 |
Antibiotics can be given through both intravenous and intramuscular injection .
|
|
|
|
7. Community pharmacy sells both prescription drugs and a wide range of non-prescription medicines and other products such as cosmetics.
8. Over-the-counter drugs are available in pharmacies and supermarkets without special restrictions.
9. Inhaler is a form of injection.
10. Warning label has information about drug side effects and potential interactions.
8. Read the text and check your answers:
 Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment
Medical diagnosis (Dx, DS), derived through Latin from Greek διάγνωσις (diágnōsis) from διαγιγνώσκειν (diagignṓskein) "to discern, distinguish", is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a patient’s symptoms and signs. It is a major component of a doctor's visit. The information required for diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the patient. To determine the correct diagnosis the clinician uses the diagnostic criteria designating the specific combination of signs, symptoms, and test results. Diagnostic procedures are the specific tools that the clinicians use to narrow the diagnostic possibilities, e.g. diagnostic tests. At all times doctors knew that diagnosis was often challenging. Many signs and symptoms are nonspecific. For example, redness of the skin (erythema), by itself, is a sign of many disorders and thus does not tell the healthcare professional what is wrong. Thus differential diagnosis, in which several possible explanations are compared and contrasted, must be performed. For substantiation of final diagnosis a clinician should list all the typical or specific symptoms and signs, and changes in the laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods data as though he puts the pieces of the puzzle together to make a picture. A diagnostic procedure may be performed by various health care providers such as a physician, a dentist, a nurse practitioner or other professional. A person who diagnoses is called a diagnostician.
While diagnosing the disease a clinician also considers etiology, pathogenesis, progression, prognosis, other outcomes, and possible treatments of patient’s ailment, as well as providing advice for maintaining health. Etiology and pathogenesis are closely related. Etiology includes risk factors and is the actual cause of disease. Pathogenesis is how those things went about causing the disease: the mechanism of disease. A provider should consider all complications possible and those found in the given patient. On the basis of number and severity of symptoms a provider may identify the course of the disease (mild, moderate, or severe). Prognosis, favorable or unfavorable, may be done for life, health, and workability.
A provider proposes a treatment plan after the final diagnosis has been made. It may include therapy and follow-up consultations, tests to monitor the condition and the progress of the treatment, if needed. The doctor determines one or more treatment goals - whether it is possible to cure a disease or just manage it, and according to these goals chooses the treatment. Medical treatment means the management and care of a patient to combat disease or disorder. Based on their potential outcomes treatments fall into: preventive treatment (prophylactic care), curative treatment, disease management (including pain management), and palliative care. No matter which goal to choose, the provider should consider the indications and contraindications of each treatment approach.
|
|
|
As a part of treatment, a doctor may prescribe a medication (medicine or drug) used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Dosage is carefully determined by the doctor and can be affected by patient’s age, weight, kidney and liver health, and other health conditions. There may be different routes of medication administrations (the process by which a patient takes a medicine ): enteral (by mouth), parenteral (into the bloodstream), and others, which includes giving a drug through intranasal, topical, inhalation, and rectal means. For example, antibiotics can be given through intravenous or intramuscular injection. Prescribing the medications a doctor gives out a prescription.
Patient takes the doctor’s prescription to the community pharmacy which sells both prescription drugs and a wide range of non-prescription medicines and other products such as cosmetics. In the UK it is a chemist’s shop or drugstore in North America. In hospitals, prescriptions are dispensed by the pharmacy (the department where the drugs are prepared).
Drugs are classified in various ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control by governments, which distinguishes over-the-counter medications (over-the-counter drugs, OTC), which are available in pharmacies and supermarkets without special restrictions; behind-the-counter medicines (or drugs), which are dispensed by a pharmacist without needing a doctor's prescription, and prescription medicines (prescription drugs), which must be prescribed by a licensed medical professional, usually a physician.
