterial and anti-fungal immunity.
| Type of microbe/ surface antigens | Innate immunity factors | Acquired immunity factors | Mechanisms of immune escape |
| Viruses | |||
| Protozoa | |||
| Helminthes |
2. Explain mechanisms of toxin and virus neutralization tests:
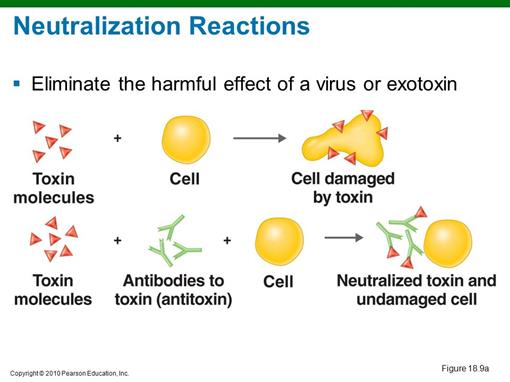
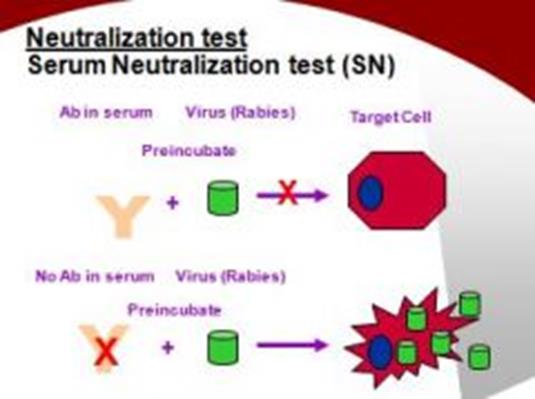
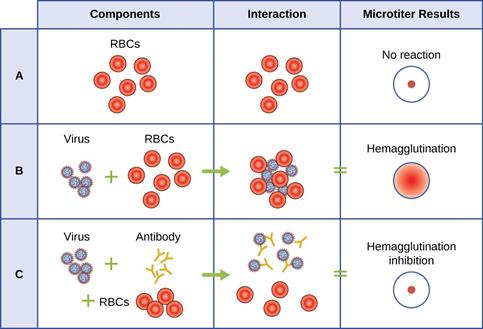
3. Explain mechanism of Hemagglutination inhibition test:
Teacher’s signature __________________
Date__________________
CLASS 11
Topic: Immunological reactions with labeled reagents (RIA, IF, ELISA, Western Blot), their application. Immunity status of the human body.
Questions to be discussed:
1. Immunological reactions with labeled reagents, their advantages.
2. Immunofluorescence tests, advantages and disadvantages of direct and indirect tests.
3. Enzyme immunoassays (EIA, ELISA), types of ELISA (sandwich, capture, competitive).
4. Immunoblotting techniques (Western Blot).
5. 1. Immunity status of the body, definition, stages of evaluation.
6. 2. 1st and 2nd level tests of the immunity status evaluation.
Practical task:
1. Draw charts of direct, indirect, and competitive ELISA, using the following symbols:
u - antigen;
Y - specific antibody;
¥ - anti-immunoglobulin (secondary antibody);
E - enzyme label.
☼ -fluorescent dye
X- isotope
1. Draw a chart of the direct and indirect immunofluorescent and Elisa tests.
| Direct IFA | Indirect IFA |
| Direct “sandwich” ELISA | Competitive ELISA |
- Draw a chart of the Western blot for patient’s anti-HIV antibody, used as confirmation test for diagnosis of HIV-infection - Fig. 3.
| gp 160 | 
|
Blotting onto NC paper |
Incubation
with patient’s serum |
Incubation with secondary Ab labeled with enzyme and conversion of the substrate | ||||||||||||||
| gp 120 | 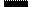
| |||||||||||||||||
| р 61 | 
| |||||||||||||||||
| gp 41 | 
| |||||||||||||||||
| р 24 | 
| |||||||||||||||||
| р 17/18 | 
| |||||||||||||||||
| р 7/9 | 
| |||||||||||||||||
| A | B | C | D |
Fig. 1. Western blot. A, distribution of the HIV antigens (Ags) separated by gel electrophoresis.
B, Ags blotted onto nitrocellulose paper. C, Strip of NC paper treated with patient’s serum. D, Strip of NC paper treated with conjugated anti-human serum. Enzyme conversion of the substrate identifies the presence of antibody to several HIV proteins.
Conclusion: _________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________.
3. Explain the mechanism of free-flow cytofluorimetry, used for immune status evaluation.
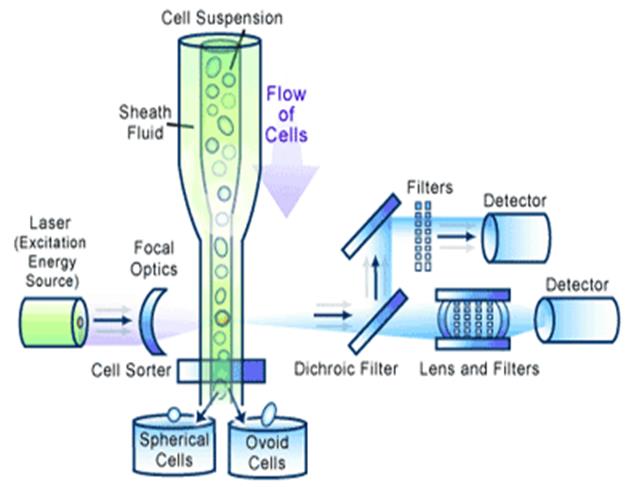
4. Fill in a table with the tests used for immunity status evaluation.
|
Immune status tests | 1st level tests | 2nd level tests |
Teacher’s signature __________________
Date__________________
CLASS 12
Topic: Control class “Applied Immunology” classes 9-11.
I. Practical task: Read the results of the diagnostic tests, find the titer of the reactions (agglutination, precipitation, CFT, HI test, Nt test, ELISA, IF) and explain the mechanisms of the Ag-Ab reactions.
II. Oral answer.
Control questions for oral answer
1. Serological agglutination tests: direct, indirect (passive), main components. Modifications of agglutination test. Application.
2. Serological precipitation tests. Characteristic of main components. Ring and gel precipitation, immunoelectrophoresis. Application.
3. Characteristic features of anti-bacterial immunity.
4. Toxin neutralizing test to identify the types of bacterial toxins in vivo and in vitro
5. Characteristic features of antiviral immunity.
6. Immune status of the human organism. Methods of immune status estimation.
7. Complement fixation test, reagents and mechanism.
8. Serological reactions used for virus identification and anti-viral immunity evaluation (Nt test, HI test).
9. Characteristic features of fungi as causative agents of infections. Anti-fungal immunity mechanisms.
10. Characteristic features of protozoan pathogens and anti-protozoa immunity.
11. Characteristic features of helminthes. Anti-helminthes immunity. `
12. Immunological reactions with labeled reagents, their advantages. IF, ELISA, RIA.
13. Virus neutralizing tests. Practical use.
14. Hemagglutination inhibition test. Practical use.
Date__________________
|
|
|





