 |
Listening. 10. Listen to a part of a lecture on engines and answer the questions. 11. Match the term and the definition. Guess the meaning of the underlined words
|
|
|
|
Listening
10. Listen to a part of a lecture on engines and answer the questions
1. What are two main types of combustion engines?
2. Where are internal combustion engines used?
3. Where are external combustion engines used?
4. How many types of internal combustion engines are there?
5. How many cylinders may be used in internal combustion engines?
11. Match the term and the definition. Guess the meaning of the underlined words
| Spark plug, cylinder head, combustion chamber, piston, crankshaft, flywheel, connecting rod, crankcase, valves |
1. It sits atop the cylinder and consists of a platform containing part of the combustion chamber, it houses the valves and the spark plug.
2. It is a rotating shaft driven by a crank.
3. It is a cylindrical piece of metal that moves up and down inside the cylinder.
4. It is a part of an engine which connects piston to the crankshaft.
5. It is a housing for a crankshaft.
6. It is a part of an engine located in the cylinder head and ignites compressed fuel-air mixture by means of an electric spark.
7. It is an enclosed space in which combustion happens.
8. It is a heavy wheel that keeps a machine working at a steady speed.
9. They are mushroom-shaped pieces of steel which move to open and close ports.
12. Read the text and the captions. Guess the meaning of the underlined words
Counting cylinders
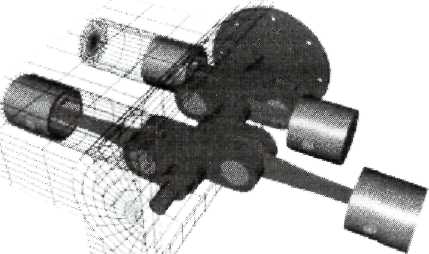
The core of the engine is the cylinder, with the piston moving up and down inside the cylinder. The simplest engine has one cylinder. This is typical of most lawn mowers (газонокосилка), but most cars have more than one cylinder (four, six and eight cylinders are common). In a multi-cylinder engine, the cylinders usually are arranged in one of three ways: inline, V or flat (also known as horizontally opposed), as shown in the following figures:
Match the figure with the caption
| Flat: the cylinders are arranged in two banks on opposite sides of the engine. |
| Inline: the cylinders are arranged in a line in a single bank. |
| V type: the cylinders are arranged in two banks set at an angle to one another. |

| 
|

|
13. Look through the text and write down the information on engines with cylinders arranged in two banks set at an angle to one another
First Internal Combustion Engines
The first internal-combustion engine was designed by the Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens in 1678; it was to have been fueled with gunpowder, but it was never built. About 1860 a French inventor, Lenoir, built the first practical internal-combustion engine; it burned illuminating gas. In 1866 two German engineers, Eugen Langen and Nikolaus August Otto, developed a more efficient gas engine, and in 1876 Otto built a four-cycle engine, a prototype of the so-called Otto-cycle engines used in most modern automobiles and airplanes.
|
|
|
The high-speed internal-combustion motor of the German engineer Gottlieb Daimler revolutionized the automobile industry. His four-cycle, single-cylinder motor, patented in 1887, achieved speeds many times those of any previous engine, thereby producing many times the power for the same weight. In 1889 he developed a two-cylinder engine that gave still greater power; the cylinders were in a V-type configuration. This engine design was adopted by a French manufacturer, Emile Levassor, who launched experiments in 1891 that subsequently led his firm, Panhard et Levassor, into automobile manufacture. Levassor's first automobile, produced in 1894, not only incorporated the Daimler engine but also was the first car in which the working parts were arranged in the operational sequence still used in present-day models. That is, the engine was in front, followed by the clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, and differential and driving axle. The superiority of the high-speed Daimler engine over the then highly developed steam engine was conclusively demonstrated at the famous Paris-Bordeaux Race of 1895. The first car, propelled by a Daimler engine, came in six hours ahead of the second car, and the next three cars to finish were all propelled by Daimler engines. Another pioneer with the gasoline engine was the German engineer Karl Benz, who in 1885, working independently of Daimler, produced a mechanically propelled tricycle.
Grammar. Infinitive
| Инфинитив — это неличная форма глагола, которая в русском языке соответствует неопределенной форме глагола, отвечающей на вопрос «что делать? », «что сделать? ». Формальным признаком инфинитива является частица to: to move, to connect, to ignite. Одна из часто встречающихся в технических текстах функций инфинитива – функция обстоятельства цели (отвечает на вопрос what for? ). Например: Combustion engines are used to convert heat energy into mechanical energy. Часто перед инфинитивом в функции обстоятельства цели используются фразы in order to, so as to. Например: A reciprocating engine is an engine that uses one or more pistons in order to convert pressure into a rotating motion. Internal combustion engines use burning of fuel so as to provide pressure. |
|
|
|