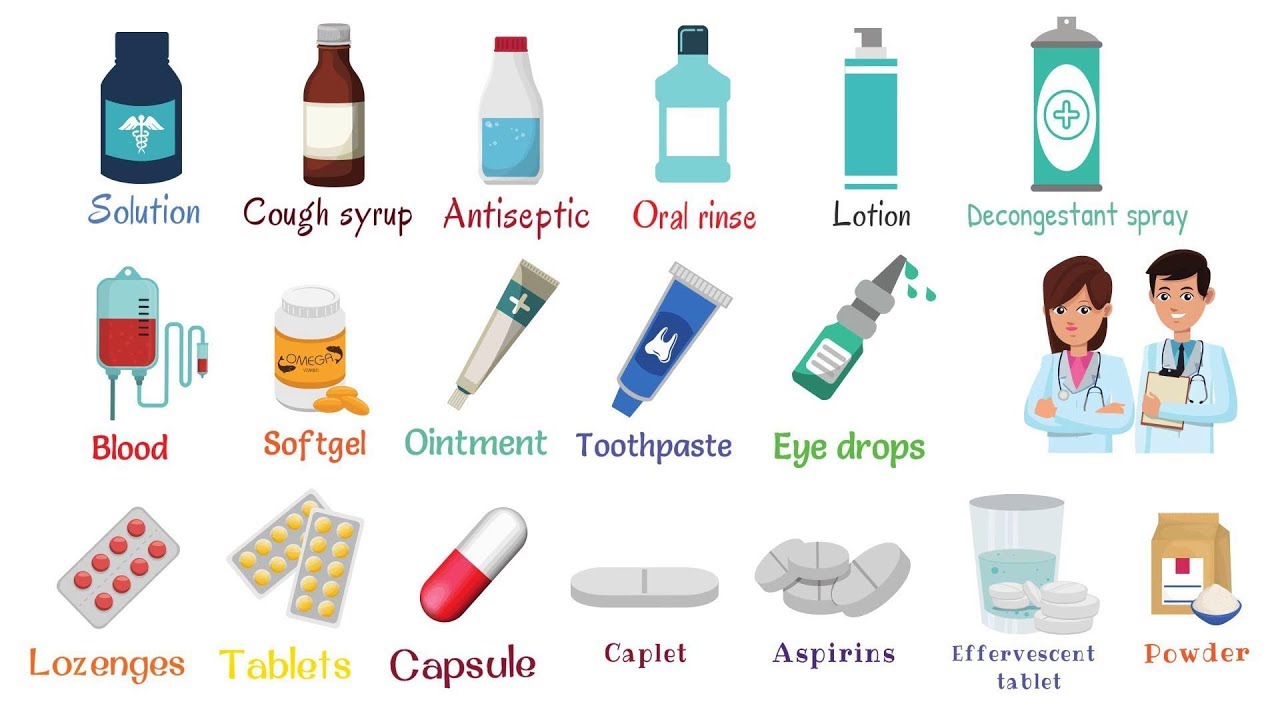
Most medicines come in a variety of types or formats. Preparations can be as follows: liquid (also called a ‘mixture’, ‘solution’ or ‘syrup’), tablet, pill, capsule, topical medicine (cream, lotion or ointment in tubs, bottles or tubes), suppository, drops, inhaler, injection and other.
The patient should always read all drug labels and patient drug information received from the healthcare provider, whether the drug is OTC or prescription one. The prescription vial may have warning labels in the form of colorful stickers located directly on medication bottle or package having information about side effects and potential interactions.
In 1980s everybody knew that there would be no continuation after handing over a prescription. The patient realized that doctor’s visit had come to the end. Nowadays except the prescription patient is provided with all the information about drugs prescribed, possible side effects, interactions with other drugs and substances, and how to manage the situations the patient may face with. It is recognized that educating the patients in their condition and involving them in management decisions contribute to both improve patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes.
|
|
|
Choose the right variant:
Diagnosis & Treatment Quiz
1. Medical diagnosisis the process of
o determining which etiology or pathogenesis explains a patient’s symptoms and signs.
o determining which disease or condition explains a patient’s symptoms and signs.
o determining which criteria or procedure explains a patient’s symptoms and signs.
2. Diagnostic procedures are
o the specific tools that the clinicians use to widen the diagnostic possibilities.
o the specific tools that the patients use to narrow the diagnostic possibilities.
o the specific tools that the clinicians use to narrow the diagnostic possibilities.
3. Diagnostician is
o a person who diagnoses.
o a person who draws the patient’s blood.
o a person who refers the patient to the inpatient department.
4. Etiology is
o  the actual main symptom of disease.
the actual main symptom of disease.
o the actual progress of disease.
o the actual cause of disease.
5. Pathogenesis is
o the cause of disease.
o the mechanism of disease.
o the prognosis of disease.
6. Medical treatment means
o the management and care of a patient to combat symptoms or signs.
o the management and care of a patient to combat a nurse or doctor.
o the management and care of a patient to combat disease or disorder.
7. Administration is
o the process by which a patient takes a medicine.
o the process by which a patient buys a medicine.
o the process by which a patient prescribes a medicine.
8. Pharmacy is
o the outpatient department where the drugs are prepared.
o the inpatient department where the drugs are prepared.
o the inpatient department where the drugs are sold.
9. Over-the-counter medications are
o available only in pharmacies without special restrictions.
o available only in supermarkets without special restrictions.
o available in pharmacies and supermarkets without special restrictions.
10. Behind-the-counter medicines are
o dispensed by a doctor without needing a pharmacist 's prescription.
o dispensed by a doctor without needing a nurse's prescription.
o dispensed by a pharmacist without needing a doctor's prescription.
11. Prescription drugs must be
o prescribed by a licensed medical professional.
o prescribed by a non-licensed medical professional.
o prescribed by a licensed medical administrator.
12. Warning label contains
o the information about major effects and potential interactions.
o the information about side effects and food interactions.
o the information about side effects and potential interactions.
10. Fill in the missing letters:
Di_gn_s_s,cr_ter_a, di_gnosti_ian, et_ol_gy, pa_hogen_sis, pr_gno_is, tr_atm_nt, dr_g, c_mpli_ation, c_re, m_di_ation, pr_scripti_n, p_arm_cy, in_ecti_n, l_bel, ef_ect, s_v_re.
11. The words below are split; try to find two corresponding parts:
cond - care
symp - genesis
si - store
health - ement
etio - rity
patho - indication
manag - cine
contra - gn
drug - macy
seve - dure
phar - ition
medi - logy
proce - tom
|
|
|


